Bilingual education enhances cognitive skills and cultural awareness by integrating two languages in the learning process. It promotes better communication abilities and academic achievement across diverse subjects. Discover how bilingual education can transform Your learning experience in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
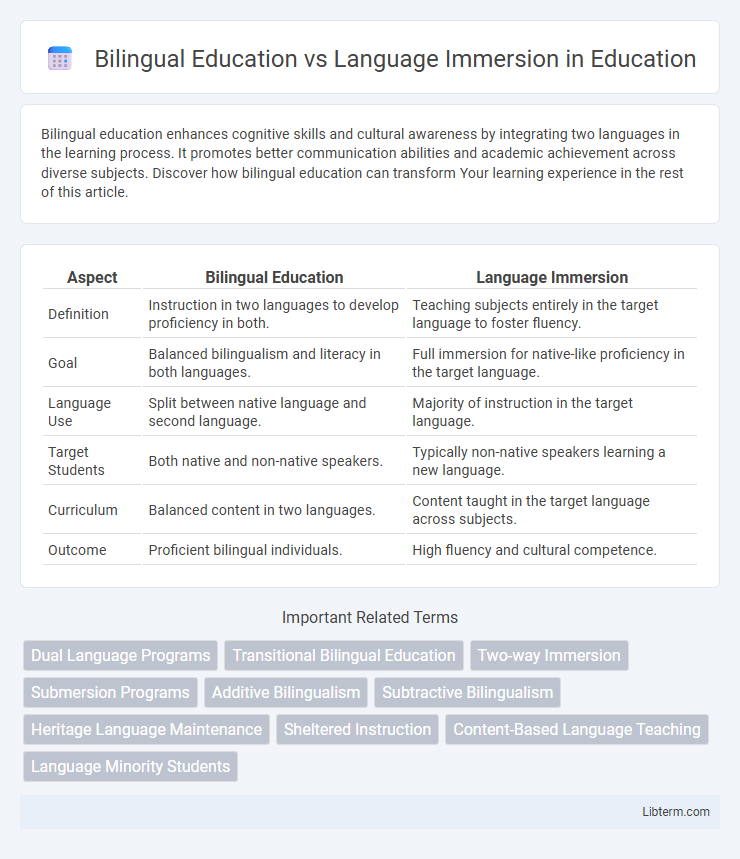
| Aspect | Bilingual Education | Language Immersion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instruction in two languages to develop proficiency in both. | Teaching subjects entirely in the target language to foster fluency. |
| Goal | Balanced bilingualism and literacy in both languages. | Full immersion for native-like proficiency in the target language. |
| Language Use | Split between native language and second language. | Majority of instruction in the target language. |
| Target Students | Both native and non-native speakers. | Typically non-native speakers learning a new language. |
| Curriculum | Balanced content in two languages. | Content taught in the target language across subjects. |
| Outcome | Proficient bilingual individuals. | High fluency and cultural competence. |
Introduction to Bilingual Education and Language Immersion
Bilingual education involves teaching academic content in two languages, aiming to develop proficiency in both the native and target languages simultaneously. Language immersion programs prioritize using the target language exclusively in instruction to foster natural language acquisition and cultural understanding. Both approaches enhance cognitive flexibility and linguistic skills but differ in intensity and instructional methods.
Defining Bilingual Education: Key Concepts
Bilingual education refers to instructional programs where students are taught literacy and subject content in two languages, emphasizing balanced proficiency in both. Key concepts include additive bilingualism, which supports maintaining the native language while acquiring a second, and content-based instruction that integrates language learning with academic subjects. This approach contrasts with language immersion programs that primarily use the target language for instruction to promote fluency through extensive exposure.
Understanding Language Immersion Programs
Language immersion programs place students in an environment where the target language is exclusively or predominantly used for instruction, fostering natural language acquisition through context and interaction. Unlike traditional bilingual education, which may alternate between two languages, immersion aims for fluency by surrounding learners with the language daily across subjects. Research shows immersion students often achieve higher proficiency and cultural competence by engaging consistently with native-speaking teachers and authentic materials.
Goals and Objectives of Each Approach
Bilingual education aims to develop proficiency in two languages by integrating both languages in academic instruction, fostering balanced literacy and cognitive growth. Language immersion focuses on achieving fluency in the target language by surrounding learners with that language for most or all of the school day, promoting natural language acquisition and cultural competence. The primary objective of bilingual education is academic success in both languages, while language immersion seeks rapid oral fluency and deep cultural understanding in one language.
Curriculum Design: Contrasts and Comparisons
Bilingual education curriculum integrates two languages systematically, aiming for balanced proficiency through content instruction and language development, whereas language immersion programs prioritize learning subject matter entirely in the target language to foster natural language acquisition. In bilingual education, curriculum design includes explicit language goals alongside academic objectives, often alternating language use by subject or day, while immersion programs emphasize extensive exposure with progressively increased target language use. Both approaches require culturally responsive materials and trained educators, but immersion leans heavily on contextual learning, making it distinct in implementation and outcome focus.
Cognitive and Academic Outcomes
Bilingual education programs promote cognitive flexibility and improved executive function by teaching academic content in two languages, fostering bilingual proficiency and cultural awareness. Language immersion enhances cognitive abilities such as problem-solving and multitasking through intensive exposure to the target language, accelerating language acquisition and academic performance in both the native and second language. Research shows that students in both bilingual education and language immersion achieve higher literacy rates, better standardized test scores, and stronger metalinguistic skills compared to monolingual peers.
Cultural Competence and Language Proficiency
Bilingual education fosters cultural competence by integrating students' native languages and cultures within the curriculum, promoting a sense of identity and inclusivity. Language immersion accelerates language proficiency by surrounding learners exclusively with the target language, enhancing fluency and real-world communication skills. Both approaches contribute uniquely to cognitive development and cross-cultural understanding, with bilingual education emphasizing cultural awareness and immersion focusing on linguistic mastery.
Teacher Qualifications and Training Requirements
Bilingual education programs require teachers to have proficiency in both the target language and English, often necessitating certifications in bilingual or ESL (English as a Second Language) instruction to effectively support dual-language learners. Language immersion teachers must possess specialized training in immersion pedagogy, including strategies for content-based language teaching and cultural competency, ensuring students acquire language skills naturally through subject matter instruction. Both models emphasize ongoing professional development to maintain language proficiency and adapt teaching methods to diverse student needs.
Challenges and Considerations in Implementation
Implementing bilingual education and language immersion programs presents challenges including resource allocation, teacher expertise, and curriculum design tailored to diverse student needs. Bilingual education often requires balancing instruction in two languages, which can complicate assessment and progress tracking, while language immersion demands comprehensive teacher training to maintain language integrity and cultural relevance. Both models must address parental involvement and community support to ensure program sustainability and effectiveness in fostering bilingual proficiency and academic achievement.
Choosing the Right Approach: Factors for Parents and Educators
Choosing between bilingual education and language immersion requires evaluating a child's language proficiency, learning style, and cultural environment to ensure optimal language acquisition. Bilingual programs often balance academic content in two languages, supporting cognitive development and literacy, while immersion focuses intensively on one language, promoting rapid fluency and cultural immersion. Parents and educators must consider program goals, community language use, and available resources to align educational methods with the child's long-term linguistic and academic success.
Bilingual Education Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com