Project-Based Learning immerses students in real-world challenges that foster critical thinking, creativity, and collaboration. By engaging in hands-on projects, learners develop deeper understanding and practical skills that traditional methods often overlook. Discover how this innovative approach can transform your educational experience by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
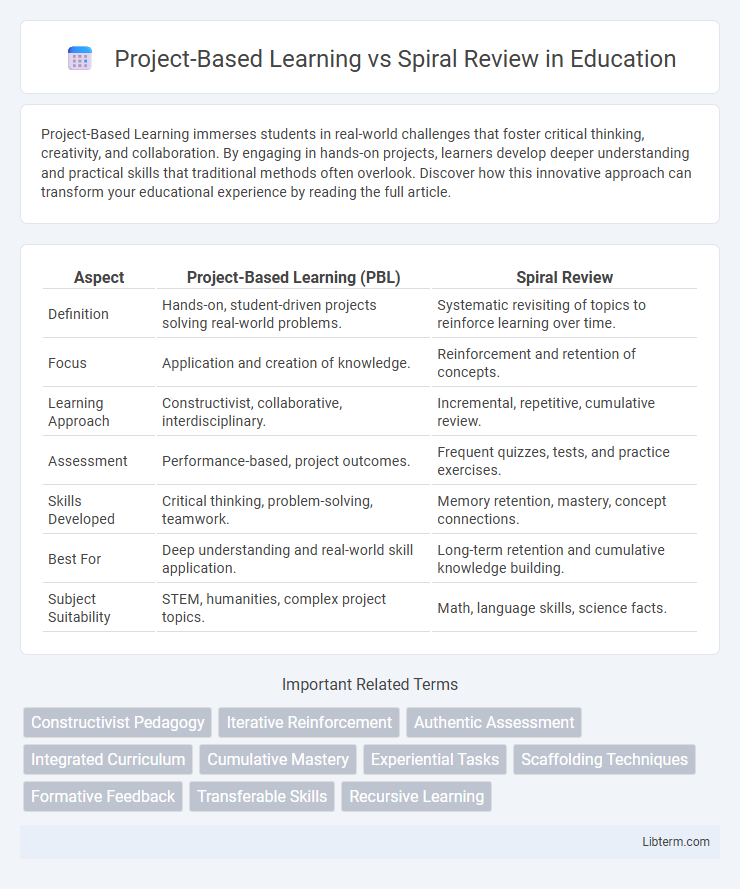
| Aspect | Project-Based Learning (PBL) | Spiral Review |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Hands-on, student-driven projects solving real-world problems. | Systematic revisiting of topics to reinforce learning over time. |
| Focus | Application and creation of knowledge. | Reinforcement and retention of concepts. |
| Learning Approach | Constructivist, collaborative, interdisciplinary. | Incremental, repetitive, cumulative review. |
| Assessment | Performance-based, project outcomes. | Frequent quizzes, tests, and practice exercises. |
| Skills Developed | Critical thinking, problem-solving, teamwork. | Memory retention, mastery, concept connections. |
| Best For | Deep understanding and real-world skill application. | Long-term retention and cumulative knowledge building. |
| Subject Suitability | STEM, humanities, complex project topics. | Math, language skills, science facts. |
Introduction to Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) immerses students in real-world challenges, promoting critical thinking and collaborative skills through active problem-solving and hands-on projects. Unlike Spiral Review, which revisits content periodically to reinforce mastery, PBL integrates interdisciplinary knowledge application in a dynamic, student-centered environment. This approach enhances student engagement and deepens understanding by connecting academic concepts to practical experiences.
What is Spiral Review?
Spiral Review is an instructional approach where previously learned concepts and skills are revisited and reinforced at regular intervals to enhance retention and mastery. This method integrates ongoing practice of prior knowledge alongside new material, promoting deeper understanding and long-term learning. It contrasts with Project-Based Learning by emphasizing iterative review rather than immersive, applied projects.
Core Principles of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) centers on active exploration through real-world projects, promoting critical thinking, collaboration, and problem-solving skills. It emphasizes student-driven inquiry, sustained engagement, and meaningful assessment tied to authentic outcomes. Unlike Spiral Review, which reinforces mastery through repeated skill practice, PBL advances learning by integrating interdisciplinary content within complex, context-rich challenges.
Key Features of Spiral Review
Spiral Review integrates continuous reinforcement of previously learned concepts through cyclic revisiting and practice, enhancing long-term retention and mastery. Its key features include systematic reintroduction of material at increasing levels of difficulty, frequent formative assessments to monitor progress, and targeted feedback to address learning gaps. This approach contrasts with Project-Based Learning by emphasizing structured repetition and incremental skill development rather than immersive, application-driven tasks.
Benefits of Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking by engaging students in real-world problems, fostering deeper understanding and retention compared to Spiral Review's repetitive practice. PBL encourages collaboration, creativity, and practical application, which improves communication skills and prepares learners for complex tasks in professional environments. The immersive nature of PBL also boosts motivation and student ownership of learning, leading to higher academic achievement and long-term knowledge retention.
Advantages of Spiral Review
Spiral Review enhances long-term retention by continuously revisiting key concepts, which strengthens student understanding over time. This method supports differentiated learning by allowing learners to progress at their own pace while reinforcing previously covered material. Improved mastery in subjects like mathematics and language arts is often observed as Spiral Review systematically builds upon prior knowledge, promoting deeper cognitive connections.
Challenges in Implementing Project-Based Learning
Project-Based Learning (PBL) presents challenges such as the significant time investment required for planning and facilitating meaningful projects, which can strain classroom schedules and teacher workloads. Differentiating instruction to meet diverse student needs within hands-on, collaborative projects demands advanced classroom management and assessment strategies. Limited resources and insufficient professional development further hinder effective PBL implementation, impacting both student engagement and learning outcomes.
Limitations of Spiral Review
Spiral review often suffers from inconsistent reinforcement, leading to gaps in student retention and mastery over time. Its repetitive nature can cause disengagement, as learners repeatedly revisit similar content without deeper application or challenge. Unlike project-based learning, spiral review lacks the context and hands-on experiences that drive critical thinking and long-term skill development.
Comparing Project-Based Learning and Spiral Review
Project-Based Learning immerses students in complex, real-world tasks promoting critical thinking and long-term retention, whereas Spiral Review emphasizes repeated exposure and practice of concepts over time to strengthen memory and mastery. While Project-Based Learning encourages creativity and problem-solving through hands-on projects, Spiral Review methodically revisits key topics ensuring cumulative skill reinforcement. Both strategies improve learning outcomes but differ in approach: experiential application versus systematic revisitation.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Classroom
Project-Based Learning engages students in real-world challenges, promoting deep understanding and collaboration, ideal for subjects requiring practical application and creative problem-solving. Spiral Review reinforces key concepts through repeated, spaced practice, boosting retention and mastery, particularly effective in math and language skills. Selecting the right approach depends on curriculum goals, student needs, and classroom dynamics to balance skill development with critical thinking.
Project-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com