Employing formal language enhances clarity and professionalism in your communication, making it essential for academic and business contexts. It involves the use of precise vocabulary, structured sentences, and avoidance of colloquial expressions to maintain respect and credibility. Explore the rest of the article to understand how formal language can improve your writing and speaking skills effectively.
Table of Comparison
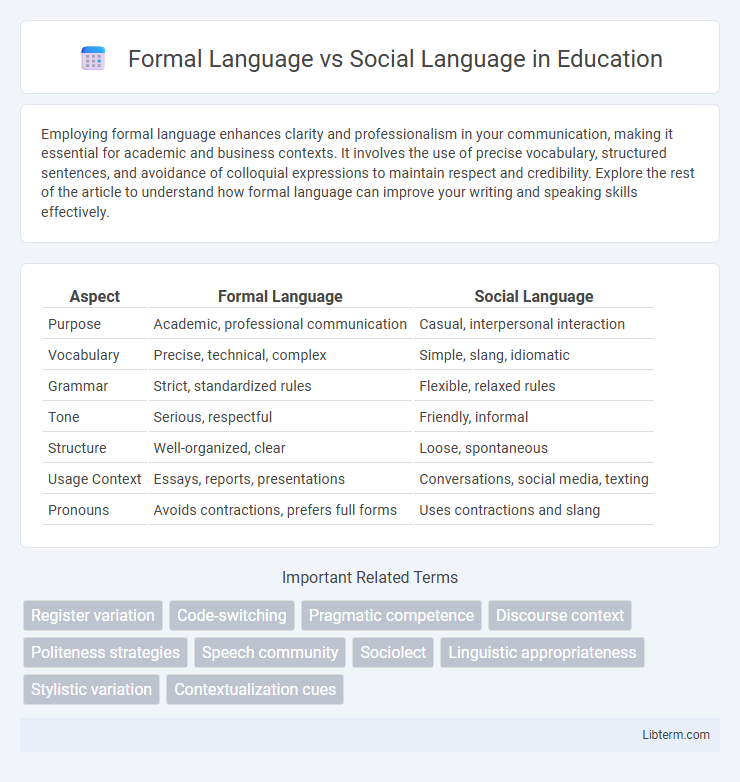
| Aspect | Formal Language | Social Language |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Academic, professional communication | Casual, interpersonal interaction |
| Vocabulary | Precise, technical, complex | Simple, slang, idiomatic |
| Grammar | Strict, standardized rules | Flexible, relaxed rules |
| Tone | Serious, respectful | Friendly, informal |
| Structure | Well-organized, clear | Loose, spontaneous |
| Usage Context | Essays, reports, presentations | Conversations, social media, texting |
| Pronouns | Avoids contractions, prefers full forms | Uses contractions and slang |
Introduction to Formal and Social Language
Formal language is characterized by structured grammar, precise vocabulary, and a serious tone used in professional, academic, or official contexts. Social language, on the other hand, is informal, conversational, and often includes slang or colloquialisms, making it suitable for casual interactions among friends or peers. Understanding these distinctions helps in choosing appropriate communication styles for different social and professional situations.
Defining Formal Language
Formal language is a structured mode of communication characterized by precise vocabulary, complete sentence structures, and adherence to grammatical rules, often used in professional, academic, or official contexts. It avoids slang, contractions, and colloquialisms to maintain clarity and professionalism. Defining formal language involves emphasizing its role in conveying information respectfully and unambiguously in settings such as business correspondence, legal documents, and academic writing.
Understanding Social (Informal) Language
Social language, often known as informal language, includes slang, idioms, colloquialisms, and regional expressions that vary widely across cultures and communities. Understanding social language requires recognizing context, tone, body language, and shared cultural knowledge to accurately interpret meaning and intent. Mastery of informal language enhances interpersonal communication and builds rapport in everyday social interactions.
Key Differences Between Formal and Social Language
Formal language employs structured grammar, precise vocabulary, and complete sentences, commonly used in academic, professional, and official contexts. Social language features informal vocabulary, contractions, slang, and colloquialisms, reflecting casual or personal communication among friends and family. The tone in formal language is objective and respectful, whereas social language is more relaxed, subjective, and emotive.
Contexts for Using Formal Language
Formal language is primarily used in professional, academic, and official contexts such as business meetings, academic papers, legal documents, and official correspondence where clarity, precision, and respect are paramount. It is essential in settings that require a serious tone and adherence to grammatical rules to convey authority and professionalism. Formal language helps establish credibility and facilitates effective communication in environments where maintaining professionalism and avoiding misunderstandings is critical.
Contexts for Using Social Language
Social language is commonly used in casual settings such as conversations with friends, family gatherings, and informal social events where relaxed tone and personal expressions are appropriate. It thrives in contexts like social media interactions, texting, and everyday dialogue, emphasizing relatability and emotional connection over grammatical precision. Understanding these contexts ensures effective communication by adapting language style to suit informal environments.
Benefits of Mastering Both Language Styles
Mastering both formal and social language enhances communication versatility, enabling precise expression in professional settings and fostering genuine connections in casual conversations. Proficiency in formal language improves clarity and credibility during presentations, reports, and official correspondence. Equally, fluency in social language strengthens interpersonal relationships and cultural understanding through informal dialogue and emotional nuance.
Common Mistakes in Switching Language Contexts
Common mistakes in switching between formal and social language contexts include using overly casual expressions in professional settings, which can undermine credibility and cause misunderstandings. Another frequent error is applying formal language in informal conversations, leading to awkwardness and social distance. Awareness of audience expectations and context-appropriate vocabulary is essential to navigate these language shifts effectively.
Tips for Improving Language Adaptability
Mastering formal and social language requires understanding context-specific vocabulary and tone; practice switching between structured grammar for professional settings and casual expressions for informal interactions. Enhancing language adaptability involves active listening to diverse communication styles and mimicking appropriate phrases to build fluency. Consistent exposure to various media formats such as business reports and social media conversations sharpens the ability to modify language use effectively.
Conclusion: Balancing Formal and Social Communication
Effective communication requires balancing formal language, which conveys professionalism and clarity, with social language that fosters approachability and rapport. Mastering both styles enhances interpersonal skills and ensures messages are appropriately tailored to varied contexts. This balance optimizes understanding and strengthens relationships in both personal and professional environments.
Formal Language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com