Drill and practice tasks are essential for reinforcing skills and improving retention through repetitive exercises targeting specific learning objectives. These tasks help You build automaticity and confidence by repeatedly practicing core concepts until mastery is achieved. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective strategies for designing and implementing drill and practice activities.
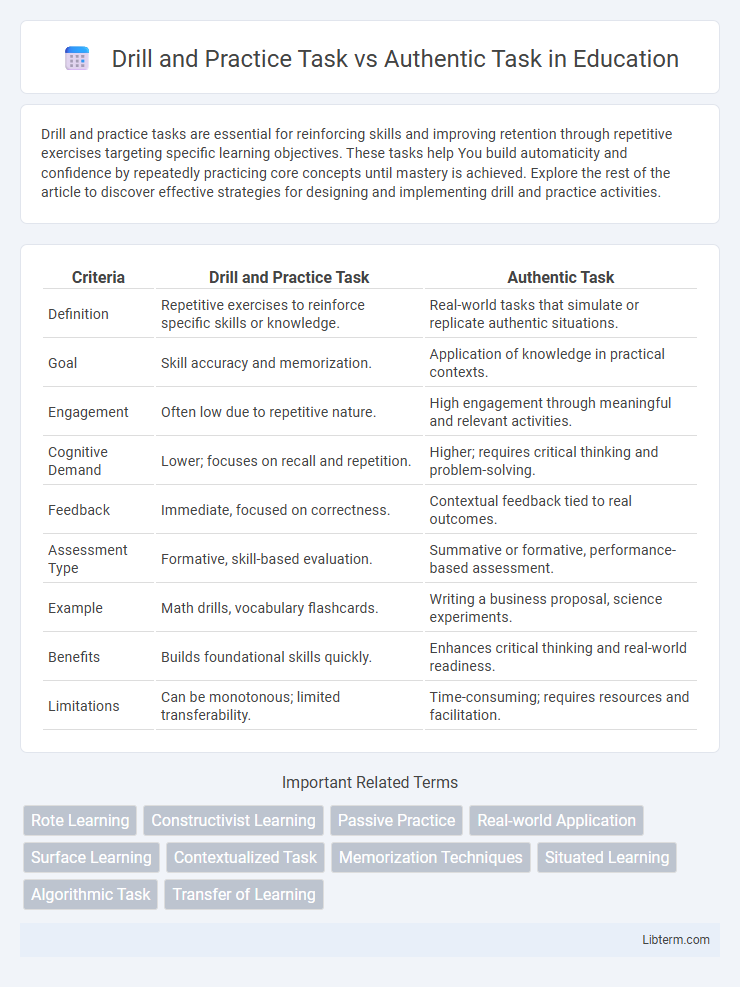
Table of Comparison
| Criteria | Drill and Practice Task | Authentic Task |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Repetitive exercises to reinforce specific skills or knowledge. | Real-world tasks that simulate or replicate authentic situations. |
| Goal | Skill accuracy and memorization. | Application of knowledge in practical contexts. |
| Engagement | Often low due to repetitive nature. | High engagement through meaningful and relevant activities. |
| Cognitive Demand | Lower; focuses on recall and repetition. | Higher; requires critical thinking and problem-solving. |
| Feedback | Immediate, focused on correctness. | Contextual feedback tied to real outcomes. |
| Assessment Type | Formative, skill-based evaluation. | Summative or formative, performance-based assessment. |
| Example | Math drills, vocabulary flashcards. | Writing a business proposal, science experiments. |
| Benefits | Builds foundational skills quickly. | Enhances critical thinking and real-world readiness. |
| Limitations | Can be monotonous; limited transferability. | Time-consuming; requires resources and facilitation. |
Introduction to Drill and Practice vs Authentic Tasks
Drill and practice tasks emphasize repetitive exercises to reinforce specific skills or knowledge, often used in early learning or skill mastery contexts. Authentic tasks require learners to apply knowledge in real-world or realistic scenarios, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving abilities. The key distinction lies in drill tasks focusing on memorization and accuracy, while authentic tasks prioritize meaningful application and transfer of learning.
