Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring their achievement against defined standards or benchmarks. It provides critical feedback on overall performance, informing both educators and students about mastery of content. Explore the rest of the article to understand effective strategies and benefits of summative assessments for your educational goals.
Table of Comparison
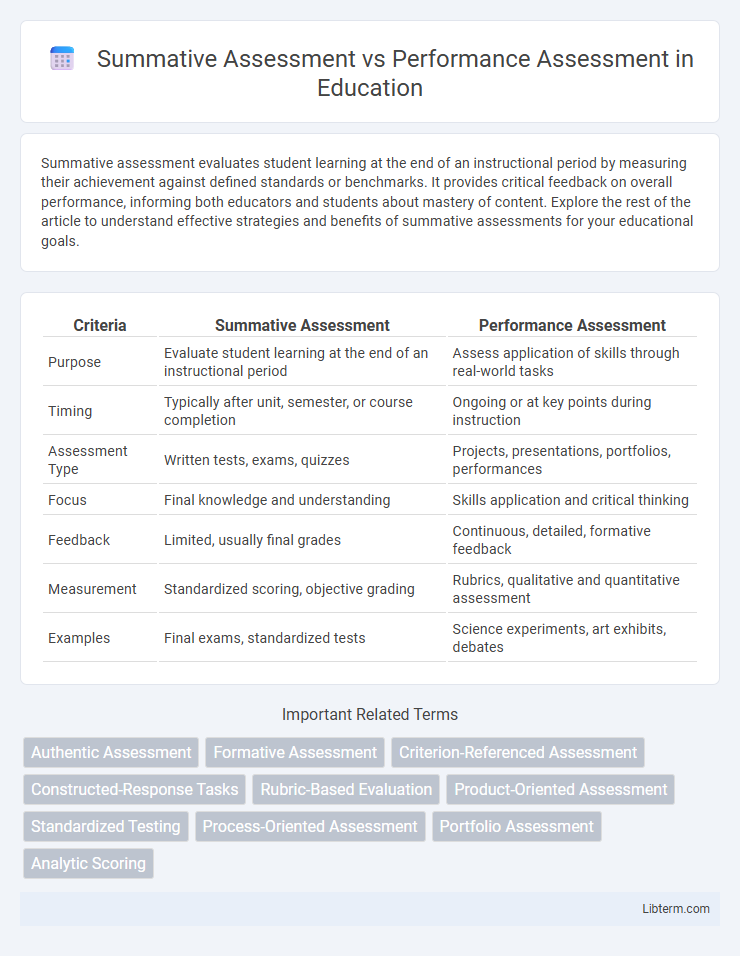
| Criteria | Summative Assessment | Performance Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period | Assess application of skills through real-world tasks |
| Timing | Typically after unit, semester, or course completion | Ongoing or at key points during instruction |
| Assessment Type | Written tests, exams, quizzes | Projects, presentations, portfolios, performances |
| Focus | Final knowledge and understanding | Skills application and critical thinking |
| Feedback | Limited, usually final grades | Continuous, detailed, formative feedback |
| Measurement | Standardized scoring, objective grading | Rubrics, qualitative and quantitative assessment |
| Examples | Final exams, standardized tests | Science experiments, art exhibits, debates |
Understanding Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring mastery of specific learning objectives through tests, quizzes, or final projects. It provides a comprehensive overview of overall academic achievement and is often used for grading or accountability purposes. This form of assessment is typically standardized, allowing educators to compare performance across different students or groups objectively.
What is Performance Assessment?
Performance assessment evaluates students' ability to apply skills and knowledge through real-world tasks, such as projects, presentations, or experiments. Unlike summative assessments that measure learning at the end of an instructional period, performance assessments provide practical insights into critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity. This method emphasizes authentic demonstration of competencies, making it essential for subjects requiring applied skills and continuous feedback.
Key Differences Between Summative and Performance Assessment
Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing a final grade or benchmark through tests or exams, while performance assessments measure students' ability to apply skills and knowledge in real-world tasks or projects. Summative assessment emphasizes content mastery and standardized evaluation, whereas performance assessment focuses on critical thinking, problem-solving, and demonstration of practical competencies. Key differences include timing, format, purpose, and the type of feedback given; summative assessments are often one-time evaluations, whereas performance assessments involve ongoing observation and formative input.
Purposes and Goals of Each Assessment Type
Summative assessment aims to evaluate student learning by measuring proficiency and achievement at the end of an instructional period, providing data for grading and accountability. Performance assessment focuses on applying skills and knowledge through real-world tasks, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. The goal of summative assessment is to quantify learning outcomes, while performance assessment seeks to enhance deeper understanding and practical application.
Advantages of Summative Assessment
Summative assessment provides a clear, objective measure of student learning by evaluating knowledge at the end of an instructional unit, ensuring alignment with curriculum standards. It offers standardized data to inform educators, policymakers, and stakeholders about overall achievement and academic progress. This type of assessment supports accountability and helps identify areas for curriculum improvement on a broad scale.
Benefits of Performance Assessment
Performance assessment enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in real-world tasks that demonstrate applied knowledge. It provides comprehensive insight into student abilities through authentic evaluations, fostering deeper learning and retention. This method also supports personalized feedback and growth, helping educators tailor instruction to individual student needs.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
Summative assessment often faces limitations such as a narrow focus on final outcomes, which may overlook the learning process and critical thinking skills, while its standardized format can create anxiety and limit opportunities for constructive feedback. Performance assessment challenges include the time-intensive nature of implementation and grading, as well as potential subjectivity in scoring, which can affect reliability and fairness across different evaluators. Both approaches require careful alignment with learning objectives and resource allocation to maximize their effectiveness in measuring student achievement.
Practical Examples in Educational Settings
Summative assessment often involves end-of-term exams or standardized tests to measure student learning outcomes against curriculum standards, such as final math exams or state-wide literacy tests. Performance assessment requires students to demonstrate skills through practical tasks like science lab experiments, oral presentations, or portfolio reviews, providing deeper insight into their application of knowledge. Both assessment types serve distinct purposes: summative assessments evaluate overall achievement, while performance assessments emphasize real-world skill integration and critical thinking.
When to Use Summative vs Performance Assessment
Summative assessment is best used at the end of a learning period to evaluate overall student achievement and mastery of content, providing a clear measure of success against standards. Performance assessment is ideal during instruction to assess skills, critical thinking, and application of knowledge through real-world tasks or projects. Use summative assessments for final grading and accountability, while performance assessments support formative feedback and skill development.
Integrating Both Assessments for Effective Learning
Integrating summative assessment and performance assessment enhances effective learning by combining objective measurement of knowledge with practical application skills. Summative assessments provide comprehensive evaluation of student achievement at the end of an instructional period, while performance assessments offer real-world tasks that assess critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. Balancing both approaches supports a holistic understanding of student progress and fosters deeper engagement with the learning material.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com