Self-contained classrooms offer a structured environment where students with similar learning needs are grouped together, allowing for tailored instruction and focused support. These classrooms promote individualized learning plans and consistency, fostering academic growth and social development. Explore the full article to understand how self-contained classrooms can benefit your child's educational journey.
Table of Comparison
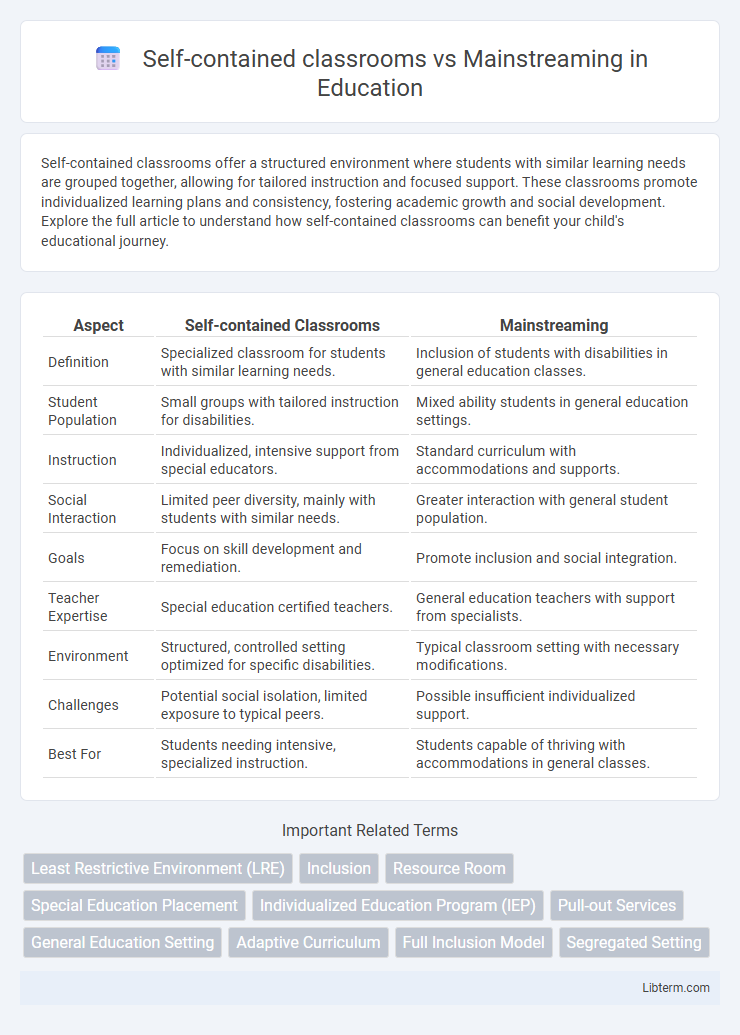
| Aspect | Self-contained Classrooms | Mainstreaming |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Specialized classroom for students with similar learning needs. | Inclusion of students with disabilities in general education classes. |
| Student Population | Small groups with tailored instruction for disabilities. | Mixed ability students in general education settings. |
| Instruction | Individualized, intensive support from special educators. | Standard curriculum with accommodations and supports. |
| Social Interaction | Limited peer diversity, mainly with students with similar needs. | Greater interaction with general student population. |
| Goals | Focus on skill development and remediation. | Promote inclusion and social integration. |
| Teacher Expertise | Special education certified teachers. | General education teachers with support from specialists. |
| Environment | Structured, controlled setting optimized for specific disabilities. | Typical classroom setting with necessary modifications. |
| Challenges | Potential social isolation, limited exposure to typical peers. | Possible insufficient individualized support. |
| Best For | Students needing intensive, specialized instruction. | Students capable of thriving with accommodations in general classes. |
Understanding Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction tailored to students with significant disabilities, offering a structured environment with a low student-to-teacher ratio to support individualized learning goals. These classrooms emphasize modified curricula, therapeutic services, and behavioral interventions to address diverse needs, ensuring students receive focused attention that may not be available in mainstream settings. Understanding self-contained classrooms is essential for recognizing how they promote skill development and social-emotional growth in students requiring intensive support.
