Hidden curriculum refers to the unspoken social norms, values, and expectations that influence student behavior and learning beyond the formal academic syllabus. Understanding this implicit learning helps educators create supportive environments that address students' holistic development. Explore the rest of the article to uncover how the hidden curriculum shapes your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
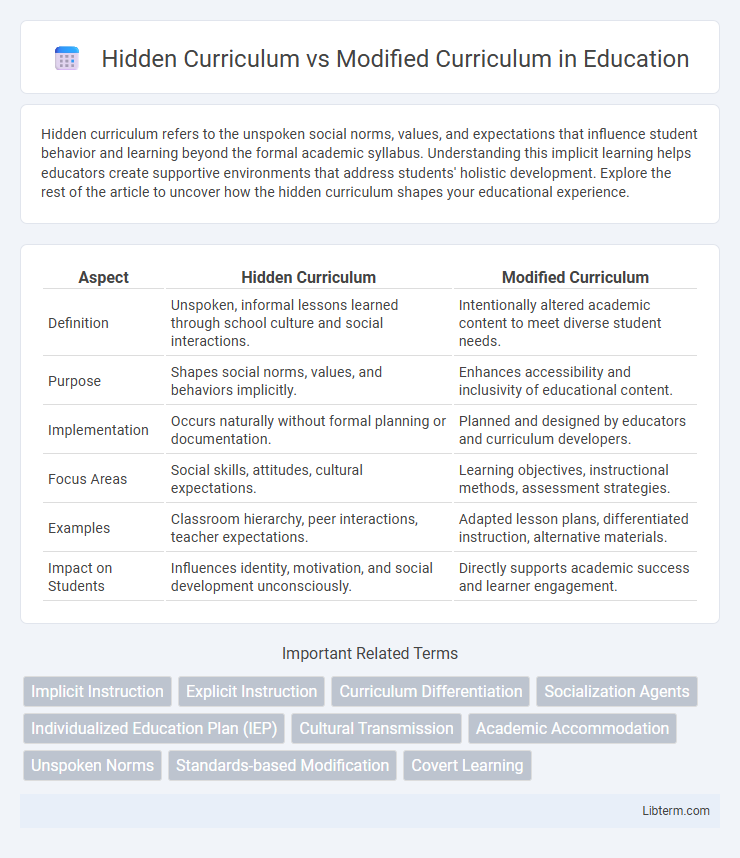
| Aspect | Hidden Curriculum | Modified Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Unspoken, informal lessons learned through school culture and social interactions. | Intentionally altered academic content to meet diverse student needs. |
| Purpose | Shapes social norms, values, and behaviors implicitly. | Enhances accessibility and inclusivity of educational content. |
| Implementation | Occurs naturally without formal planning or documentation. | Planned and designed by educators and curriculum developers. |
| Focus Areas | Social skills, attitudes, cultural expectations. | Learning objectives, instructional methods, assessment strategies. |
| Examples | Classroom hierarchy, peer interactions, teacher expectations. | Adapted lesson plans, differentiated instruction, alternative materials. |
| Impact on Students | Influences identity, motivation, and social development unconsciously. | Directly supports academic success and learner engagement. |
Understanding Hidden Curriculum
Understanding hidden curriculum involves recognizing the implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through school culture, routines, and social interactions that are not part of the formal syllabus. It shapes student behavior, social skills, and attitudes, influencing learning outcomes beyond academic content. Unlike modified curriculum, which explicitly alters educational content to meet specific needs, hidden curriculum operates subtly, often reinforcing social hierarchies and institutional expectations.
Defining Modified Curriculum
Modified Curriculum refers to an educational plan tailored to meet the unique learning needs of students with disabilities or learning challenges, differing significantly from the standard curriculum in content complexity, scope, and instructional strategies. It emphasizes individualized goals and objectives, allowing flexibility in teaching methods and assessment to facilitate student success. This approach contrasts with the Hidden Curriculum, which involves implicit lessons and social norms learned outside the formal educational content.
