Formative assessment provides continuous feedback during the learning process, helping educators identify areas where students need improvement and adjust instruction accordingly. This approach enhances student engagement and promotes a deeper understanding of course material by focusing on progress rather than final results. Discover how formative assessment can transform your teaching strategy and boost student success throughout the article.
Table of Comparison
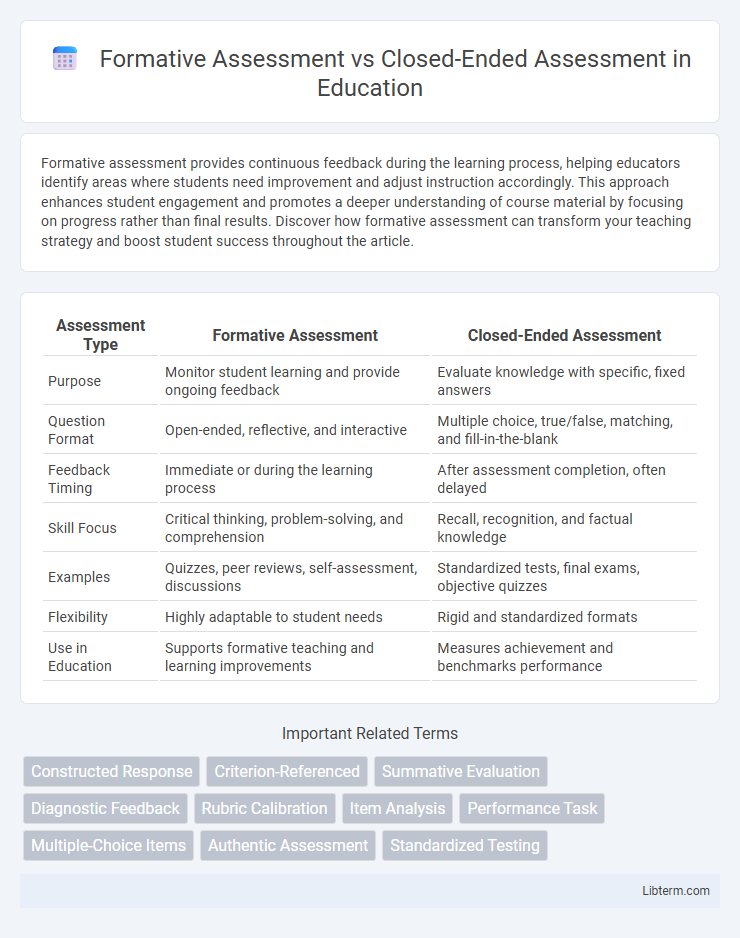
| Assessment Type | Formative Assessment | Closed-Ended Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback | Evaluate knowledge with specific, fixed answers |
| Question Format | Open-ended, reflective, and interactive | Multiple choice, true/false, matching, and fill-in-the-blank |
| Feedback Timing | Immediate or during the learning process | After assessment completion, often delayed |
| Skill Focus | Critical thinking, problem-solving, and comprehension | Recall, recognition, and factual knowledge |
| Examples | Quizzes, peer reviews, self-assessment, discussions | Standardized tests, final exams, objective quizzes |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to student needs | Rigid and standardized formats |
| Use in Education | Supports formative teaching and learning improvements | Measures achievement and benchmarks performance |
Understanding Formative Assessment
Formative assessment emphasizes continuous feedback to enhance learning by identifying student strengths and areas for improvement during the instructional process. Unlike closed-ended assessments, which utilize fixed-choice questions like multiple-choice or true/false, formative assessments employ open-ended tasks, discussions, and observations to gauge understanding. This approach prioritizes student engagement and adaptive teaching strategies to foster deeper comprehension and skill development.
Defining Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessment consists of questions with predetermined answers, such as multiple-choice, true/false, or matching formats, enabling quick and objective grading. This type of evaluation measures specific knowledge or skills by restricting responses to fixed options that facilitate straightforward scoring and analysis. It contrasts with formative assessments that emphasize open-ended feedback and detailed understanding through ongoing, flexible evaluation methods.
Core Differences Between Formative and Closed-Ended Assessments
Formative assessment provides ongoing feedback that guides student learning through open-ended questions, self-assessment, and reflection, promoting critical thinking and deeper understanding. Closed-ended assessment typically involves fixed-response formats like multiple-choice or true/false questions, focusing on measuring knowledge retention and accuracy of specific facts. The core difference lies in formative assessments being diagnostic and developmental, while closed-ended assessments primarily serve summative evaluation purposes.
Purposes and Goals of Each Assessment Type
Formative assessment aims to monitor student learning and provide ongoing feedback to improve instructional methods and student comprehension, promoting skill development and mastery. Closed-ended assessment primarily measures knowledge acquisition and retention through objective questions, facilitating standardized evaluation and easy grading. The goal of formative assessment is to support learning progress, while closed-ended assessment focuses on quantifiable outcomes and summative judgment.
Examples of Formative Assessment Techniques
Formative assessment techniques include methods such as think-pair-share, exit tickets, and concept maps, which actively engage students in the learning process and provide ongoing feedback. Other examples are peer reviews, self-assessments, and observation checklists that help identify learning gaps and guide instructional adjustments. Unlike closed-ended assessments, formative assessments emphasize open-ended questions and discussions to promote deeper understanding and critical thinking.
Typical Closed-Ended Assessment Formats
Typical closed-ended assessment formats include multiple-choice questions, true/false statements, matching exercises, and fill-in-the-blank items that require specific, predetermined answers. These formats enable objective scoring and efficient data collection for standardized testing, making them suitable for measuring knowledge recall and comprehension. Closed-ended assessments contrast with formative assessments by focusing on summative evaluation rather than ongoing feedback and learning adjustments.
Impact on Student Engagement and Learning
Formative assessment enhances student engagement by providing ongoing feedback that encourages active participation and fosters a growth mindset, which leads to improved learning outcomes. Closed-ended assessments, such as multiple-choice tests, often limit student interaction and critical thinking, potentially reducing motivation and deeper understanding. Research indicates that formative assessments support personalized learning pathways and promote higher-order cognitive skills, while closed-ended assessments primarily measure recall and factual knowledge.
Advantages of Formative Assessment
Formative assessment provides continuous feedback that enhances student learning by identifying strengths and areas for improvement in real-time, promoting personalized instruction. It encourages active engagement and critical thinking, making the learning process more dynamic and adaptive compared to the fixed nature of closed-ended assessment. The flexibility of formative assessment supports scaffolding and deeper understanding, leading to improved academic outcomes and learner motivation.
Limitations of Closed-Ended Assessment
Closed-ended assessments limit student responses to predetermined answers, restricting the ability to evaluate critical thinking and problem-solving skills. These assessments often fail to capture the depth of student understanding, as they do not allow for explanation or elaboration. Additionally, closed-ended formats can encourage guessing and do not provide meaningful feedback for personalized learning improvements.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Educational Objectives
Choosing the right assessment aligns closely with educational objectives, where formative assessment offers ongoing feedback to enhance learning and adapt instruction, while closed-ended assessment provides quantifiable data for measuring specific knowledge or skills at a point in time. Formative assessments such as quizzes, observations, and discussions promote deeper understanding and skill development by identifying learning gaps early. Closed-ended assessments, including multiple-choice tests and true/false questions, are efficient for evaluating factual recall and objective standards, making them suitable for summative evaluation and large-scale testing contexts.
Formative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com