Defining Mainstreaming in Education
Mainstreaming in education refers to the practice of integrating students with disabilities into general education classrooms for at least part of the school day, allowing them to learn alongside their non-disabled peers. This approach supports inclusive education by providing students access to the standard curriculum while receiving necessary accommodations and support services. Mainstreaming aims to promote social interaction, reduce stigma, and enhance academic opportunities compared to self-contained classrooms, where students with disabilities are educated in separate, specialized settings.
Key Differences Between Self-Contained and Mainstreamed Settings
Self-contained classrooms provide specialized instruction in a separate, smaller setting tailored for students with significant learning disabilities, promoting individualized attention and targeted support. Mainstreaming integrates students with disabilities into general education classrooms, encouraging social interaction and exposure to the standard curriculum alongside peers without disabilities. Key differences include the level of individualized support, social integration opportunities, and instructional environment, with self-contained settings focusing on specialized needs and mainstreaming prioritizing inclusivity within regular education.
Pros and Cons of Self-Contained Classrooms
Self-contained classrooms offer tailored instruction for students with significant learning disabilities, providing specialized support and smaller class sizes that enhance individualized attention. However, they may limit social interaction with typically developing peers, potentially impacting social skill development and inclusion. The structured environment of self-contained classrooms can foster focused learning, but might reduce exposure to diverse perspectives found in mainstream settings.
Advantages and Challenges of Mainstreaming
Mainstreaming allows students with special needs to participate in general education classrooms, fostering social integration and promoting diversity awareness among all students. Benefits include access to the standard curriculum, enhanced peer interactions, and improved communication skills, although challenges such as insufficient individualized support, potential for social isolation, and teacher training gaps can hinder effective inclusion. Balancing academic expectations with personalized accommodations remains critical to maximizing mainstreaming success.
Student Outcomes in Self-Contained vs Mainstreaming
Self-contained classrooms tend to provide specialized instruction tailored to individual needs, often resulting in improved academic performance and behavioral outcomes for students with significant disabilities. Mainstreaming promotes social integration and exposure to grade-level curriculum, which benefits students with mild to moderate impairments through enhanced peer interactions and higher expectations. Studies show that combining both approaches based on student profiles can optimize educational achievements and social skills development.
Teacher Roles and Responsibilities in Each Setting
Teachers in self-contained classrooms manage specialized instruction for students with significant needs, customizing curriculum to individual learning goals and providing intensive behavioral support. In mainstreaming environments, teachers adapt general education content and collaborate with special educators to accommodate diverse learners while fostering inclusive participation. Both roles require ongoing assessment and tailored interventions to support academic and social development effectively.
Parental Perspectives on Classroom Placement
Parents often weigh the benefits of self-contained classrooms versus mainstreaming based on their child's individual needs and social development. Many express concerns about the potential isolation in self-contained settings, preferring mainstreaming to promote inclusion and peer interaction. Conversely, some parents prioritize specialized instruction and tailored support in self-contained classrooms to address specific learning challenges effectively.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Placement
When choosing between self-contained classrooms and mainstreaming, key factors to consider include the student's individual learning needs, social development, and behavioral challenges. Academic goals must align with the environment's ability to provide specialized instruction or inclusive experiences. Evaluating available support services, peer interactions, and the student's comfort level ensures the placement maximizes educational outcomes and personal growth.
Future Trends in Inclusive Education
Future trends in inclusive education emphasize the integration of technology and personalized learning plans to support both self-contained classrooms and mainstreaming approaches. Data from the National Center for Education Statistics suggest a growing shift towards hybrid models that blend individualized instruction with collaborative, inclusive settings. Advances in AI-driven educational tools and universal design for learning (UDL) frameworks are expected to enhance accessibility and engagement for students across diverse learning environments.
Self-contained classrooms Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com