Punitive discipline focuses on imposing consequences to correct undesirable behavior, often involving penalties or reprimands. While it aims to discourage negative actions, this approach can sometimes foster resentment or fear rather than understanding and growth. Explore this article to learn how punitive discipline impacts behavior and discover more effective alternatives for your discipline strategies.
Table of Comparison
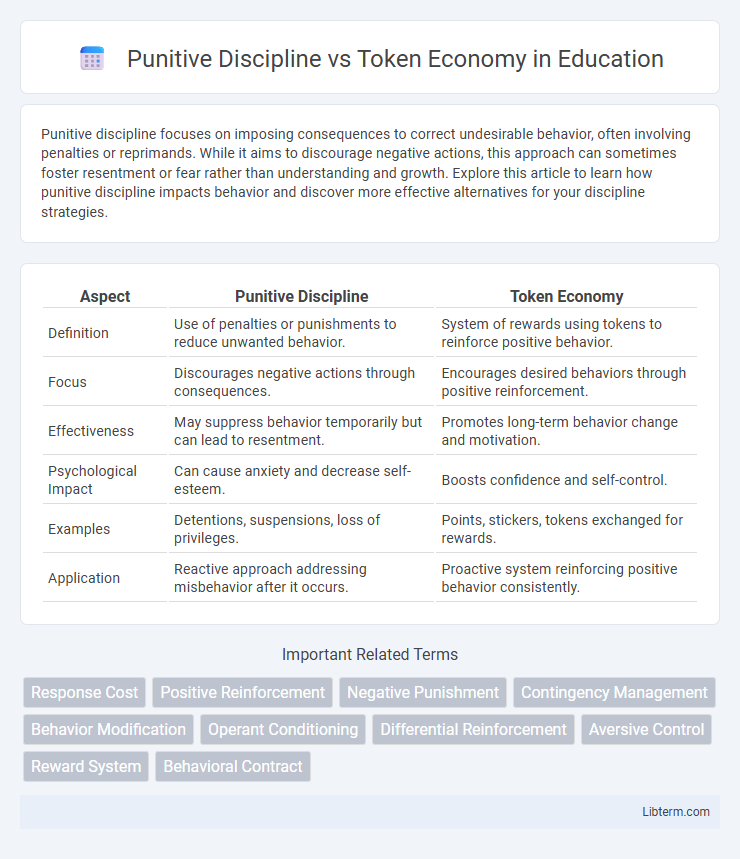
| Aspect | Punitive Discipline | Token Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of penalties or punishments to reduce unwanted behavior. | System of rewards using tokens to reinforce positive behavior. |
| Focus | Discourages negative actions through consequences. | Encourages desired behaviors through positive reinforcement. |
| Effectiveness | May suppress behavior temporarily but can lead to resentment. | Promotes long-term behavior change and motivation. |
| Psychological Impact | Can cause anxiety and decrease self-esteem. | Boosts confidence and self-control. |
| Examples | Detentions, suspensions, loss of privileges. | Points, stickers, tokens exchanged for rewards. |
| Application | Reactive approach addressing misbehavior after it occurs. | Proactive system reinforcing positive behavior consistently. |
Understanding Punitive Discipline
Punitive discipline involves applying negative consequences or punishment to reduce undesired behaviors, often relying on penalties like detention, suspension, or verbal reprimands. Research indicates that while punitive discipline may immediately suppress unwanted actions, it can lead to increased aggression, anxiety, and a decline in student motivation over time. Understanding the psychological impact of punitive measures highlights the importance of alternative systems like token economies, which reinforce positive behavior through rewards rather than punishment.
Defining the Token Economy System
The Token Economy system is a behavior modification technique that uses symbolic tokens as rewards for desired behavior, which can later be exchanged for meaningful privileges or items. This positive reinforcement strategy contrasts with punitive discipline by emphasizing motivation and skill-building instead of punishment or negative consequences. Established in applied behavior analysis, the token economy system effectively increases desired behaviors in educational, therapeutic, and organizational settings.
Historical Background and Origins
Punitive discipline traces back to ancient legal codes, such as the Code of Hammurabi, emphasizing punishment to enforce social order and deter misbehavior. Token economy emerged in the 1960s within behavioral psychology, pioneered by B.F. Skinner's operant conditioning principles to reinforce positive behaviors through symbolic rewards. The shift from punitive measures to token economies reflects evolving educational and psychological approaches prioritizing motivation and behavior modification over punishment.
Core Principles of Each Approach
Punitive discipline centers on applying negative consequences to reduce undesirable behaviors, emphasizing deterrence and behavioral control through punishment or reprimands. Token economy operates on positive reinforcement, where individuals earn tokens for desired behaviors that can be exchanged for rewards, promoting motivation and consistent behavior change. Core principles of punitive discipline include consequence-based behavior modification, while token economy relies on systematic reinforcement and reward contingency.
Behavioral Outcomes and Effectiveness
Punitive discipline often leads to increased aggression, resentment, and avoidance behaviors, reducing long-term effectiveness in promoting positive behavioral change. In contrast, token economy systems reinforce desired behaviors by providing tangible rewards, leading to higher rates of sustained compliance and motivation. Research indicates that token economies improve behavioral outcomes more effectively by enhancing intrinsic motivation and promoting consistent positive reinforcement.
Impact on Student Motivation
Punitive discipline often decreases student motivation by fostering fear and resentment, leading to disengagement and reduced intrinsic interest in learning. In contrast, token economy systems enhance motivation by rewarding positive behaviors with tangible tokens that can be exchanged for privileges, reinforcing desired conduct through positive reinforcement. Research shows token economies increase student participation and persistence, making them more effective for sustained behavioral change than punishment-based approaches.
Psychological Effects on Children
Punitive discipline often results in increased anxiety, fear, and diminished self-esteem in children, negatively impacting their emotional development and long-term mental health. Token economy systems, which reward positive behavior through tokens exchangeable for privileges or items, promote motivation, self-regulation, and reinforcement of prosocial behaviors without inducing stress. Research indicates that token economies foster a supportive learning environment, encouraging intrinsic motivation while punitive measures can lead to avoidance behaviors and aggression.
Classroom Management Strategies
Punitive discipline in classroom management involves imposing penalties or negative consequences to reduce undesirable behaviors, often leading to resistance and decreased student motivation. Token economy systems reinforce positive behavior through a structured reward system, where students earn tokens exchangeable for privileges or items, promoting engagement and self-regulation. Research indicates token economies enhance classroom climate and academic performance more effectively than punitive approaches by focusing on reinforcement rather than punishment.
Ethical Considerations and Criticisms
Punitive discipline raises ethical concerns due to its potential to cause psychological harm and reinforce negative behaviors, as it relies on punishment that may lead to fear or resentment. Token economy systems are often praised for promoting positive reinforcement but face criticism regarding the manipulation of behavior and possible dependency on external rewards. Both approaches require careful ethical evaluation to balance effective behavior management with respect for individual dignity and autonomy.
Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the right behavior management strategy depends on the goals and context; punitive discipline emphasizes consequences such as time-outs or loss of privileges to reduce undesirable behaviors, while token economy systems reinforce positive behavior through rewards and tokens exchangeable for privileges. Research shows token economies tend to promote long-term behavior change and motivation by encouraging desired actions, whereas punitive measures may suppress behavior temporarily but risk negative side effects like resentment or fear. Tailoring the approach to the individual's needs and the environment ensures effective behavior modification and fosters a supportive atmosphere conducive to learning and growth.
Punitive Discipline Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com