State autonomy empowers regions to govern independently, tailoring laws and policies to local needs while maintaining alignment with national interests. Balancing this autonomy with federal oversight ensures stability and respects diverse community priorities. Discover how state autonomy influences governance and affects your everyday life in the detailed analysis ahead.
Table of Comparison
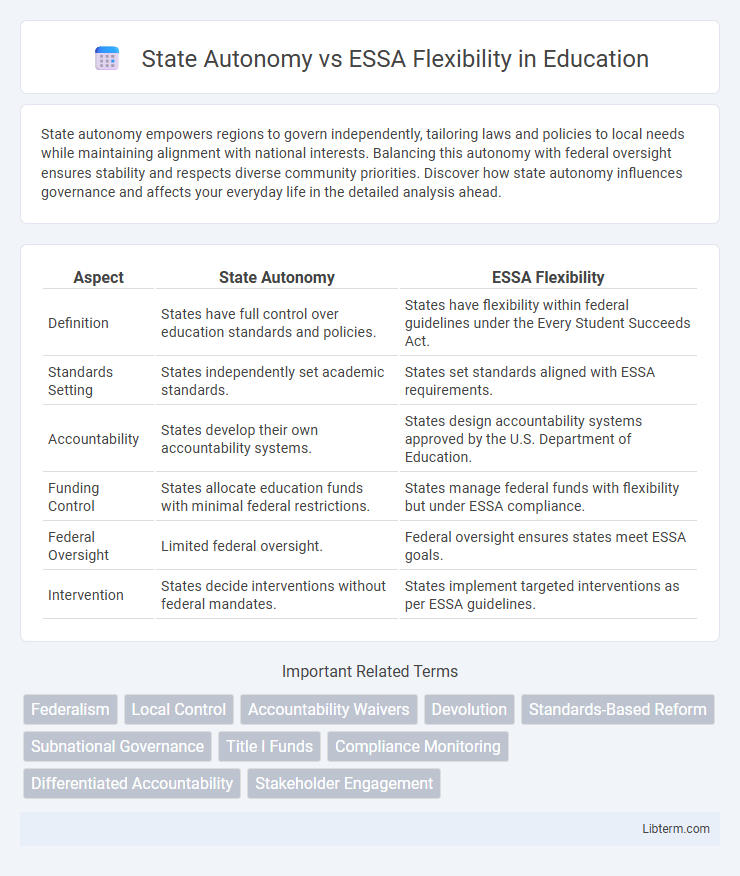
| Aspect | State Autonomy | ESSA Flexibility |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | States have full control over education standards and policies. | States have flexibility within federal guidelines under the Every Student Succeeds Act. |
| Standards Setting | States independently set academic standards. | States set standards aligned with ESSA requirements. |
| Accountability | States develop their own accountability systems. | States design accountability systems approved by the U.S. Department of Education. |
| Funding Control | States allocate education funds with minimal federal restrictions. | States manage federal funds with flexibility but under ESSA compliance. |
| Federal Oversight | Limited federal oversight. | Federal oversight ensures states meet ESSA goals. |
| Intervention | States decide interventions without federal mandates. | States implement targeted interventions as per ESSA guidelines. |
Understanding State Autonomy in Education
State autonomy in education allows individual states to design and implement education policies tailored to their unique demographics, economic conditions, and cultural values, ensuring that local needs and priorities shape educational outcomes. The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) provides states significant flexibility by reducing federal control and empowering state education agencies to set academic standards, develop accountability systems, and determine intervention strategies for underperforming schools. This balance between federal oversight and state autonomy fosters innovation while maintaining a commitment to equity and high-quality education nationwide.
Overview of the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA)
The Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) grants states significant autonomy to design their own accountability systems, academic standards, and interventions for underperforming schools, replacing the more prescriptive mandates of the No Child Left Behind Act. ESSA requires states to establish challenging academic standards and implement statewide assessments while allowing flexibility in determining school accountability measures and support strategies. This shift empowers states to tailor education policies to local needs while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity and quality in K-12 education.
Historical Context: From NCLB to ESSA
The transition from No Child Left Behind (NCLB) to Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) marked a significant shift in education policy, emphasizing increased state autonomy over federally mandated accountability. NCLB, enacted in 2001, imposed stringent federal requirements and standardized testing benchmarks, often criticized for limiting state control and flexibility. ESSA, signed into law in 2015, restored substantial decision-making power to states, allowing tailored accountability systems while maintaining federal oversight to ensure equity and performance standards.
Defining Flexibility under ESSA
Defining flexibility under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) centers on granting states greater authority to design accountability systems tailored to their unique educational contexts. ESSA allows states to set their own goals for student achievement, determine interventions for underperforming schools, and allocate federal funds based on state-identified priorities. This flexibility contrasts with the more prescriptive mandates of previous federal laws, enabling states to balance innovation with accountability while maintaining compliance with federal guidelines.
Balancing State Control and Federal Oversight
State autonomy under ESSA (Every Student Succeeds Act) allows states significant control over education standards, accountability systems, and funding distribution, promoting localized decision-making. ESSA flexibility requires states to develop plans that meet federal guidelines while tailoring strategies to address specific educational challenges. Balancing state control and federal oversight ensures consistent nationwide educational equity while respecting diverse state priorities and contexts.
Benefits of Increased State Autonomy
Increased state autonomy under ESSA allows states to design tailored education policies that address local needs and priorities more effectively. States can implement targeted interventions and innovate in curriculum development, assessment methods, and teacher evaluation systems without stringent federal mandates. This flexibility promotes accountability, fosters community engagement, and enhances the overall quality of education by empowering state and local stakeholders.
Challenges and Limitations of ESSA Flexibility
ESSA flexibility allows states to tailor education policies but faces challenges like inconsistent implementation and limited federal oversight, leading to varied educational outcomes. States often struggle with balancing local control and meeting federal accountability standards, causing disparities in resource allocation and student performance monitoring. The lack of uniform guidelines under ESSA can result in uneven support for historically underserved populations, undermining equitable educational opportunities.
Impact on School Accountability Systems
State autonomy under the Every Student Succeeds Act (ESSA) allows states to design tailored school accountability systems that reflect local priorities and contexts, contrasting with the rigid federal mandates of previous legislation. This flexibility enables states to incorporate multiple measures of student success beyond standardized test scores, such as graduation rates and school climate indicators, fostering a more comprehensive evaluation framework. However, the variation in accountability approaches may pose challenges for comparability and equity across states, influencing policy implementation and resource allocation at the local level.
State Innovation vs. Federal Standardization
State autonomy under ESSA empowers states to design tailored education systems reflecting local priorities, promoting innovation in curriculum, assessment, and accountability. ESSA flexibility allows states to experiment with diverse educational models, fostering approaches that address unique demographic and regional needs. Federal standardization provides a uniform framework ensuring equity and compliance, but may limit states' ability to innovate freely in pursuit of improved student outcomes.
Policy Implications and Future Directions
State autonomy under ESSA flexibility enables tailored education policies that address local needs while maintaining federal standards. Policy implications include balancing accountability with innovation, as states navigate ESSA's provisions to customize assessments, teacher evaluations, and funding allocations. Future directions emphasize enhancing collaboration between federal and state governments, leveraging data-driven strategies to improve educational outcomes and equity nationwide.
State Autonomy Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com