Self-regulation involves managing your emotions, thoughts, and behaviors to achieve long-term goals and maintain personal well-being. Developing strong self-regulation skills can enhance decision-making, reduce stress, and improve relationships. Discover practical strategies to strengthen your self-regulation and transform your daily life by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
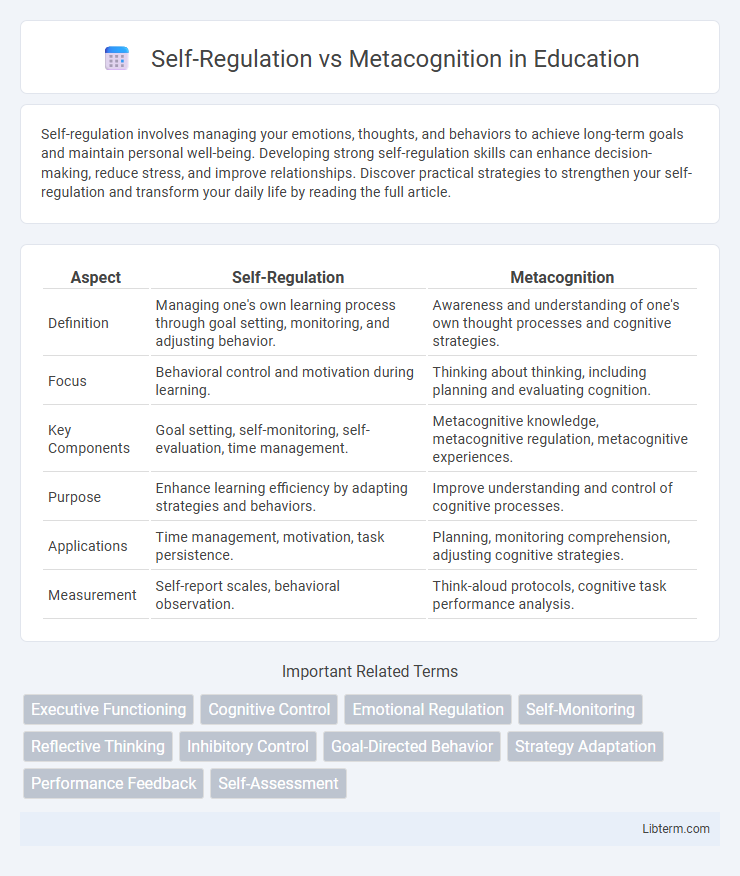
| Aspect | Self-Regulation | Metacognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing one's own learning process through goal setting, monitoring, and adjusting behavior. | Awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes and cognitive strategies. |
| Focus | Behavioral control and motivation during learning. | Thinking about thinking, including planning and evaluating cognition. |
| Key Components | Goal setting, self-monitoring, self-evaluation, time management. | Metacognitive knowledge, metacognitive regulation, metacognitive experiences. |
| Purpose | Enhance learning efficiency by adapting strategies and behaviors. | Improve understanding and control of cognitive processes. |
| Applications | Time management, motivation, task persistence. | Planning, monitoring comprehension, adjusting cognitive strategies. |
| Measurement | Self-report scales, behavioral observation. | Think-aloud protocols, cognitive task performance analysis. |
Introduction to Self-Regulation and Metacognition
Self-regulation involves managing one's emotions, behaviors, and thoughts to achieve personal goals, emphasizing control and adaptation in various situations. Metacognition refers to the awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes, enabling strategic planning, monitoring, and evaluation of learning activities. Both concepts play critical roles in effective learning and personal development, with self-regulation focusing on behavior management and metacognition on cognitive awareness.
Defining Self-Regulation
Self-regulation refers to the ability to manage one's emotions, thoughts, and behaviors effectively in different situations to achieve long-term goals. It involves setting goals, monitoring progress, and adjusting actions accordingly to maintain focus and motivation. Unlike metacognition, which centers on awareness and control of cognitive processes, self-regulation emphasizes behavioral and emotional control as key components of personal and academic success.
Understanding Metacognition
Metacognition involves the awareness and control of one's cognitive processes, encompassing self-monitoring, self-evaluation, and strategic regulation of learning. It enables individuals to plan, monitor, and adjust their approaches to problem-solving and learning tasks effectively. Understanding metacognition enhances academic performance by promoting reflective thinking and adaptive learning strategies beyond basic self-regulation techniques.
Key Differences Between Self-Regulation and Metacognition
Self-regulation involves controlling one's emotions, behaviors, and thoughts to achieve long-term goals, emphasizing goal-setting, self-monitoring, and self-discipline. Metacognition refers to awareness and understanding of one's own thought processes, including planning, monitoring, and evaluating cognitive strategies during learning. The key difference lies in self-regulation's focus on managing actions and emotions versus metacognition's focus on cognitive awareness and strategic thinking.
The Role of Self-Regulation in Learning
Self-regulation plays a critical role in learning by enabling students to set goals, monitor their progress, and adjust strategies to improve understanding and performance. It involves managing emotions, motivation, and behavior to maintain focus and resilience during challenging tasks. Effective self-regulation strengthens learners' ability to independently control their cognitive processes and achieve academic success.
How Metacognition Enhances Cognitive Processes
Metacognition enhances cognitive processes by enabling individuals to monitor, assess, and adjust their thinking strategies for improved problem-solving and learning outcomes. It involves self-awareness of one's cognitive strengths and weaknesses, allowing for targeted regulation of attention, memory, and comprehension. This heightened cognitive control facilitates more effective decision-making and adaptability in complex tasks, surpassing basic self-regulation skills focused primarily on behavior management.
Self-Regulation Strategies for Success
Self-regulation strategies for success involve goal setting, time management, and self-monitoring to enhance focus and persistence in tasks. Techniques such as setting specific, measurable objectives, breaking tasks into manageable steps, and using feedback to adjust approaches boost motivation and achievement. Effective self-regulation empowers learners to control impulses, maintain attention, and adapt behaviors to overcome challenges and improve performance.
Metacognitive Techniques for Better Thinking
Metacognitive techniques enhance thinking by encouraging learners to plan, monitor, and evaluate their cognitive processes, which improves problem-solving and decision-making skills. Strategies like self-questioning, reflective journaling, and concept mapping facilitate awareness of one's understanding and foster deeper comprehension. Implementing these methods systematically leads to more effective learning outcomes and adaptive thinking behaviors.
Integrating Self-Regulation and Metacognition
Integrating self-regulation and metacognition enhances personal learning efficiency by combining goal-setting, monitoring, and adapting strategies with awareness of one's cognitive processes. This integration promotes stronger executive control, allowing learners to plan, evaluate, and adjust their approach to complex tasks more effectively. Research shows that training in both domains improves academic performance by fostering adaptive problem-solving and sustained motivation.
Practical Applications in Education and Daily Life
Self-regulation empowers students to control their emotions, behaviors, and attention, leading to improved classroom management and academic performance. Metacognition enhances learners' ability to plan, monitor, and evaluate their thinking processes, fostering deeper comprehension and problem-solving skills. In daily life, combining self-regulation with metacognitive strategies promotes effective goal-setting, time management, and adaptive learning in various personal and professional contexts.
Self-Regulation Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com