Accurate diagnostic processes are essential for identifying medical conditions swiftly and effectively, enabling timely treatment and improved patient outcomes. Utilizing advanced technologies and evidence-based protocols enhances diagnostic precision and reduces errors. Explore the rest of this article to understand how cutting-edge diagnostics can support your health journey.
Table of Comparison
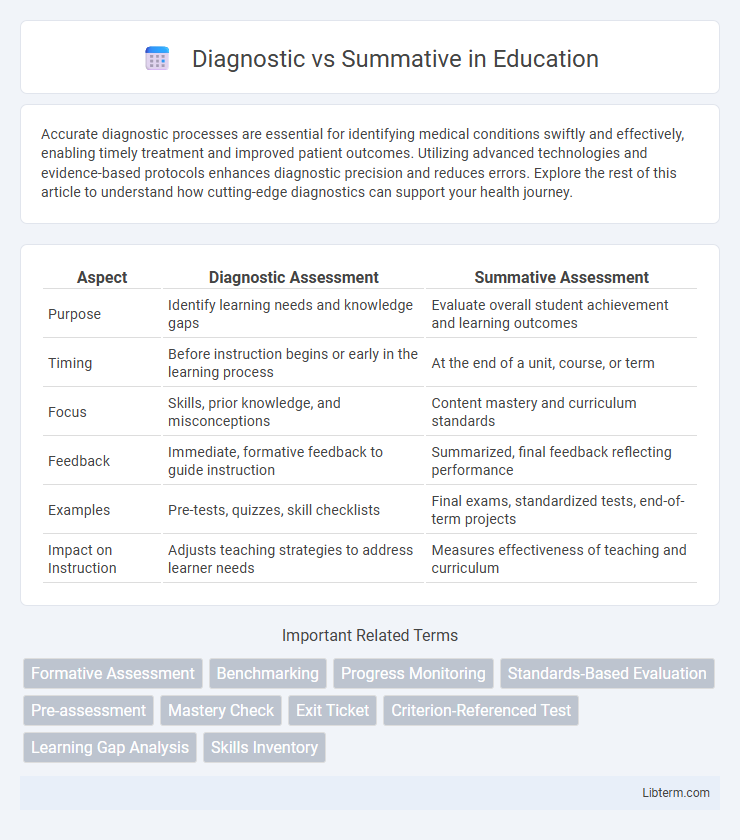
| Aspect | Diagnostic Assessment | Summative Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify learning needs and knowledge gaps | Evaluate overall student achievement and learning outcomes |
| Timing | Before instruction begins or early in the learning process | At the end of a unit, course, or term |
| Focus | Skills, prior knowledge, and misconceptions | Content mastery and curriculum standards |
| Feedback | Immediate, formative feedback to guide instruction | Summarized, final feedback reflecting performance |
| Examples | Pre-tests, quizzes, skill checklists | Final exams, standardized tests, end-of-term projects |
| Impact on Instruction | Adjusts teaching strategies to address learner needs | Measures effectiveness of teaching and curriculum |
Introduction to Diagnostic and Summative Assessment
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' prior knowledge and skills before instruction begins, enabling targeted teaching strategies. Summative assessment evaluates overall learning outcomes at the end of an instructional period, measuring student achievement against predefined standards. Both assessments play crucial roles in effective educational planning and student performance analysis.
Defining Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps before instruction begins to tailor teaching strategies effectively. It involves pre-tests, questionnaires, or informal observations designed to understand individual learner needs. Accurate diagnostic evaluation enhances personalized learning and improves overall academic outcomes.
Defining Summative Assessment
Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring mastery of specific content against defined standards. It typically includes exams, final projects, or standardized tests designed to assign grades or certify proficiency. This form of assessment provides a conclusive overview of academic achievement rather than ongoing feedback during the learning process.
Key Differences Between Diagnostic and Summative Assessments
Diagnostic assessments identify students' existing knowledge and skills before instruction, focusing on pinpointing learning gaps and misconceptions to tailor teaching strategies effectively. Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, measuring overall achievement against predefined learning objectives or standards. The key differences lie in their timing, purpose, and impact on instruction: diagnostic assessments inform and guide teaching, while summative assessments judge cumulative performance and assign grades.
Purpose and Goals of Diagnostic Assessments
Diagnostic assessments aim to identify students' existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps before instruction begins, enabling educators to tailor teaching strategies effectively. These assessments provide detailed insights into specific areas of strength and weakness, facilitating personalized learning plans and early intervention. The primary goal is to inform instruction and support student growth rather than assign final grades, distinguishing them from summative assessments designed to evaluate overall learning outcomes at the end of a course.
Purpose and Goals of Summative Assessments
Summative assessments aim to evaluate student learning by measuring achievement against predefined learning objectives at the end of an instructional period. They provide quantifiable data used to determine grades, guide curriculum decisions, and assess overall effectiveness of educational programs. The primary goal is to certify mastery and inform stakeholders about student performance and instructional quality.
Timing and Implementation in the Learning Process
Diagnostic assessments are conducted at the beginning of a learning unit to identify students' prior knowledge and learning gaps, enabling tailored instruction plans. Summative assessments occur at the end of an instructional period to evaluate overall comprehension and mastery of the content. Implementing diagnostic assessments early optimizes targeted teaching strategies, while summative assessments provide a final measure of educational effectiveness and student achievement.
Impact on Teaching and Learning Strategies
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' prior knowledge and learning gaps early, enabling teachers to tailor instructional strategies to meet individual needs effectively. Summative assessment measures overall student achievement at the end of instruction, guiding curriculum evaluation but offering limited immediate feedback for teaching adjustments. Integrating both assessments enhances personalized learning and informs targeted interventions, improving educational outcomes.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Assessment Type
Diagnostic assessments identify students' prior knowledge and learning gaps, enabling targeted instruction and personalized support, but they can be time-consuming and may not cover all content areas comprehensively. Summative assessments evaluate overall student learning and proficiency at the end of an instructional period, providing clear data for grading and accountability, yet they often lack insight into the learning process and may induce high-stakes stress. Both assessment types play crucial roles in education by balancing formative insights with evaluative outcomes, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of student progress.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Educational Objectives
Diagnostic assessments identify students' existing knowledge gaps and learning needs early in the instructional process, enabling targeted interventions to improve outcomes. Summative assessments evaluate cumulative student learning at the end of an instructional period, measuring mastery of specific educational objectives for grading or accountability purposes. Selecting the right assessment depends on whether the goal is to inform instruction through ongoing feedback or to assess final achievement and curriculum effectiveness.
Diagnostic Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com