The Grammar-Translation Method focuses on teaching language through detailed analysis of grammar rules and direct translation of texts between the target language and the native language. This traditional approach emphasizes reading and writing skills while often neglecting speaking and listening practice. Discover how this method can impact Your language learning journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
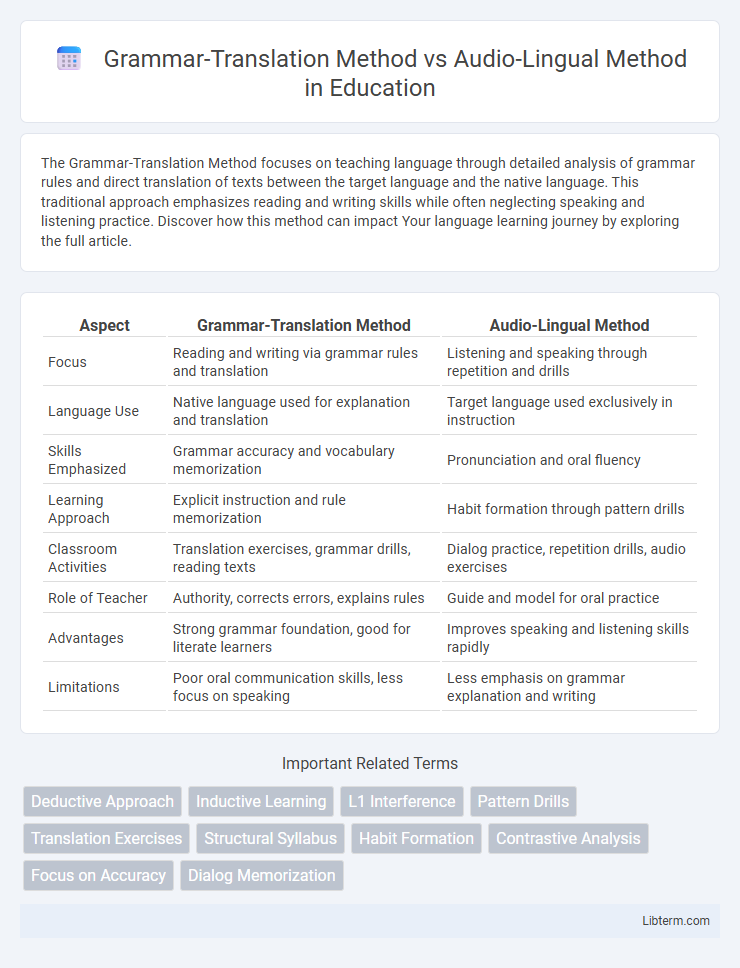
| Aspect | Grammar-Translation Method | Audio-Lingual Method |
|---|---|---|
| Focus | Reading and writing via grammar rules and translation | Listening and speaking through repetition and drills |
| Language Use | Native language used for explanation and translation | Target language used exclusively in instruction |
| Skills Emphasized | Grammar accuracy and vocabulary memorization | Pronunciation and oral fluency |
| Learning Approach | Explicit instruction and rule memorization | Habit formation through pattern drills |
| Classroom Activities | Translation exercises, grammar drills, reading texts | Dialog practice, repetition drills, audio exercises |
| Role of Teacher | Authority, corrects errors, explains rules | Guide and model for oral practice |
| Advantages | Strong grammar foundation, good for literate learners | Improves speaking and listening skills rapidly |
| Limitations | Poor oral communication skills, less focus on speaking | Less emphasis on grammar explanation and writing |
Introduction to Language Teaching Methods
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes reading and writing skills through direct translation of texts and explicit grammar instruction, making it effective for understanding language structure but often neglecting speaking and listening skills. The Audio-Lingual Method focuses on listening and speaking through repetitive drills and pattern practice, promoting language acquisition via habit formation without explicit grammar explanation. Both methods highlight different approaches in language teaching, with Grammar-Translation rooted in classical pedagogy and Audio-Lingual based on behaviorist psychology.
