Creative Commons resources provide a vast collection of images, music, videos, and texts that are free to use legally, offering flexible licensing options to suit your project's needs. These resources empower creators and learners to share and build upon content without the usual copyright restrictions. Explore the article to discover how you can leverage Creative Commons materials effectively for your next project.
Table of Comparison
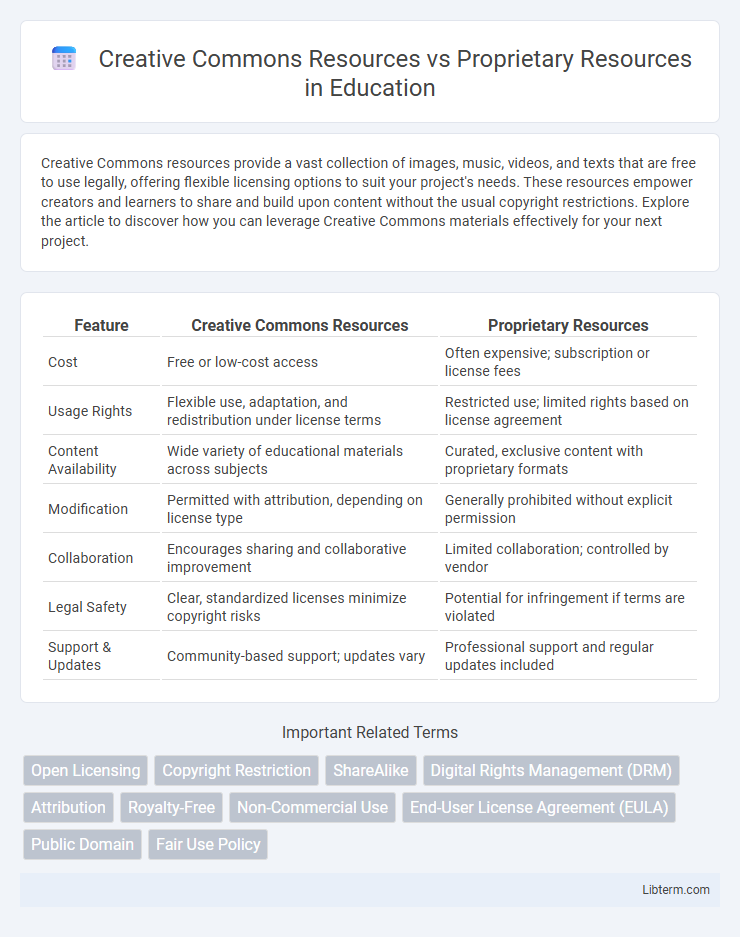
| Feature | Creative Commons Resources | Proprietary Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Free or low-cost access | Often expensive; subscription or license fees |
| Usage Rights | Flexible use, adaptation, and redistribution under license terms | Restricted use; limited rights based on license agreement |
| Content Availability | Wide variety of educational materials across subjects | Curated, exclusive content with proprietary formats |
| Modification | Permitted with attribution, depending on license type | Generally prohibited without explicit permission |
| Collaboration | Encourages sharing and collaborative improvement | Limited collaboration; controlled by vendor |
| Legal Safety | Clear, standardized licenses minimize copyright risks | Potential for infringement if terms are violated |
| Support & Updates | Community-based support; updates vary | Professional support and regular updates included |
Introduction to Creative Commons and Proprietary Resources
Creative Commons resources offer legally shared content under flexible licenses that encourage reuse, remixing, and distribution, fostering collaboration and innovation across digital platforms. Proprietary resources, by contrast, are protected by exclusive rights and restrictions that limit access, copying, and modification, typically requiring direct permission or purchase from the owner. Understanding these licensing models is essential for navigating content usage rights and maximizing resource accessibility in creative and academic projects.
