The lecture method is a traditional teaching approach that delivers information systematically to a large audience, enhancing comprehension through structured presentations. It effectively transfers knowledge while allowing for clarifications and focused explanations. Explore the rest of this article to understand how the lecture method can optimize your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
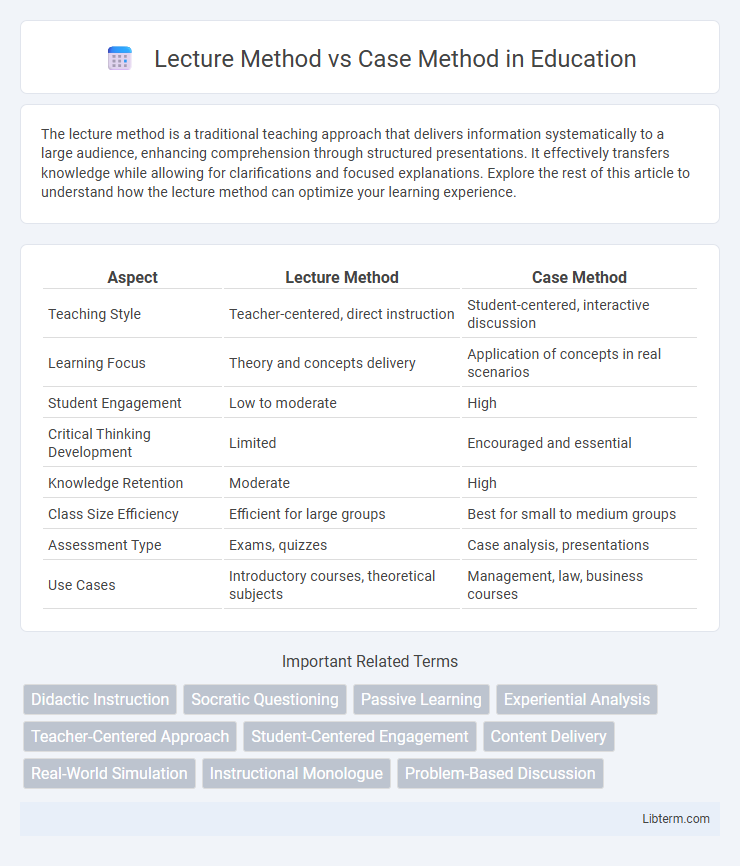
| Aspect | Lecture Method | Case Method |
|---|---|---|
| Teaching Style | Teacher-centered, direct instruction | Student-centered, interactive discussion |
| Learning Focus | Theory and concepts delivery | Application of concepts in real scenarios |
| Student Engagement | Low to moderate | High |
| Critical Thinking Development | Limited | Encouraged and essential |
| Knowledge Retention | Moderate | High |
| Class Size Efficiency | Efficient for large groups | Best for small to medium groups |
| Assessment Type | Exams, quizzes | Case analysis, presentations |
| Use Cases | Introductory courses, theoretical subjects | Management, law, business courses |
Introduction to Teaching Methodologies
Lecture method emphasizes structured information delivery through verbal presentations, promoting comprehensive coverage of theoretical concepts. Case method focuses on interactive learning by analyzing real-world scenarios, enhancing critical thinking and practical application skills. Both methodologies serve distinct pedagogical purposes in mastering teaching techniques and improving student engagement.
Defining the Lecture Method
The Lecture Method is a traditional teaching strategy where an instructor delivers structured information verbally to a large audience, emphasizing content transmission and factual knowledge. It relies heavily on passive learning, with students primarily listening and taking notes rather than engaging in interactive discussions. This method is efficient for covering extensive material quickly but may limit critical thinking and student participation compared to more interactive approaches like the Case Method.
Understanding the Case Method
The Case Method fosters active learning by engaging students in real-world problem-solving, promoting critical thinking and decision-making skills. Unlike the Lecture Method, which relies on passive information delivery, the Case Method encourages discussion, analysis, and application of theoretical concepts to practical scenarios. This approach enhances understanding by immersing learners in complex situations, improving retention and practical expertise in various fields such as business, law, and medicine.
Historical Context and Evolution
The lecture method, originating in ancient Greek and Roman education, emphasized direct knowledge transmission through oral presentations, dominating formal education until the 19th century. The case method, developed at Harvard Law School in the early 20th century by Dean Christopher Langdell, introduced experiential learning by analyzing real-life legal cases to foster critical thinking and practical application. Over time, the case method expanded beyond law into business and medical education, reflecting a shift towards interactive, student-centered learning environments.
Core Principles of the Lecture Method
The Lecture Method centers on direct knowledge transfer from instructor to student through structured verbal presentations, emphasizing clarity and organization. Core principles include a well-prepared, logically sequenced delivery, focused content that highlights key concepts, and limited student interaction to maintain attention on the material. This method aims to efficiently disseminate foundational information, relying on listening and note-taking as primary learning activities.
Key Features of the Case Method
The Case Method emphasizes active learning through real-world business scenarios that develop critical thinking and decision-making skills. It encourages student participation, debate, and application of theoretical concepts to practical problems, fostering analytical reasoning. Unlike the Lecture Method, it relies less on passive information delivery and more on interactive discussion and problem-solving exercises.
Comparative Advantages and Disadvantages
The Lecture Method offers structured content delivery and efficient coverage of extensive material but often lacks interactive engagement and critical thinking development. In contrast, the Case Method promotes active learning, problem-solving skills, and real-world application through student participation but can be time-consuming and may require substantial preparation. Balancing both methods can enhance comprehension by leveraging lecture's clarity and case discussion's depth.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning Outcomes
Lecture method often results in passive student engagement, limiting critical thinking and retention, as information flows unidirectionally from instructor to students. Case method enhances active participation by encouraging analysis, discussion, and application of concepts, leading to deeper understanding and improved problem-solving skills. Research shows that students involved in case-based learning demonstrate higher cognitive engagement and better long-term learning outcomes compared to traditional lecture formats.
Applicability Across Different Disciplines
The Lecture Method is widely applicable across disciplines such as humanities, sciences, and business due to its efficiency in delivering structured content and large volumes of information. The Case Method excels in fields like law, medicine, and management by promoting critical thinking through real-world problem analysis and active student engagement. Combining both methods can enhance learning outcomes by balancing theoretical knowledge with practical application across diverse academic areas.
Choosing the Right Method for Educational Goals
Selecting the appropriate instructional method depends on educational goals, with the Lecture Method being effective for delivering foundational knowledge to large groups quickly. In contrast, the Case Method promotes critical thinking and practical problem-solving skills through active student engagement and real-world scenarios. Educators should align the teaching approach with desired outcomes, balancing content coverage and interactive learning to maximize educational impact.
Lecture Method Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com