A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal agreement between two or more parties outlining their mutual intentions and responsibilities without creating legally binding obligations. It serves as a foundation for cooperation, clarifying expectations and fostering transparent communication. Explore the article to understand how an MOU can benefit your collaborative projects and ensure clear partnerships.
Table of Comparison
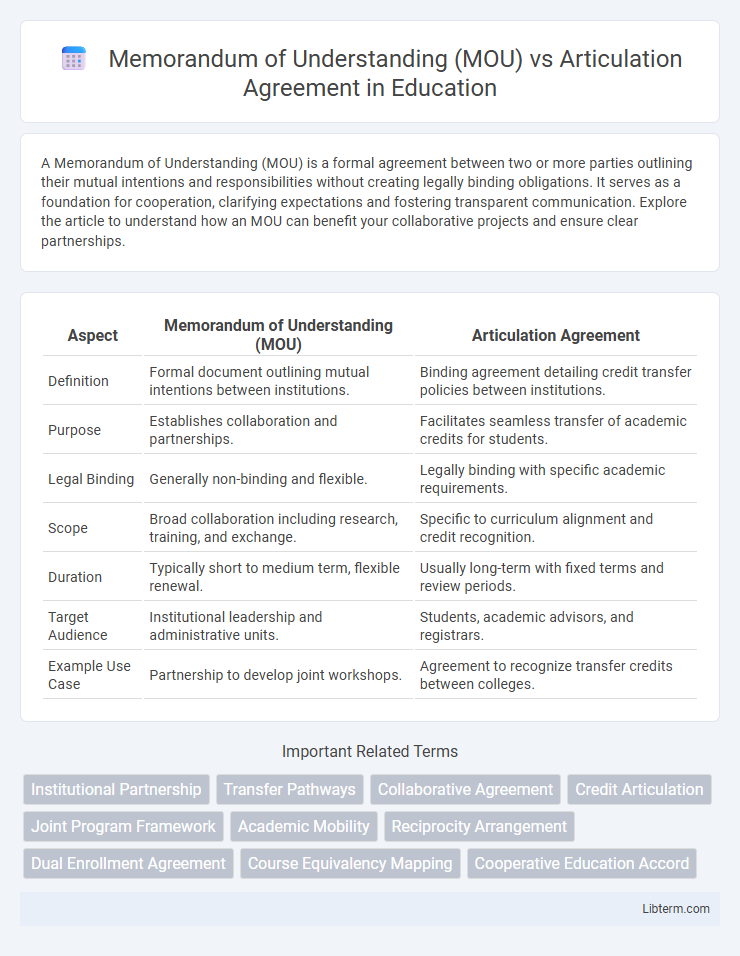
| Aspect | Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) | Articulation Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Formal document outlining mutual intentions between institutions. | Binding agreement detailing credit transfer policies between institutions. |
| Purpose | Establishes collaboration and partnerships. | Facilitates seamless transfer of academic credits for students. |
| Legal Binding | Generally non-binding and flexible. | Legally binding with specific academic requirements. |
| Scope | Broad collaboration including research, training, and exchange. | Specific to curriculum alignment and credit recognition. |
| Duration | Typically short to medium term, flexible renewal. | Usually long-term with fixed terms and review periods. |
| Target Audience | Institutional leadership and administrative units. | Students, academic advisors, and registrars. |
| Example Use Case | Partnership to develop joint workshops. | Agreement to recognize transfer credits between colleges. |
Introduction to MOUs and Articulation Agreements
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) establishes a formal, non-binding agreement between parties to outline mutual goals and responsibilities, often used in collaborations or partnerships. An Articulation Agreement specifically defines the transfer policies and credit equivalencies between educational institutions to facilitate student progression. Both documents serve as foundational frameworks to clarify expectations and streamline cooperative efforts across organizations.
Definition and Purpose of a Memorandum of Understanding
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a formal agreement between two or more parties that outlines the terms and details of a mutual understanding or collaboration without creating legally binding obligations. Its primary purpose is to establish a clear framework for cooperation, clarify roles and responsibilities, and document shared goals before entering into a detailed contract or partnership. Unlike an Articulation Agreement, which specifically facilitates credit transfer between educational institutions, an MOU serves broader purposes across various sectors.
Definition and Purpose of an Articulation Agreement
An Articulation Agreement is a formal partnership between two educational institutions designed to streamline student transfer from one school to another by clearly outlining the recognition of coursework and credits. This agreement ensures that students who complete specified courses at a community college or lower-division institution can transfer seamlessly to a four-year university without loss of credit. Its primary purpose is to facilitate academic continuity and reduce barriers in credit acceptance, supporting student progression toward degree completion.
Key Differences Between MOUs and Articulation Agreements
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is a non-binding agreement outlining general terms and intentions between parties, often used to establish collaboration frameworks without legal obligations. In contrast, an Articulation Agreement is a formal, binding contract between educational institutions specifying credit transfer policies to ensure seamless student progression. MOUs emphasize mutual cooperation and shared goals, while Articulation Agreements focus on detailed academic credit recognition and transferability.
Common Elements in Both Agreements
Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) and Articulation Agreement both establish a formal framework for collaboration, articulating shared goals, responsibilities, and terms of engagement between parties. Common elements include clear definitions of roles, specific objectives, duration of the agreement, confidentiality clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms. These agreements ensure mutual understanding and streamline cooperation, often facilitating educational partnerships or institutional collaborations.
Legal Implications and Binding Nature
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) typically outlines the intent of parties to collaborate without creating legally binding obligations, serving as a formal but non-binding agreement. In contrast, an Articulation Agreement is a legally binding contract between educational institutions that ensures credit transfer and academic progression, imposing enforceable obligations on the parties. Understanding the distinct legal implications is crucial for institutions to manage risks and uphold educational commitments effectively.
Use Cases: When to Use an MOU vs Articulation Agreement
A Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) is ideal for formalizing general partnerships, outlining mutual goals, and expressing intent without creating legally binding obligations, commonly used in early-stage collaborations or non-contractual agreements. Articulation Agreements specifically govern the transfer of academic credits between educational institutions, ensuring students receive proper recognition for completed coursework, and are essential when establishing clear pathways for credit acceptance in higher education. Use an MOU for broad cooperation frameworks and an Articulation Agreement when defining precise academic credit transfer policies.
Benefits and Limitations of MOUs
Memorandums of Understanding (MOUs) facilitate flexible, non-binding agreements between parties to outline mutual intentions without legal obligations, offering quick establishment and fostering collaboration. Their benefits include ease of modification, clarity in roles, and foundation for future binding contracts, while limitations involve lack of enforceability and potential ambiguity in terms. MOUs may not guarantee commitment or performance, making them less suitable for formalizing complex, legally binding arrangements compared to articulation agreements.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Articulation Agreements
Articulation agreements streamline credit transfer between institutions, reducing course redundancy and saving students time and money, but they may limit flexibility due to rigid curriculum alignment. These agreements enhance academic planning by clearly defining transferable courses, yet they can become outdated if institutions change program requirements or policies. While beneficial for ensuring a smooth transition, articulation agreements often require continuous updates and cooperation between educational partners to remain effective.
Choosing the Right Agreement for Your Institution
Selecting the right agreement between a Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) and an Articulation Agreement depends on institutional goals and partnership specifics. MOUs provide flexible frameworks for collaboration without binding credit transfer obligations, ideal for research or resource-sharing partnerships. Articulation Agreements ensure formal credit transfer policies between educational institutions, supporting streamlined student progression and degree completion.
Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com