Peeragogy emphasizes collaborative learning where individuals actively contribute knowledge and skills within a community. It leverages shared experiences to foster continuous growth and innovation without relying solely on formal instruction. Discover how adopting peeragogy can transform your learning environment by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
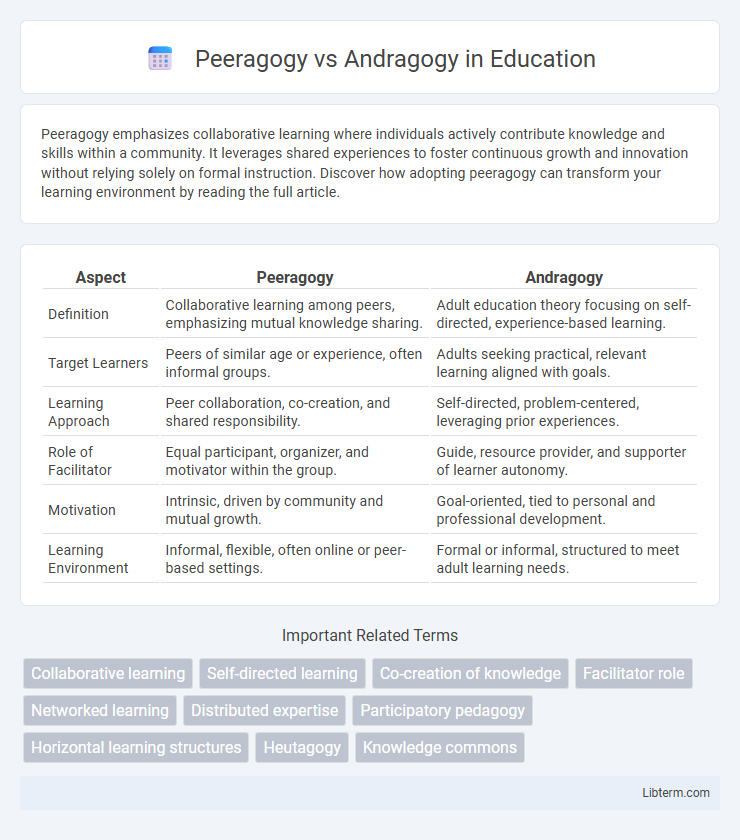
| Aspect | Peeragogy | Andragogy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Collaborative learning among peers, emphasizing mutual knowledge sharing. | Adult education theory focusing on self-directed, experience-based learning. |
| Target Learners | Peers of similar age or experience, often informal groups. | Adults seeking practical, relevant learning aligned with goals. |
| Learning Approach | Peer collaboration, co-creation, and shared responsibility. | Self-directed, problem-centered, leveraging prior experiences. |
| Role of Facilitator | Equal participant, organizer, and motivator within the group. | Guide, resource provider, and supporter of learner autonomy. |
| Motivation | Intrinsic, driven by community and mutual growth. | Goal-oriented, tied to personal and professional development. |
| Learning Environment | Informal, flexible, often online or peer-based settings. | Formal or informal, structured to meet adult learning needs. |
Understanding Peeragogy: A Collaborative Learning Approach
Peeragogy emphasizes collaborative learning where peers actively co-create knowledge, differing from andragogy's focus on self-directed adult learning guided by an instructor. This approach fosters mutual support, shared responsibility, and collective problem-solving, enhancing engagement and critical thinking within diverse learner groups. Technologies like online forums and social media platforms enable effective peer interaction, making peeragogy a dynamic method for promoting lifelong learning and knowledge exchange.
Defining Andragogy: Principles of Adult Learning
Andragogy centers on the principles of adult learning, emphasizing self-direction, practical experience, and the readiness to learn based on real-life tasks. This approach prioritizes learners' intrinsic motivation and draws upon their accumulated knowledge, fostering a collaborative environment that supports problem-solving and application. Unlike peeragogy, which relies heavily on peer collaboration, andragogy specifically tailors strategies to adult learners' cognitive and developmental needs, facilitating effective knowledge retention and skill acquisition.