Key Differences Between Hidden and Modified Curricula
Hidden curriculum refers to the implicit lessons, values, and norms conveyed through the educational environment and social interactions, whereas modified curriculum involves deliberate alterations to instructional content or methods to accommodate diverse learner needs. Key differences include the visibility and intentionality of learning goals: hidden curriculum operates subconsciously through school culture and practices, while modified curriculum is explicitly designed and implemented by educators. Furthermore, hidden curriculum shapes students' socialization and attitudes without formal acknowledgment, whereas modified curriculum aims at providing equitable access to academic material tailored to individual abilities or disabilities.
The Role of Hidden Curriculum in Education
The hidden curriculum plays a crucial role in education by shaping students' social norms, values, and behaviors through implicit lessons embedded in school culture and practices. Unlike the modified curriculum, which involves deliberate changes to the official instructional content to accommodate diverse learning needs, the hidden curriculum influences attitudes and skills that are not formally assessed but significantly impact student development. Understanding the hidden curriculum helps educators foster inclusive environments and address disparities in educational experiences.
Purpose and Implementation of Modified Curriculum
Modified Curriculum is purposefully designed to accommodate students with diverse learning needs by adjusting content complexity, instructional methods, and assessment strategies to enhance accessibility and understanding. Implementation involves targeted Individualized Education Programs (IEPs), differentiated instruction, and collaboration among educators, therapists, and families to ensure personalized learning outcomes. Unlike the Hidden Curriculum, which deals with implicit social norms and behaviors, the Modified Curriculum explicitly addresses academic modifications to support student success.
Impact on Student Learning Outcomes
Hidden curriculum influences student learning outcomes by shaping attitudes, values, and social norms through implicit lessons learned in the school environment, often affecting motivation and engagement. Modified curriculum directly alters academic content and instructional strategies to accommodate diverse learning needs, improving accessibility and comprehension for students with varying abilities. Both impact cognitive and socio-emotional development, but while hidden curriculum shapes holistic growth subtly, modified curriculum produces measurable changes in academic performance and skill acquisition.
Teacher Perspectives on Hidden vs Modified Curriculum
Teachers perceive the hidden curriculum as the implicit lessons, values, and social norms conveyed through classroom interactions and institutional culture, which often shape student behavior unconsciously. In contrast, the modified curriculum involves intentional adaptations and alterations to the formal curriculum designed to meet diverse learner needs or educational goals. Educators recognize that while the hidden curriculum influences student development subtly, the modified curriculum requires deliberate planning and implementation to achieve specific educational outcomes.
Challenges in Addressing Hidden Curriculum
Hidden curriculum presents challenges in educational settings due to its implicit nature, encompassing unspoken cultural norms and social expectations that are difficult to identify and regulate compared to the structured and explicit modified curriculum. Addressing hidden curriculum requires educators to develop awareness and reflective practices to mitigate unintended biases and reinforce equitable learning environments, which is complex due to varying interpretations among students and staff. Unlike the modified curriculum, which is deliberately designed and reviewed, the hidden curriculum's covert influence on student behavior and values poses significant obstacles for systematic assessment and intervention.
Strategies for Effective Curriculum Modification
Effective strategies for curriculum modification include aligning learning objectives with student needs, incorporating culturally responsive materials, and using diverse instructional methods to accommodate different learning styles. Teachers can also implement ongoing formative assessments to adjust content and pacing dynamically, ensuring inclusivity and engagement. Collaboration between educators, specialists, and stakeholders fosters a supportive environment that bridges the gap between the hidden curriculum and explicit instructional goals.
Balancing Equity and Inclusion in Curriculum Design
Balancing equity and inclusion in curriculum design requires addressing both the hidden curriculum, which involves the unspoken social norms and values transmitted implicitly, and the modified curriculum, which entails deliberate adjustments to content and pedagogy to meet diverse learner needs. Effective strategies integrate culturally responsive teaching practices and differentiated instruction to ensure all students have equitable access to meaningful learning experiences. Emphasizing transparency and intentional inclusivity helps mitigate biases embedded in the hidden curriculum while promoting a more inclusive academic environment.
Hidden Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com