Summative assessment evaluates student learning at the end of an instructional period by measuring knowledge, skills, and academic achievement. It provides valuable insights into your overall performance and helps educators determine whether learning objectives have been successfully met. Explore the full article to understand how summative assessments impact education and your academic journey.
Table of Comparison
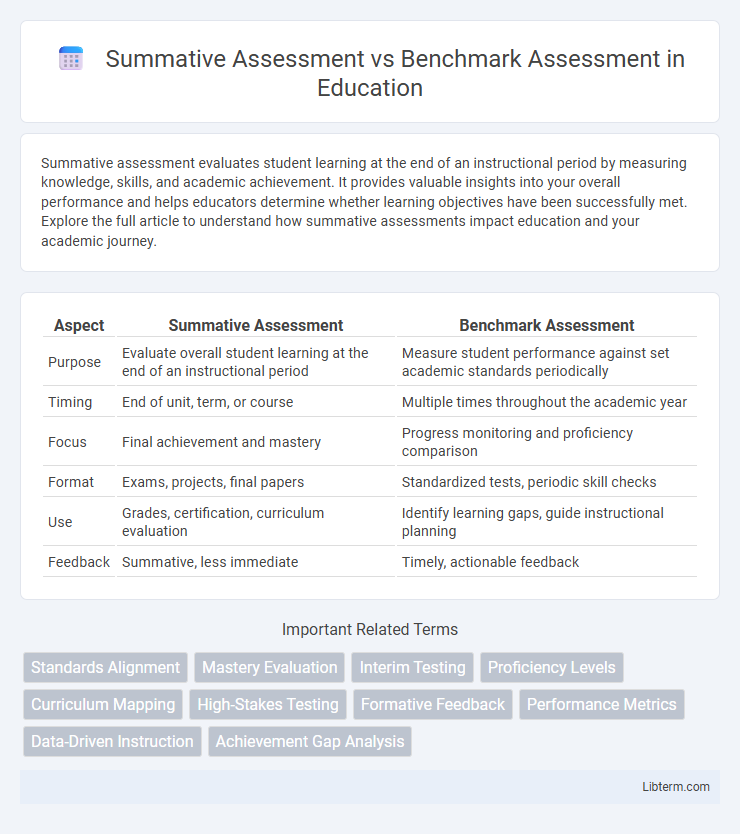
| Aspect | Summative Assessment | Benchmark Assessment |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Evaluate overall student learning at the end of an instructional period | Measure student performance against set academic standards periodically |
| Timing | End of unit, term, or course | Multiple times throughout the academic year |
| Focus | Final achievement and mastery | Progress monitoring and proficiency comparison |
| Format | Exams, projects, final papers | Standardized tests, periodic skill checks |
| Use | Grades, certification, curriculum evaluation | Identify learning gaps, guide instructional planning |
| Feedback | Summative, less immediate | Timely, actionable feedback |
Introduction to Summative and Benchmark Assessments
Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing comprehensive data on overall achievement and mastery of standards. Benchmark assessments occur periodically throughout the academic year to measure progress against specific learning goals and identify areas needing intervention. Both assessments play critical roles in guiding instruction and improving educational outcomes by offering data-driven insights.
Defining Summative Assessment
Summative assessment is a comprehensive evaluation method used to measure student learning, skill acquisition, and academic achievement at the conclusion of an instructional period. It typically includes final exams, end-of-unit tests, and standardized assessments designed to assess the overall effectiveness of instruction. Unlike benchmark assessments, summative assessments provide a summation of student performance for grading and accountability purposes.
Defining Benchmark Assessment
Benchmark assessments are periodic evaluations designed to measure students' academic progress relative to established learning standards or benchmarks throughout the school year. These assessments help educators identify students' strengths and weaknesses, enabling timely instructional adjustments to improve learning outcomes before final evaluations. Unlike summative assessments, which evaluate overall achievement at the end of an instructional period, benchmark assessments provide ongoing data that guide teaching strategies and promote continuous academic growth.
Key Differences Between Summative and Benchmark Assessments
Summative assessments evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional period, measuring overall achievement against standards, typically through final exams or end-of-unit tests. Benchmark assessments occur periodically throughout the academic year, providing interim data to monitor student progress and guide instructional adjustments. Key differences include timing--summative assessments are administered post-instruction, while benchmark assessments are formative checkpoints--and purpose, where summative results inform final grading and accountability, whereas benchmark results drive ongoing instructional decisions.
Purposes and Objectives of Each Assessment Type
Summative assessment aims to evaluate student learning by measuring mastery of specific curriculum standards at the end of an instructional period, providing a comprehensive overview of academic achievement. Benchmark assessment is designed to monitor student progress at regular intervals throughout the academic year, identifying strengths and weaknesses to inform instructional adjustments. The primary objective of summative assessment is to assign grades or determine promotion readiness, while benchmark assessment focuses on data-driven decision making to enhance teaching strategies and improve student outcomes.
Timing and Frequency of Administration
Summative assessments occur at the end of an instructional period, such as the conclusion of a semester or school year, providing a comprehensive evaluation of student learning outcomes. Benchmark assessments are administered periodically throughout the school year, often quarterly or monthly, to monitor student progress and guide instructional adjustments. The timing of summative assessments captures final achievement, while benchmark assessments offer ongoing data to inform teaching strategies.
Data Utilization: Impact on Instruction and Learning
Summative assessments provide comprehensive data on student learning outcomes at the end of instructional periods, guiding educators in curriculum evaluation and future planning but offering limited immediate feedback for instructional adjustment. Benchmark assessments generate periodic data throughout the academic year, enabling teachers to identify learning gaps early and tailor instruction to improve student performance continuously. Effective utilization of benchmark data supports targeted interventions and personalized learning strategies, while summative data informs long-term instructional decisions and accountability measures.
Examples of Summative and Benchmark Assessments
Summative assessments include final exams, end-of-unit tests, and standardized state assessments designed to evaluate overall student learning at the conclusion of an instructional period. Benchmark assessments, such as mid-term exams, quarterly progress tests, and formative reading inventories, monitor student progress and predict performance on summative evaluations. Schools commonly use summative assessments like the SAT or ACT, while benchmark assessments include tools like NWEA MAP tests or district-specific interim assessments.
Advantages and Limitations of Each Assessment
Summative assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of student learning at the end of an instructional period, offering clear evidence of overall achievement but lack immediate feedback for instructional improvement. Benchmark assessments allow educators to monitor student progress regularly, enabling timely interventions and targeted instruction, though they may not capture the full scope of mastery or final learning outcomes. Both assessments play crucial roles in educational settings by balancing broad achievement measurements with ongoing performance tracking to optimize teaching strategies and student success.
Choosing the Right Assessment for Educational Goals
Summative assessments measure overall student learning at the end of an instructional period, providing data on achievement against standards, while benchmark assessments track progress periodically throughout the year to inform instruction and identify learning gaps early. Choosing the right assessment depends on educational goals: summative assessments are ideal for evaluating cumulative knowledge and accountability, whereas benchmark assessments support ongoing formative feedback and targeted interventions. Effective educational strategies integrate both assessment types to balance long-term achievement evaluation with continuous progress monitoring.
Summative Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com