Private schools offer tailored educational experiences with smaller class sizes and specialized programs that foster academic excellence and personal growth. Families often choose private schooling for its rigorous curriculum, strong community values, and enhanced extracurricular opportunities. Discover how private schools can benefit Your child's future by exploring the key advantages and considerations in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
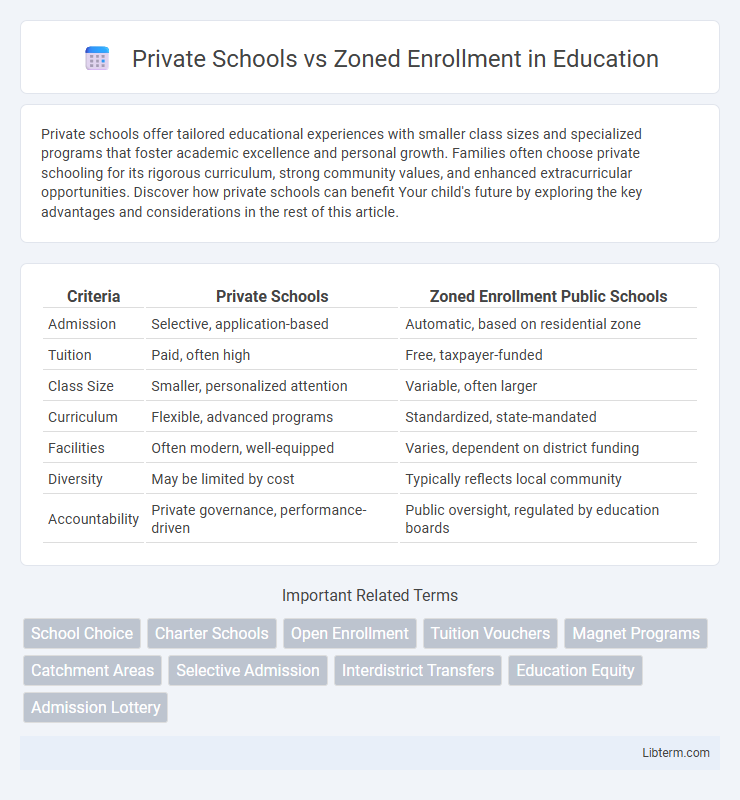
| Criteria | Private Schools | Zoned Enrollment Public Schools |
|---|---|---|
| Admission | Selective, application-based | Automatic, based on residential zone |
| Tuition | Paid, often high | Free, taxpayer-funded |
| Class Size | Smaller, personalized attention | Variable, often larger |
| Curriculum | Flexible, advanced programs | Standardized, state-mandated |
| Facilities | Often modern, well-equipped | Varies, dependent on district funding |
| Diversity | May be limited by cost | Typically reflects local community |
| Accountability | Private governance, performance-driven | Public oversight, regulated by education boards |
Introduction to Private Schools and Zoned Enrollment
Private schools operate independently of government funding, offering specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and diverse educational philosophies tailored to student needs. Zoned enrollment restricts public school attendance to students living within specific geographic boundaries, ensuring local access but limiting school choice. Comparing these enrollment models reveals distinct advantages in flexibility, resources, and community integration impacting student outcomes.
Key Differences Between Private and Zoned Schools
Private schools offer specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and selective admissions, allowing for tailored educational experiences and often higher academic achievement. Zoned schools serve students based on geographic boundaries, ensuring access for all children within a community but typically with larger class sizes and standardized resources. Funding sources also differ, as private schools rely on tuition and donations, while zoned schools receive public funding from local taxes.
Academic Performance: Private vs. Zoned Enrollment
Private schools often demonstrate higher academic performance based on standardized test scores and college admission rates compared to zoned public schools. Factors contributing to this include smaller class sizes, specialized curricula, and access to enhanced resources. Zoned public schools may face challenges such as funding disparities and diverse student populations, impacting consistent academic outcomes.
Admission Processes and Criteria
Private schools often implement selective admission processes involving entrance exams, interviews, and evaluation of academic records, prioritizing students with strong academic performance or specific talents. Zoned enrollment systems allocate students based on geographic boundaries, typically accepting all applicants from designated areas regardless of academic standing. Admission criteria in private schools emphasize individualized assessments and holistic review, contrasting with the standardized, location-based criteria used in public school zoning policies.
Tuition Costs and Financial Considerations
Private schools typically require tuition payments ranging from $5,000 to over $50,000 annually, depending on the institution and location, whereas zoned public schools usually have no tuition fees as they are funded by local taxes. Families must consider additional expenses in private education such as registration fees, uniforms, and extracurricular activities, which can significantly increase the overall cost. Financial aid, scholarships, and payment plans are often available at private schools to offset tuition costs, while public schools generally provide education free of charge but may have costs for supplies and optional programs.
Curriculum and Educational Approach
Private schools typically offer specialized curricula emphasizing advanced academics, arts, or specific pedagogical philosophies like Montessori or STEM-focused education, allowing for tailored learning experiences. Zoned enrollment public schools follow standardized state-mandated curricula designed to meet broad educational standards and accommodate diverse student populations within geographic boundaries. This results in private schools often promoting a more flexible, innovative approach, while zoned schools provide consistent, equitable educational frameworks aligned with local district requirements.
Class Size and Student-to-Teacher Ratio
Private schools typically offer smaller class sizes and lower student-to-teacher ratios compared to zoned public schools, enhancing individualized instruction and student engagement. Zoned enrollment in public schools often results in larger classes due to fixed geographic boundaries, which can impact personalized attention and learning outcomes. Research indicates that lower student-to-teacher ratios in private schools contribute to higher academic performance and improved teacher-student interaction.
Diversity and Community Environment
Private schools often offer diverse student populations through selective admissions and specialized programs, fostering unique cultural and intellectual environments. Zoned enrollment public schools reflect the demographic composition of their local neighborhoods, promoting community cohesion and inclusive engagement among residents. Both systems influence diversity and community environment differently, with private schools emphasizing curated diversity and public schools anchored in geographic and socioeconomic representation.
Extracurricular Activities and Facilities
Private schools often offer a wider range of extracurricular activities and state-of-the-art facilities, including specialized sports complexes, art studios, and advanced science labs, enhancing student engagement beyond academics. Zoned enrollment public schools may have limited resources, resulting in fewer club options and older or shared facilities, which can affect students' access to diverse extracurricular experiences. Access to quality facilities and programs plays a crucial role in student development and can influence families' choice between private education and public zoned schools.
Making the Right Choice: Factors for Families
Private schools often offer specialized curricula, smaller class sizes, and enhanced extracurricular activities, appealing to families seeking tailored education and individual attention. Zoned enrollment ensures children attend schools based on geographic boundaries, promoting community ties and ease of access but may limit choice and program variety. Families should weigh factors such as educational goals, budget, location, and the child's specific needs to determine the ideal fit between private schooling and zoned public options.
Private Schools Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com