Effective evaluation measures the success and impact of a project by analyzing key performance indicators and outcomes. Understanding evaluation techniques helps optimize processes and ensures your goals are met efficiently. Explore the rest of the article to discover essential evaluation strategies for achieving better results.
Table of Comparison
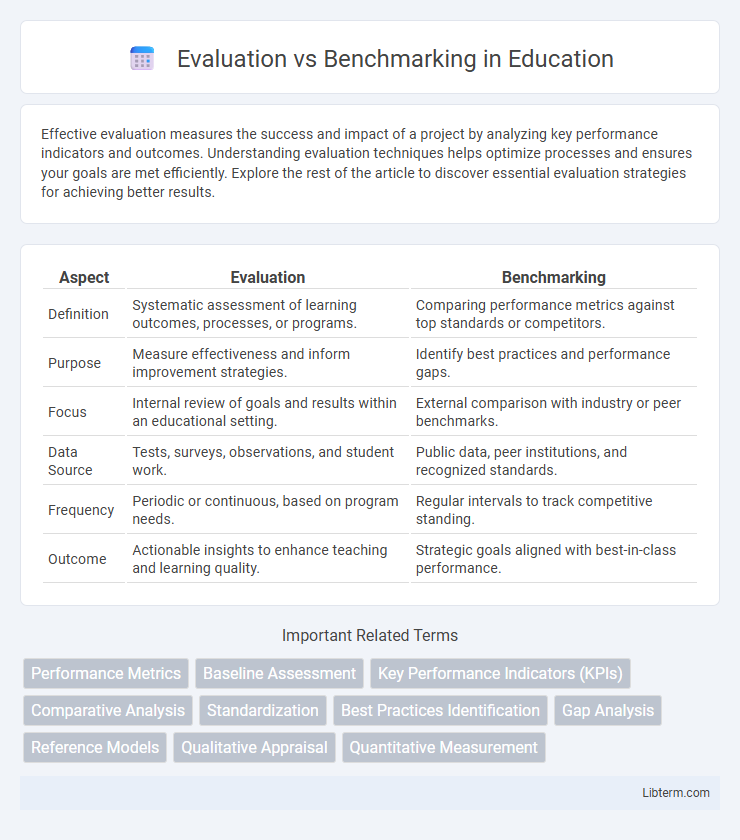
| Aspect | Evaluation | Benchmarking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Systematic assessment of learning outcomes, processes, or programs. | Comparing performance metrics against top standards or competitors. |
| Purpose | Measure effectiveness and inform improvement strategies. | Identify best practices and performance gaps. |
| Focus | Internal review of goals and results within an educational setting. | External comparison with industry or peer benchmarks. |
| Data Source | Tests, surveys, observations, and student work. | Public data, peer institutions, and recognized standards. |
| Frequency | Periodic or continuous, based on program needs. | Regular intervals to track competitive standing. |
| Outcome | Actionable insights to enhance teaching and learning quality. | Strategic goals aligned with best-in-class performance. |
Understanding Evaluation and Benchmarking
Evaluation measures the performance or quality of a system, product, or process against predefined criteria to determine effectiveness and identify areas for improvement. Benchmarking compares these performance metrics against industry standards or top competitors to establish relative standing and best practices. Understanding both allows organizations to assess internal capabilities while striving for competitive excellence.
Key Differences Between Evaluation and Benchmarking
Evaluation involves assessing a process, product, or service against specific criteria to determine its quality or effectiveness, while benchmarking compares these entities against industry standards or competitors to identify performance gaps. Key differences include evaluation's focus on internal performance measures versus benchmarking's external comparative approach. Evaluation aims to understand strengths and weaknesses internally, whereas benchmarking seeks to drive improvement by learning from best practices and market leaders.
Goals and Objectives of Evaluation
Evaluation focuses on assessing the effectiveness, efficiency, and impact of a program or process to determine whether it meets predefined goals and objectives. Its primary objective is to provide evidence-based insights that support decision-making, accountability, and continuous improvement. Benchmarking, on the other hand, aims to compare performance metrics against industry standards or best practices to identify gaps and drive competitive advantage.
Purposes and Benefits of Benchmarking
Benchmarking systematically compares an organization's processes and performance metrics against industry bests or competitors to identify gaps and opportunities for improvement. Its primary purpose is to enhance operational efficiency, drive innovation, and achieve superior competitive advantage by learning from exemplary standards. The benefits of benchmarking include improved quality, increased customer satisfaction, cost reduction, and strategic alignment with market leaders.
Types of Evaluation Methods
Evaluation methods include formative, summative, diagnostic, and developmental approaches, each designed to assess processes, outcomes, or specific components. Benchmarking involves comparative evaluations such as competitive, functional, or internal benchmarking, aimed at measuring performance against industry standards or best practices. Both methods utilize qualitative and quantitative data, but evaluations focus on value judgment and improvement, while benchmarking emphasizes performance metrics and gap analysis.
Types of Benchmarking Techniques
Evaluation involves assessing performance, quality, or outcomes based on specific criteria, while benchmarking compares processes or metrics against industry leaders to identify improvement areas. Types of benchmarking techniques include internal benchmarking, which analyzes similar processes within the same organization; competitive benchmarking, focusing on direct competitors; functional benchmarking, comparing similar functions across different industries; and generic benchmarking, which examines best practices regardless of industry. Each technique provides unique insights to enhance operational efficiency and strategic planning.
Steps Involved in the Evaluation Process
The evaluation process involves defining clear objectives, selecting appropriate criteria, collecting relevant data, and analyzing results to determine performance or effectiveness. Key steps include establishing evaluation goals, designing data collection methods such as surveys or tests, implementing the data gathering phase, followed by data analysis and interpretation. Finally, generating actionable insights and recommendations based on the evaluation findings ensures continuous improvement and informed decision-making.
Benchmarking Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
Benchmarking process involves identifying key performance metrics, selecting best-in-class organizations for comparison, and systematically gathering data to assess performance gaps. The next steps include analyzing the collected information to pinpoint improvement opportunities, developing actionable strategies based on insights, and implementing changes to enhance processes or outcomes. Continuous monitoring and reassessment ensure that improvements are sustained and benchmarking remains effective over time.
Challenges in Evaluation vs Benchmarking
Evaluation faces challenges such as subjective criteria, difficulty in measuring qualitative outcomes, and limited comparability across different contexts. Benchmarking struggles with finding relevant standards, data availability issues, and adapting best practices from diverse industries. Both require careful consideration of context-specific variables to ensure meaningful results and actionable insights.
When to Use Evaluation or Benchmarking
Evaluation is used when assessing a system's or process's performance against predefined criteria to determine its effectiveness or quality, especially during development, implementation, or after modifications. Benchmarking comes into play when comparing performance metrics with industry standards or competitors to identify gaps, best practices, and opportunities for improvement. Choose evaluation for internal performance verification and benchmarking for strategic positioning against external standards.
Evaluation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com