Lecture-based learning remains a foundational teaching method where instructors deliver structured content directly to students, facilitating efficient knowledge transfer in various subjects. This approach emphasizes clear communication and expert guidance, helping learners grasp complex concepts quickly. Explore the article to discover how lecture-based learning can enhance Your educational experience and when it might be most effective.
Table of Comparison
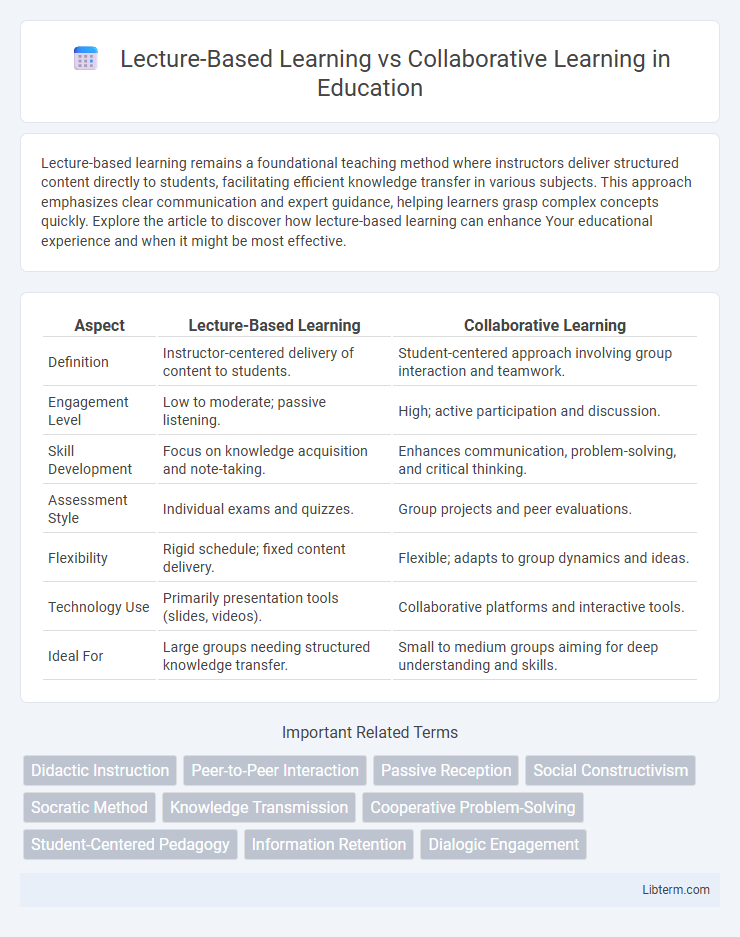
| Aspect | Lecture-Based Learning | Collaborative Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instructor-centered delivery of content to students. | Student-centered approach involving group interaction and teamwork. |
| Engagement Level | Low to moderate; passive listening. | High; active participation and discussion. |
| Skill Development | Focus on knowledge acquisition and note-taking. | Enhances communication, problem-solving, and critical thinking. |
| Assessment Style | Individual exams and quizzes. | Group projects and peer evaluations. |
| Flexibility | Rigid schedule; fixed content delivery. | Flexible; adapts to group dynamics and ideas. |
| Technology Use | Primarily presentation tools (slides, videos). | Collaborative platforms and interactive tools. |
| Ideal For | Large groups needing structured knowledge transfer. | Small to medium groups aiming for deep understanding and skills. |
Introduction to Lecture-Based and Collaborative Learning
Lecture-Based Learning emphasizes a structured delivery of content by an instructor, facilitating efficient dissemination of core knowledge and concepts. Collaborative Learning promotes active engagement among students through group interactions, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Both approaches offer unique benefits in educational environments, balancing content absorption with interactive skill development.
Defining Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-based learning centers on a traditional educational model where an instructor delivers content directly to students, emphasizing passive reception of information. This method prioritizes structured presentation, clear organization of material, and individual note-taking to facilitate knowledge acquisition. Typically, lecture-based learning suits large groups and subjects requiring foundational understanding before advancing to interactive or application-based activities.
Key Features of Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning emphasizes active student participation, group problem-solving, and mutual knowledge construction, fostering communication and critical thinking skills. This approach leverages diverse perspectives and peer feedback to deepen understanding and enhance retention compared to passive information reception in lecture-based learning. The interactive nature of collaborative learning also improves social skills and accountability among learners, promoting a more engaging and dynamic educational environment.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Methods
Lecture-based learning, dominant since the medieval university era, emphasized knowledge transmission from teacher to student through oral presentation, reflecting the authoritative role of educators in classical education. Collaborative learning emerged prominently in the 20th century, influenced by constructivist theories from psychologists like Vygotsky, who highlighted social interaction as crucial for cognitive development. The shift toward collaborative methods marks a significant evolution, integrating peer engagement and active participation to enhance critical thinking and deeper understanding beyond passive listening.
Advantages of Lecture-Based Learning
Lecture-based learning offers a structured and efficient delivery of information, allowing instructors to cover extensive content quickly to large audiences. It provides clear, authoritative explanations that help students grasp foundational knowledge and complex concepts systematically. This method also facilitates standardized assessments by ensuring all learners receive the same core material.
Benefits of Collaborative Learning
Collaborative learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging active participation and diverse perspectives among students. It fosters communication, teamwork, and social interaction, which are essential for real-world success and improved knowledge retention. Research shows that collaborative learning environments increase student motivation and engagement, leading to higher academic achievement compared to traditional lecture-based learning.
Challenges in Implementing Both Approaches
Lecture-Based Learning faces challenges such as limited student engagement, passive knowledge absorption, and difficulty addressing diverse learning paces. Collaborative Learning encounters obstacles including coordinating group dynamics, ensuring equal participation, and managing time-intensive discussions. Both approaches require tailored strategies to overcome these issues and optimize educational outcomes.
Student Engagement and Motivation Comparison
Lecture-based learning often results in lower student engagement and motivation due to its passive nature, limiting opportunities for interaction and active participation. Collaborative learning enhances engagement by promoting peer interaction, critical thinking, and shared responsibility, which boosts intrinsic motivation and deepens understanding. Studies show that students in collaborative settings report higher motivation levels and greater enthusiasm for learning compared to those in traditional lecture environments.
Best Practices for Blending Both Methods
Effective integration of lecture-based learning and collaborative learning enhances student engagement and knowledge retention by combining structured content delivery with interactive group activities. Implementing brief, focused lectures followed by collaborative problem-solving sessions maximizes cognitive absorption and fosters critical thinking skills. Utilizing technology, such as learning management systems and real-time feedback tools, supports seamless transitions between individual instruction and teamwork, optimizing educational outcomes.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Education
Lecture-based learning offers structured, expert-driven content delivery ideal for foundational knowledge acquisition, while collaborative learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving through peer interaction and shared perspectives. The most effective education approach depends on course objectives, student demographics, and subject complexity, often benefiting from a blended model that integrates both methods. Educators should assess learning outcomes and adapt strategies to maximize engagement and knowledge retention in diverse learning environments.
Lecture-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com