Overview of the Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes learning a language through detailed analysis of grammatical rules and the translation of sentences between the target language and the native language. Its primary focus is on reading and writing skills, with little attention given to speaking and listening proficiency. This method is historically rooted in classical language teaching and is characterized by rote memorization and explicit grammar instruction.
Key Principles of the Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes the systematic study of grammar rules and vocabulary, relying heavily on written texts and translation exercises to develop reading and writing skills. Key principles include a focus on accuracy, explicit grammar instruction, and memorization of vocabulary and paradigms rather than oral proficiency. This method prioritizes understanding of language structure through direct comparison with the native language, often neglecting speaking and listening skills.
Overview of the Audio-Lingual Method
The Audio-Lingual Method (ALM) emphasizes repetitive drills and pattern practice to develop oral proficiency, relying heavily on mimicry, memorization, and structured dialogues. Rooted in behaviorist psychology, ALM focuses on habit formation through stimulus-response conditioning, minimizing explicit grammar explanations in favor of listening and speaking skills. It contrasts with the Grammar-Translation Method by prioritizing spoken language fluency over translation and grammatical analysis.
Key Principles of the Audio-Lingual Method
The Audio-Lingual Method emphasizes habit formation through repetitive drills and pattern practice, focusing on spoken language proficiency rather than explicit grammar explanation. Its key principles include the use of mimicry, memorization, and reinforcement to develop automatic responses to language stimuli. This method prioritizes listening and speaking skills, employing a stimulus-response-reinforcement model to internalize correct language use.
Teaching Techniques: Grammar-Translation vs Audio-Lingual
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes direct instruction of grammatical rules and vocabulary translation, relying heavily on written exercises and rote memorization. In contrast, the Audio-Lingual Method focuses on repetitive oral drills and pattern practice to develop language habits, prioritizing listening and speaking skills over explicit grammar explanation. These techniques reflect distinct approaches: the former centers on reading and writing proficiency, while the latter aims to build communicative competence through structured verbal interaction.
Role of the Teacher and Learner in Both Methods
The Grammar-Translation Method positions the teacher as the authoritative source of knowledge, guiding students through explicit grammar rules and translation exercises, while learners play a passive role, focusing mainly on reading and writing skills. In contrast, the Audio-Lingual Method emphasizes the teacher as a facilitator who models correct language use through drills and repetition, encouraging learners to actively participate in speaking and listening activities to develop oral proficiency. Both methods highlight different dynamics: the former centers on teacher-led explanation and student memorization, whereas the latter prioritizes learner engagement through mimicry and practice.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Grammar-Translation Method
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes reading and writing skills, helping learners develop a strong understanding of grammar rules and vocabulary through translation exercises, which enhances their ability to read classical texts. However, this method often neglects speaking and listening skills, leading to limited oral proficiency and real-life communication ability. The emphasis on rote memorization can also result in a lack of student engagement and practical language usage.
Advantages and Disadvantages: Audio-Lingual Method
The Audio-Lingual Method enhances listening and speaking skills through repetitive drills and pattern practice, leading to improved pronunciation and automatic language use. Its focus on habit formation and immediate error correction benefits learners in acquiring oral proficiency quickly. However, the method often neglects grammar explanations and meaningful communication, which can limit critical thinking and deeper language understanding.
Comparative Analysis and Modern Relevance
The Grammar-Translation Method emphasizes reading and writing through explicit grammar rules and vocabulary memorization, often neglecting spoken fluency, whereas the Audio-Lingual Method centers on listening and speaking skills using repetitive drills and pattern practice to instill language habits. Comparative analysis reveals that while Grammar-Translation supports literary proficiency and translation accuracy, the Audio-Lingual Method is more effective for oral communication and immediate language use. Modern language teaching increasingly integrates communicative approaches, drawing from the strengths of both methods to balance grammatical competence with practical speaking skills.
Grammar-Translation Method Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com