Cooperative learning enhances student engagement and improves understanding through structured group activities that promote collaboration and shared responsibility. This approach develops critical social skills and fosters deeper comprehension by encouraging active participation and diverse perspectives. Explore the rest of the article to discover effective cooperative learning strategies that can elevate your educational experience.
Table of Comparison
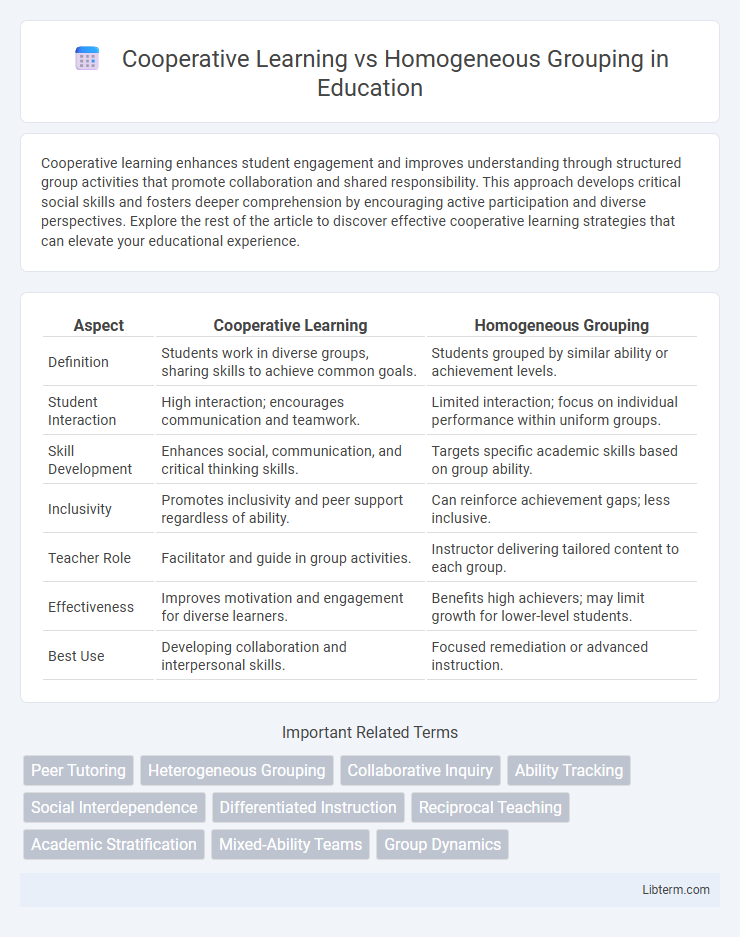
| Aspect | Cooperative Learning | Homogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students work in diverse groups, sharing skills to achieve common goals. | Students grouped by similar ability or achievement levels. |
| Student Interaction | High interaction; encourages communication and teamwork. | Limited interaction; focus on individual performance within uniform groups. |
| Skill Development | Enhances social, communication, and critical thinking skills. | Targets specific academic skills based on group ability. |
| Inclusivity | Promotes inclusivity and peer support regardless of ability. | Can reinforce achievement gaps; less inclusive. |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator and guide in group activities. | Instructor delivering tailored content to each group. |
| Effectiveness | Improves motivation and engagement for diverse learners. | Benefits high achievers; may limit growth for lower-level students. |
| Best Use | Developing collaboration and interpersonal skills. | Focused remediation or advanced instruction. |
Introduction to Cooperative Learning and Homogeneous Grouping
Cooperative learning involves students working together in diverse groups to achieve shared academic goals, enhancing collaboration, communication, and critical thinking skills. Homogeneous grouping organizes students based on similar abilities or learning levels, aiming to provide targeted instruction and improve educational outcomes within each group. Both strategies impact classroom dynamics and student achievement differently, with cooperative learning promoting inclusive interaction and homogeneous grouping focusing on specialized support.
