Test exemption policies allow students to bypass certain exams based on prior achievements or qualifications, reducing stress and saving valuable time. These policies vary by institution and exam type, impacting your academic planning and progression. Explore this article to understand how test exemptions work and how they could benefit your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
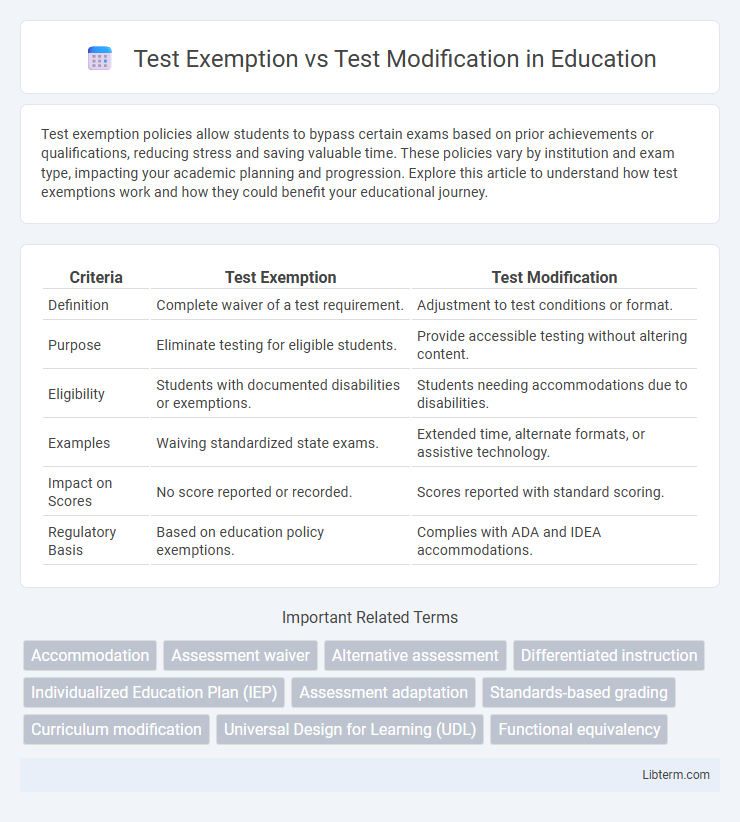
| Criteria | Test Exemption | Test Modification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Complete waiver of a test requirement. | Adjustment to test conditions or format. |
| Purpose | Eliminate testing for eligible students. | Provide accessible testing without altering content. |
| Eligibility | Students with documented disabilities or exemptions. | Students needing accommodations due to disabilities. |
| Examples | Waiving standardized state exams. | Extended time, alternate formats, or assistive technology. |
| Impact on Scores | No score reported or recorded. | Scores reported with standard scoring. |
| Regulatory Basis | Based on education policy exemptions. | Complies with ADA and IDEA accommodations. |
Introduction to Test Exemption and Test Modification
Test exemption allows candidates to bypass specific exam requirements based on prior qualifications, experience, or credentials, streamlining their certification process. Test modification refers to adjustments made to the testing environment or procedures to accommodate individuals with disabilities, ensuring equitable access without altering the exam content. Both practices aim to enhance fairness and accessibility in professional and educational assessments.
Defining Test Exemption
Test exemption refers to the official authorization allowing a vehicle, component, or system to bypass specific regulatory testing requirements under defined conditions. This exemption is granted based on prior evidence demonstrating compliance or minimal impact on emissions, safety, or performance standards. Regulatory bodies issue test exemptions to streamline approval processes while ensuring continued adherence to legal standards.
Understanding Test Modification
Test modification involves altering the format, setting, or administration procedures of a test to accommodate specific needs without changing the content or skill being assessed. It ensures fairness by providing equitable access for individuals with disabilities or unique challenges while maintaining the integrity and validity of the test results. Understanding test modification is crucial for educators and administrators to implement appropriate adjustments that support test-takers' abilities and promote accurate measurement of their knowledge or skills.
Key Differences Between Test Exemption and Test Modification
Test exemption allows students to bypass specific exams entirely based on eligibility criteria such as prior mastery or disability, while test modification involves altering test conditions or formats to accommodate individual needs without eliminating the assessment itself. Exemptions remove the requirement to take the test, ensuring no impact on student records, whereas modifications provide tailored support like extended time or alternate question formats to maintain fair assessment. These distinctions highlight differing approaches to accommodating diverse learner needs within educational testing frameworks.
Criteria for Granting Test Exemption
Test exemption is granted when a student demonstrates mastery of content through prior coursework, alternative assessments, or documented disabilities, ensuring eligibility based on state or institutional policies. Criteria include proof of competence aligned with curriculum standards, submission of qualifying documentation, and equivalency of learning outcomes without compromising academic integrity. This process prioritizes validated evidence of knowledge to waive standard testing requirements effectively.
When is Test Modification Appropriate?
Test modification is appropriate when a test-taker requires accommodations to demonstrate their skills accurately without altering the test's content or validity. This includes adjustments such as extended time, alternative formats, or assistive technology for individuals with disabilities. Modifications ensure equitable assessment conditions while maintaining the integrity of standardized testing procedures.
Benefits of Test Exemption
Test exemption eliminates the need for repeat assessments, saving time and reducing costs for both students and institutions. It allows learners with prior knowledge or qualifications to progress efficiently without redundant testing. By streamlining the evaluation process, test exemption enhances educational flexibility and supports individualized learning paths.
Advantages of Test Modification
Test modification offers the advantage of providing tailored accommodations that address specific individual needs while preserving assessment integrity. It allows for adjustments in test format, timing, or presentation, enabling equitable evaluation without compromising the standardization of the test. This flexibility supports diverse learners by enhancing accessibility and performance accuracy compared to full test exemptions.
Challenges of Implementing Test Exemptions and Modifications
Implementing test exemptions and modifications presents challenges such as ensuring compliance with regulatory standards while maintaining assessment validity and reliability. Educational institutions must balance fairness and academic integrity, often facing difficulties in standardizing accommodations across diverse student needs. Data management and training staff to appropriately apply exemptions or modifications further complicate the operational process.
Choosing the Best Approach: Test Exemption or Modification
Choosing between test exemption and test modification depends on the specific needs of the testing population and the objectives of the assessment. Test exemptions remove the requirement for certain individuals to take the test altogether, often based on eligibility criteria such as disabilities or prior knowledge, ensuring accessibility without altering the test structure. Test modifications adapt the test format, timing, or environment to accommodate individual needs while maintaining the integrity and comparability of test results.
Test Exemption Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com