Constructivist teaching emphasizes active learning through experience, encouraging students to build their own understanding by connecting new knowledge with prior beliefs. This approach fosters critical thinking and problem-solving skills, making education more personalized and engaging. Explore the rest of this article to discover how constructivist teaching can transform Your classroom experience.
Table of Comparison
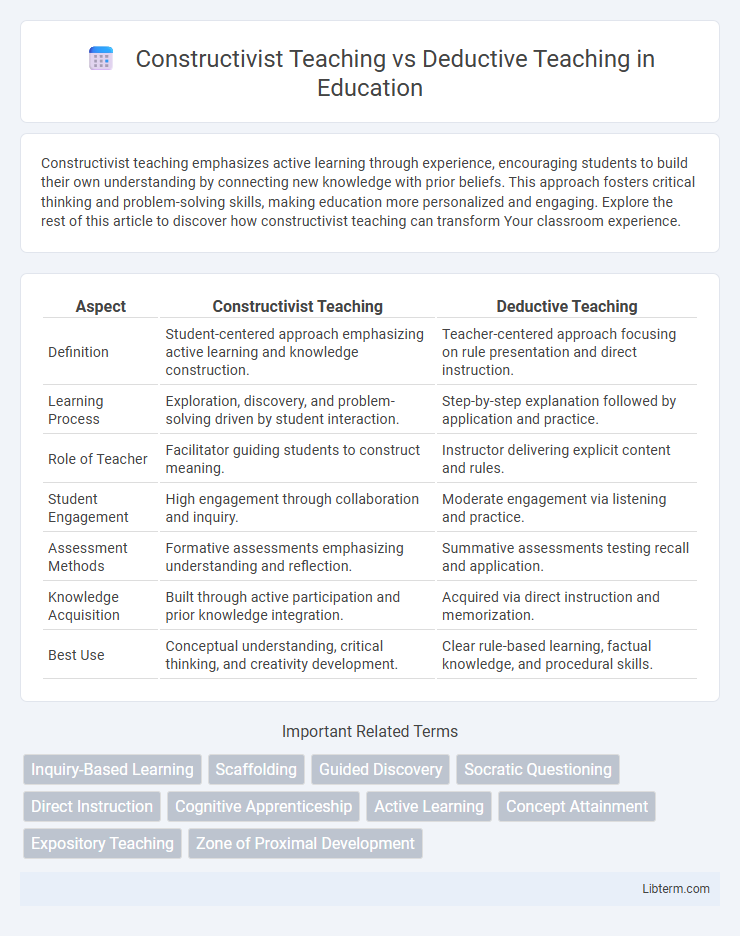
| Aspect | Constructivist Teaching | Deductive Teaching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach emphasizing active learning and knowledge construction. | Teacher-centered approach focusing on rule presentation and direct instruction. |
| Learning Process | Exploration, discovery, and problem-solving driven by student interaction. | Step-by-step explanation followed by application and practice. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator guiding students to construct meaning. | Instructor delivering explicit content and rules. |
| Student Engagement | High engagement through collaboration and inquiry. | Moderate engagement via listening and practice. |
| Assessment Methods | Formative assessments emphasizing understanding and reflection. | Summative assessments testing recall and application. |
| Knowledge Acquisition | Built through active participation and prior knowledge integration. | Acquired via direct instruction and memorization. |
| Best Use | Conceptual understanding, critical thinking, and creativity development. | Clear rule-based learning, factual knowledge, and procedural skills. |
Introduction to Teaching Approaches
Constructivist teaching emphasizes active student engagement through exploration and knowledge construction, fostering critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Deductive teaching relies on direct instruction where teachers present general principles followed by specific examples, promoting clarity and structured learning paths. Understanding these approaches highlights diverse strategies to support varied learner needs and optimize educational outcomes.
Defining Constructivist Teaching
Constructivist teaching centers on learners actively constructing their own understanding through hands-on experiences and reflection, emphasizing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. It contrasts with deductive teaching, which follows a top-down approach where concepts and rules are presented first before application. Constructivist methods foster deeper comprehension by encouraging students to explore, question, and connect new knowledge to prior understanding.
Understanding Deductive Teaching
Deductive teaching is a structured instructional approach where concepts and rules are presented explicitly before students apply them to specific examples, emphasizing direct transmission of knowledge. This method is effective for teaching clear, well-defined subjects such as grammar or mathematics, enabling learners to grasp foundational principles quickly. Deductive teaching supports efficient knowledge acquisition by providing a clear framework, which reduces ambiguity and guides students through logical steps to ensure comprehension.
Core Principles of Constructivism
Constructivist teaching emphasizes active learning where students build their own understanding through experiences and reflection, focusing on knowledge construction rather than passive reception. Core principles include learner-centered education, the importance of prior knowledge, social interaction, and real-world context to promote deep comprehension. In contrast, deductive teaching follows a structured, teacher-led approach where general principles are presented first and then applied to specific examples.
Key Features of Deductive Methods
Deductive teaching methods prioritize presenting general principles or rules first, followed by specific examples to illustrate these concepts, enabling learners to apply predefined knowledge systematically. This approach emphasizes structured, teacher-centered instruction with clear learning objectives and assessment criteria, facilitating efficient knowledge transmission. Key features include explicit explanation, sequential reasoning, and reinforcement through practice to consolidate understanding.
Classroom Practices: Constructivist vs Deductive
Constructivist teaching in the classroom emphasizes student-centered activities, encouraging learners to explore, question, and build understanding through hands-on experiences and collaborative problem-solving. Deductive teaching, by contrast, involves direct instruction where teachers present general principles or rules followed by specific examples, focusing on clear explanation and practice of predetermined content. Classroom practices in constructivist settings prioritize inquiry and discovery, while deductive approaches rely on structured lessons and guided repetition to reinforce learning outcomes.
Student Engagement and Participation
Constructivist teaching promotes student engagement by encouraging active exploration, collaboration, and hands-on learning, which fosters deeper understanding through real-world problem-solving. Deductive teaching, characterized by direct instruction and structured lessons, often leads to passive reception but can efficiently transmit foundational knowledge when student participation is guided through targeted questioning. Studies show constructivist methods increase motivation and sustained interaction, while deductive approaches may limit engagement but ensure clarity and organization in concept delivery.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Approach
Constructivist teaching promotes active learning by encouraging students to build knowledge through experience, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills, but it may lead to inconsistent coverage of curriculum content and requires more class time. Deductive teaching offers structured, clear instruction that efficiently covers specific content and is easier to assess, but it can limit creativity and deeper understanding by focusing on rote memorization rather than exploration. Both approaches have merit depending on educational goals, with constructivism fostering conceptual understanding and deductive methods supporting foundational knowledge acquisition.
Choosing the Right Method for Learners
Constructivist teaching emphasizes active learner engagement through exploration and problem-solving, making it ideal for students who benefit from hands-on experiences and critical thinking development. Deductive teaching provides clear, structured instruction and is effective for learners who prefer direct guidance and concise explanations to grasp foundational concepts quickly. Selecting the right method depends on the learner's cognitive style, prior knowledge, and the subject complexity, ensuring optimal comprehension and retention.
Conclusion: Balancing Constructivist and Deductive Teaching
Balancing constructivist and deductive teaching methods enhances student comprehension by integrating hands-on exploration with structured guidance. Constructivist approaches foster critical thinking and creativity through active learning, while deductive teaching ensures clarity and efficient knowledge transfer via explicit instruction. Combining these strategies creates a dynamic classroom environment that accommodates diverse learning styles and maximizes educational outcomes.
Constructivist Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com