Key Differences Between Peeragogy and Andragogy
Peeragogy emphasizes collaborative learning among equals, with participants actively co-creating knowledge through peer interactions, while Andragogy focuses on adult learners' self-directed education guided by an instructor or expert. In Peeragogy, learning is decentralized and driven by mutual engagement, whereas Andragogy relies on structured frameworks tailored to adult motivations and experiences. The key difference lies in Peeragogy's informal, peer-based approach contrasted with Andragogy's formal, instructor-led methodology targeting adult education principles.
Historical Roots and Theoretical Foundations
Peeragogy originated from collaborative learning theories popularized in the early 2000s, emphasizing peer-to-peer interaction and co-creation of knowledge, drawing on social constructivism and connectivism. Andragogy, introduced by Malcolm Knowles in the 1960s, is rooted in adult learning theory, focusing on self-directed learning, experiential knowledge, and the distinct needs of adult learners. Both frameworks reflect evolving educational paradigms, with peeragogy highlighting collaborative peer learning dynamics and andragogy centering on the autonomy and practical experience of adult students.
The Role of Facilitators in Peeragogy vs Andragogy
In peeragogy, facilitators act as co-learners who encourage collaboration, shared knowledge construction, and mutual support among participants, fostering a democratic learning environment. In contrast, andragogy involves facilitators who guide adult learners by providing structure, leveraging experiential knowledge, and promoting self-directed learning tailored to individual goals. The facilitator's role in peeragogy emphasizes participatory engagement, while in andragogy it centers on enabling autonomy and practical application.
Learner Autonomy: Contrasts and Overlaps
Peeragogy emphasizes learner autonomy by promoting collaborative, peer-driven knowledge construction where individuals actively co-create learning experiences without a formal instructor. Andragogy focuses on adult learners' self-direction and intrinsic motivation, encouraging them to take responsibility for their learning process but often within more structured frameworks. Both approaches overlap in fostering autonomy but differ in the balance between collaborative peer engagement and individual self-regulation.
Application Contexts: When to Use Peeragogy or Andragogy
Peeragogy excels in collaborative environments such as online communities, project teams, and peer-to-peer learning platforms where shared knowledge construction fosters innovation and engagement. Andragogy is best applied in professional training, workforce development, and adult education settings where learners benefit from structured guidance, practical experience, and goal-oriented instruction. Choosing between peeragogy and andragogy depends on factors like learner autonomy, the complexity of content, and the need for facilitation or self-directed learning.
Benefits and Challenges of Each Approach
Peeragogy promotes collaborative learning among equals, fostering critical thinking and shared responsibility, but it may face challenges in maintaining structure and consistent participation. Andragogy emphasizes self-directed learning tailored to adult experiences, enhancing motivation and practical application, yet it can encounter difficulties when learners lack intrinsic motivation or require more guidance. Both approaches offer valuable benefits for diverse educational contexts but must address specific limitations to maximize effectiveness.
Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Peeragogy emphasizes collaborative learning among peers in environments like online communities and coworking spaces, exemplified by platforms such as Wikipedia where users co-create knowledge. Andragogy focuses on adult learning principles tailored to practical, real-world applications, as seen in workplace training programs like those implemented by corporate giants like IBM and General Electric. Case studies reveal that peeragogy fosters innovation through shared experiences, while andragogy enhances skill acquisition by leveraging adults' prior knowledge and motivation.
Future Trends in Collaborative and Adult Learning
Peeragogy fosters decentralized, learner-driven collaboration leveraging digital platforms to enhance knowledge co-creation among peers. Andragogy emphasizes self-directed learning principles tailored to adult learners' experiences, promoting practical application and critical reflection. Future trends indicate a convergence where technology-enabled peer collaboration integrates with adult learning theories to create adaptive, personalized, and scalable educational ecosystems.
Peeragogy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com