Defining Cooperative Learning: Key Features
Cooperative learning is an educational approach where students work together in small, diverse groups to achieve shared learning goals, promoting positive interdependence and individual accountability. It emphasizes active participation, structured interaction, and the development of social and communication skills, enhancing both academic achievement and personal growth. Unlike homogeneous grouping, which organizes students by similar abilities, cooperative learning leverages diverse strengths to foster collaboration and deeper understanding.
Understanding Homogeneous Grouping
Homogeneous grouping clusters students based on similar ability levels, enabling tailored instruction that meets specific learning needs and accelerates mastery of content. This approach enhances focused skill development by reducing peer disparities, allowing teachers to target gaps effectively and streamline lesson pacing. Research indicates that when homogeneous groups are well-managed, they boost student confidence and foster an environment conducive to individualized academic growth.
Academic Outcomes: A Comparative Analysis
Cooperative learning fosters higher academic achievement by promoting peer interaction and diverse problem-solving approaches, leading to improved critical thinking and retention of material. In contrast, homogeneous grouping often results in uniform pacing but may limit exposure to varied perspectives, potentially hindering cognitive development for advanced or struggling students. Comparative studies reveal cooperative learning yields better standardized test scores and deeper conceptual understanding across heterogeneous classrooms.
Social and Emotional Impacts
Cooperative learning fosters positive social interactions and emotional support by promoting collaboration and empathy among diverse students, enhancing their communication and conflict-resolution skills. Homogeneous grouping, while potentially increasing academic focus, can limit social diversity and reduce opportunities for students to develop adaptability and perspective-taking abilities. The social and emotional outcomes of cooperative learning often lead to improved self-esteem and reduced anxiety compared to the more segregated environment in homogeneous groups.
Classroom Dynamics and Student Engagement
Cooperative learning fosters dynamic classroom interactions by encouraging diverse perspectives and peer collaboration, leading to increased student engagement and deeper understanding. In contrast, homogeneous grouping can limit social interaction but allows tailored instruction targeting specific skill levels, which may benefit focused academic progress. Effective implementation of cooperative learning strategies enhances motivation and participation across varied learner abilities, while homogeneous groups require careful monitoring to maintain engagement and prevent disengagement among students.
Teacher Roles and Instructional Strategies
In cooperative learning, teachers act as facilitators who guide group interactions and promote positive interdependence through structured roles and collaborative tasks. Instructional strategies emphasize diverse skill sets within heterogeneous groups, fostering peer teaching and critical thinking. In homogeneous grouping, educators tailor instruction to specific ability levels, using targeted strategies that focus on skill reinforcement and direct feedback to address uniform learning needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Cooperative learning often faces challenges such as uneven participation, where dominant students may overshadow quieter peers, leading to imbalanced skill development and potential group conflict. Homogeneous grouping can limit peer learning by reducing diverse perspectives and can reinforce achievement gaps by grouping lower-performing students together, potentially impacting motivation and self-esteem. Both approaches require careful management to address social dynamics and ensure equitable learning opportunities for all students.
Case Studies and Research Findings
Research findings reveal that cooperative learning significantly enhances student engagement and academic achievement compared to homogeneous grouping, as seen in multiple case studies across diverse educational settings. Case studies highlight that cooperative learning fosters critical thinking, interpersonal skills, and higher-order problem-solving by promoting interaction among diverse ability levels, whereas homogeneous grouping may limit exposure to varied perspectives and peer support. Cognitive and social benefits documented in longitudinal studies confirm cooperative learning's role in improving comprehension and retention over traditional homogeneous group structures.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Grouping Strategy
Selecting the appropriate grouping strategy depends on specific educational goals and student needs, with cooperative learning fostering diverse perspectives and social skills through heterogeneous groups. Homogeneous grouping, by clustering students of similar abilities, enables targeted instruction and accelerates mastery in particular subjects. Effective educators assess classroom dynamics, curriculum demands, and individual learner profiles to balance these approaches for optimal academic and social outcomes.
Cooperative Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com