Defining Drill and Practice Tasks
Drill and practice tasks involve repetitive exercises designed to reinforce specific skills or knowledge, often through memorization or repeated application of concepts. These tasks emphasize accuracy and speed in responding to standardized prompts, enhancing automaticity in fundamental skills like math facts or language vocabulary. Such tasks contrast with authentic tasks by prioritizing skill repetition over real-world context or problem-solving complexity.
Understanding Authentic Tasks
Authentic tasks involve real-world challenges that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and the application of knowledge in meaningful contexts, contrasting with drill and practice tasks that emphasize repetition and memorization. These tasks promote deeper understanding by engaging learners in activities that mirror professional or everyday scenarios, fostering transferable skills and intrinsic motivation. Understanding authentic tasks means recognizing their role in developing competencies that extend beyond academic performance to practical, lifelong learning outcomes.
Key Differences Between Drill and Practice and Authentic Tasks
Drill and practice tasks emphasize repetitive exercises targeting specific skills for mastery, often using structured formats like quizzes or flashcards, aimed at reinforcing memorization and automaticity. Authentic tasks require learners to apply knowledge in real-world or complex scenarios, promoting critical thinking, problem-solving, and transfer of skills beyond the classroom context. The key difference lies in drill tasks focusing on isolated skill repetition, whereas authentic tasks integrate multiple competencies in meaningful, practical applications.
Cognitive Benefits of Drill and Practice
Drill and Practice tasks enhance cognitive skills by promoting automaticity and reinforcing memory through repetitive exercises, which solidify foundational knowledge and improve speed in information retrieval. These tasks facilitate pattern recognition and skill fluency, enabling learners to process information more efficiently in complex problem-solving scenarios. Repetitive engagement strengthens neural pathways associated with specific cognitive functions, resulting in improved accuracy and confidence in task performance.
Real-World Relevance of Authentic Tasks
Authentic tasks engage learners by replicating real-world challenges that require critical thinking, problem-solving, and application of knowledge in context, enhancing motivation and retention. Unlike drill and practice tasks that emphasize repetition and memorization, authentic tasks promote higher-order cognitive skills through meaningful, relevant activities such as project-based assignments or case studies. This real-world relevance aligns learning objectives with practical experiences, preparing learners for real-life situations and professional environments.
When to Use Drill and Practice Tasks
Drill and practice tasks are most effective during early stages of learning when foundational skills and factual knowledge need to be reinforced through repetition. These tasks help learners achieve automaticity and accuracy in specific skills such as arithmetic operations, vocabulary acquisition, or grammar rules. Use drill and practice tasks when quick retrieval of information and precision are essential before advancing to more complex or authentic tasks.
When to Use Authentic Tasks
Authentic tasks are best used when the goal is to develop higher-order thinking skills and real-world problem-solving abilities, as they require learners to apply knowledge in meaningful contexts. These tasks enhance critical thinking, creativity, and transfer of learning by engaging students in completing complex, relevant activities similar to those they might encounter outside the classroom. In contrast to drill and practice tasks, authentic tasks are ideal for assessments that measure understanding and application rather than rote memorization.
Integrating Both Task Types in Instructional Design
Integrating Drill and Practice Tasks with Authentic Tasks in instructional design enhances skill acquisition and application by balancing repetition with real-world relevance. Drill tasks reinforce foundational knowledge through targeted exercises, while authentic tasks engage learners in contextual problem-solving that promotes deeper comprehension and transferability of skills. This combination ensures effective learning outcomes by aligning practice with meaningful, practical experiences.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Approach for Learning Outcomes
Drill and practice tasks enhance skill retention through repetition, making them ideal for foundational knowledge acquisition and automated responses. Authentic tasks engage higher-order thinking by applying skills to real-world scenarios, promoting deeper understanding and transferability. Selecting between these approaches depends on desired learning outcomes: mastery of basic skills favors drill and practice, while developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills benefits from authentic tasks.
Drill and Practice Task Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com