Key Definitions: Creative Commons and Proprietary Licenses
Creative Commons licenses provide a standardized way for creators to grant permission for use, sharing, and adaptation of their works while maintaining certain rights, enhancing accessibility and collaboration. Proprietary licenses, in contrast, restrict usage, modification, and distribution, granting rights exclusively to the owner or licensed parties under specific terms and conditions. Understanding these key definitions highlights the fundamental differences in control, flexibility, and legal obligations between freely accessible Creative Commons resources and tightly controlled proprietary resources.
Types of Creative Commons Licenses
Creative Commons licenses include Attribution (CC BY), Attribution-ShareAlike (CC BY-SA), Attribution-NoDerivs (CC BY-ND), Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC), Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike (CC BY-NC-SA), and Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivs (CC BY-NC-ND), each allowing different levels of reuse, modification, and commercial use. These licenses enable creators to share their works while retaining specific rights, contrasting proprietary resources that restrict access and modification. Understanding the distinctions among these licenses is essential for content creators and users to comply with legal and ethical guidelines when using open content.
Attributes of Proprietary Resources
Proprietary resources are characterized by exclusive ownership, restricted access, and controlled distribution, often requiring licensing fees or subscription payments. These resources typically offer specialized content, enhanced security, and dedicated support, making them suitable for commercial applications where quality assurance and intellectual property protection are priorities. Unlike Creative Commons resources, proprietary materials limit modifications and sharing to protect the creator's rights and maintain market value.
Benefits of Using Creative Commons Resources
Creative Commons resources provide free, legally shareable content that facilitates collaboration and innovation across diverse fields. These resources enable creators and users to access, modify, and distribute works without the need for costly licensing fees or complex permissions, promoting educational and cultural growth. Utilizing Creative Commons materials enhances accessibility, supports open knowledge ecosystems, and encourages ethical reuse of intellectual property.
Limitations and Risks of Proprietary Resources
Proprietary resources often impose strict licensing restrictions that limit modification, distribution, and usage rights, thereby reducing flexibility for users and creators. Dependence on proprietary formats and software can lead to compatibility issues, vendor lock-in, and increased costs due to subscription fees or licensing renewals. These limitations increase the risk of data loss or access denial if the provider discontinues support or changes terms, making proprietary resources less sustainable for long-term projects.
Comparing Accessibility and Usage Rights
Creative Commons resources offer broad accessibility with flexible usage rights that permit sharing, adapting, and redistribution under specific conditions, enhancing collaboration and innovation. Proprietary resources restrict access and usage, typically requiring licenses or payments that limit modification and redistribution, preserving exclusive control. This distinction profoundly impacts content availability, cost efficiency, and legal freedom for users and creators in various fields.
Cost Implications: Free vs Paid Resources
Creative Commons resources offer cost-effective access to images, music, and texts through free licenses that promote sharing and adaptation without monetary fees, making them ideal for budget-conscious projects. Proprietary resources often require upfront payments, subscriptions, or royalties, which can significantly increase costs depending on usage rights and exclusivity. Choosing between these options involves balancing budget constraints with the need for specific legal protections and content quality.
Best Practices for Resource Selection
Creative Commons resources offer flexible licensing that facilitates legal sharing and adaptation, making them ideal for projects requiring wide distribution and collaboration. Proprietary resources provide exclusive rights and often superior quality or specialized features, suitable for projects demanding high security or brand control. Best practices for resource selection include evaluating licensing terms, assessing project goals for distribution or exclusivity, and verifying the resource's credibility and compatibility with intended use.
Conclusion: Making Informed Choices
Choosing between Creative Commons resources and proprietary resources depends on the intended use, budget, and legal considerations. Creative Commons materials offer flexible licensing and cost-effective access, ideal for educational and collaborative projects, while proprietary resources provide exclusive rights and higher control suited for commercial ventures. Evaluating the specific project needs and licensing terms ensures informed decisions that balance accessibility, legal compliance, and creative freedom.
Creative Commons Resources Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com