Maximizing efficiency enhances productivity and minimizes wasted resources in any process or system. Streamlined workflows and smart time management are key strategies that help you achieve optimal results. Explore the rest of the article to discover practical tips for boosting efficiency in your daily routine.
Table of Comparison
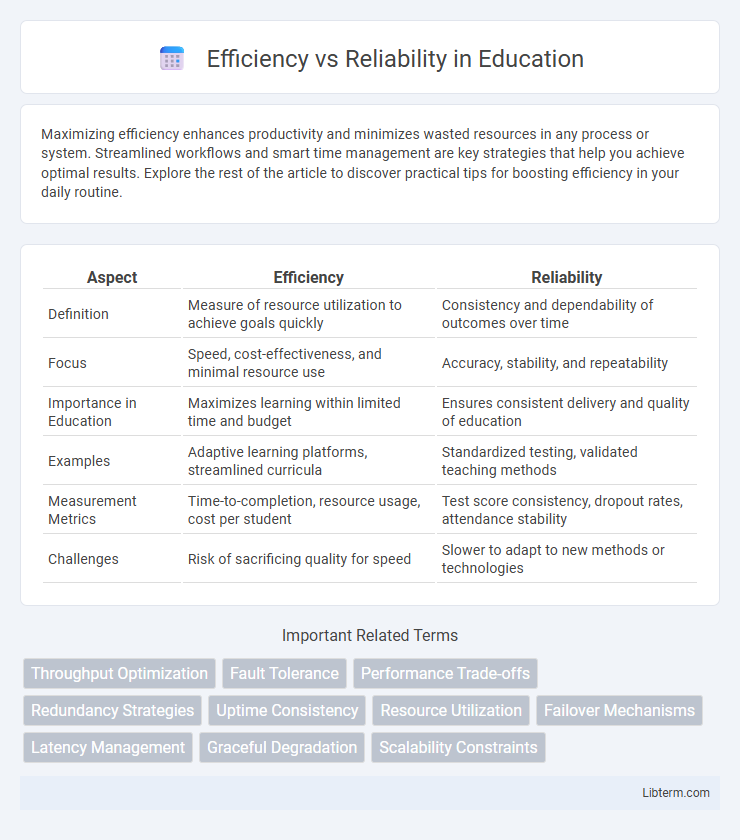
| Aspect | Efficiency | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measure of resource utilization to achieve goals quickly | Consistency and dependability of outcomes over time |
| Focus | Speed, cost-effectiveness, and minimal resource use | Accuracy, stability, and repeatability |
| Importance in Education | Maximizes learning within limited time and budget | Ensures consistent delivery and quality of education |
| Examples | Adaptive learning platforms, streamlined curricula | Standardized testing, validated teaching methods |
| Measurement Metrics | Time-to-completion, resource usage, cost per student | Test score consistency, dropout rates, attendance stability |
| Challenges | Risk of sacrificing quality for speed | Slower to adapt to new methods or technologies |
Understanding Efficiency and Reliability
Efficiency measures the ratio of useful output to total input, emphasizing resource utilization and time management in processes, whereas reliability assesses the consistency of performance and the probability of failure-free operation over time. Understanding efficiency involves analyzing productivity metrics, energy consumption, and cost-effectiveness, while reliability focuses on durability, maintenance intervals, and system robustness. Optimizing both requires balancing rapid output with sustained operational dependability to ensure long-term business success.
Key Differences Between Efficiency and Reliability
Efficiency measures how well resources are utilized to achieve maximum output with minimal waste, emphasizing speed and cost-effectiveness. Reliability focuses on consistent performance over time, ensuring systems or products function correctly without failure under specified conditions. The key difference lies in efficiency prioritizing optimal resource use, while reliability prioritizes durability and dependability.
Importance of Efficiency in Modern Systems
Efficiency in modern systems drives reduced energy consumption, faster processing speeds, and lower operational costs, making it critical for sustainable technology development. High efficiency enhances system scalability and responsiveness, enabling seamless user experiences and supporting increased workloads. Optimizing resource utilization directly impacts overall performance, ensuring that modern systems meet growing demands while maintaining economic and environmental viability.
The Critical Role of Reliability
Reliability plays a critical role in balancing efficiency by ensuring consistent performance and minimizing downtime, which directly impacts productivity and cost-effectiveness. Systems designed with high reliability reduce the risk of failures and maintenance interruptions, allowing efficient processes to operate smoothly over time. Prioritizing reliability enhances long-term operational stability, making efficiency sustainable and preventing costly disruptions.
Trade-offs: When to Prioritize Efficiency Over Reliability
Prioritizing efficiency over reliability is crucial in scenarios where speed and cost reduction directly impact business outcomes, such as high-frequency trading or real-time data processing. Systems with optimized efficiency can handle larger workloads with minimal resource consumption but may compromise fault tolerance and durability. Organizations managing non-critical processes or seeking rapid iteration cycles often accept reduced reliability to maximize throughput and operational agility.
Case Studies: Efficiency vs Reliability in Real-World Applications
Case studies in industries such as aerospace, manufacturing, and IT illustrate that prioritizing efficiency often leads to increased productivity and cost savings, while emphasizing reliability ensures system stability and long-term performance. A notable example is Toyota's production system, which balances lean efficiency with robust quality controls to minimize downtime and defects. In cloud computing, Amazon Web Services employs redundancy strategies to maintain high availability, sacrificing some efficiency to guarantee reliable service delivery.
Measuring Efficiency and Reliability: Key Metrics
Measuring efficiency involves metrics such as throughput, cycle time, and resource utilization, which quantify how effectively inputs are converted into outputs. Reliability is assessed through mean time between failures (MTBF), failure rate, and uptime percentage, indicating system dependability and performance consistency. Balancing these key metrics enables organizations to optimize operational processes while maintaining robust and dependable systems.
Strategies to Balance Efficiency and Reliability
Implementing predictive maintenance leverages data analytics to prevent unexpected failures while optimizing resource allocation, effectively balancing reliability and operational efficiency. Adopting modular system designs allows rapid replacements and upgrades, minimizing downtime without sacrificing performance consistency. Integrating real-time monitoring systems provides continuous feedback for adaptive decision-making, enhancing both efficiency and reliability in dynamic environments.
Common Challenges in Achieving Both
Balancing efficiency and reliability presents common challenges such as resource allocation conflicts, where optimizing for speed can compromise system stability. Implementation of redundant safeguards often reduces efficiency due to increased complexity and overhead costs. Maintaining consistent performance requires continuous monitoring and adaptive strategies to prevent trade-offs between rapid operation and dependable outcomes.
Future Trends in Efficiency and Reliability
Future trends in efficiency and reliability emphasize the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize system performance and predict maintenance needs, reducing downtime and operational costs. Advanced materials and smart sensors enhance reliability by providing real-time data analytics for proactive issue detection and adaptive control. The convergence of Internet of Things (IoT) technologies and edge computing enables more efficient resource management and resilient infrastructure across industries.
Efficiency Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com