Expanding your vocabulary enhances communication skills, improves reading comprehension, and boosts confidence in both speaking and writing. Mastering new words allows you to express ideas more precisely and engage your audience more effectively. Explore this article to discover strategies for building a rich and versatile vocabulary.
Table of Comparison
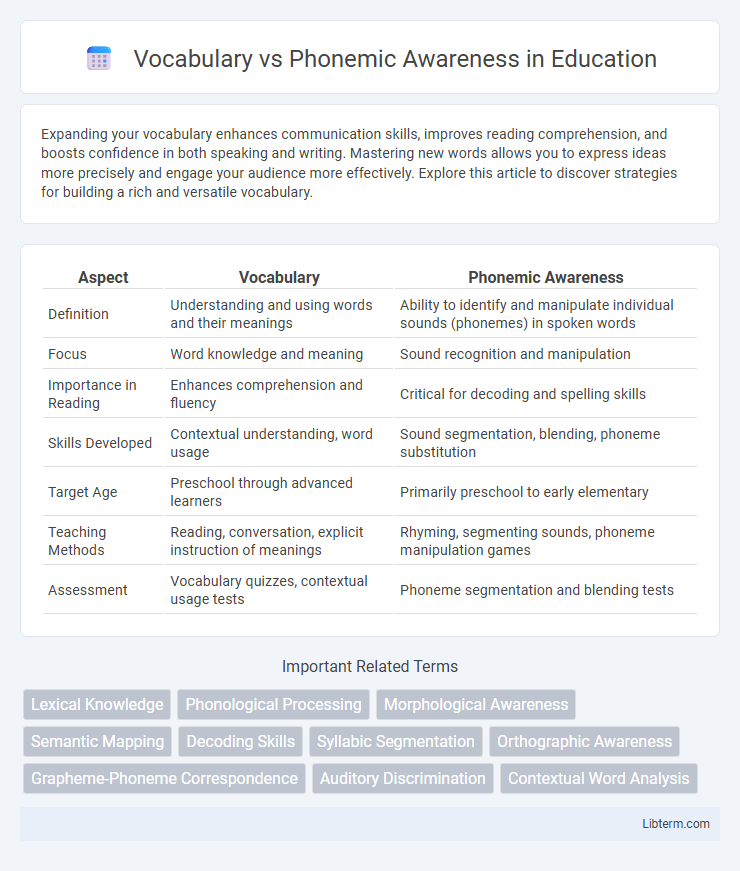
| Aspect | Vocabulary | Phonemic Awareness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Understanding and using words and their meanings | Ability to identify and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken words |
| Focus | Word knowledge and meaning | Sound recognition and manipulation |
| Importance in Reading | Enhances comprehension and fluency | Critical for decoding and spelling skills |
| Skills Developed | Contextual understanding, word usage | Sound segmentation, blending, phoneme substitution |
| Target Age | Preschool through advanced learners | Primarily preschool to early elementary |
| Teaching Methods | Reading, conversation, explicit instruction of meanings | Rhyming, segmenting sounds, phoneme manipulation games |
| Assessment | Vocabulary quizzes, contextual usage tests | Phoneme segmentation and blending tests |
Understanding Vocabulary: Definition and Importance
Vocabulary encompasses the collection of words a person knows and uses, playing a crucial role in communication and comprehension. Understanding vocabulary improves reading skills by enabling accurate interpretation of text and context. Mastery of vocabulary supports academic success and effective language development, distinguishing it from phonemic awareness, which focuses on recognizing and manipulating sounds in spoken language.
What Is Phonemic Awareness?
Phonemic awareness is the ability to identify, hear, and manipulate individual sounds--phonemes--in spoken words, which is a critical skill for early reading development. Unlike vocabulary, which involves understanding the meanings of words, phonemic awareness focuses on the auditory and oral manipulation of sounds without relying on visual text. Mastering phonemic awareness improves decoding skills essential for fluent reading and effective communication.
Key Differences Between Vocabulary and Phonemic Awareness
Vocabulary refers to the collection of words a person knows and understands, encompassing meanings, uses, and contexts, while phonemic awareness involves the ability to recognize and manipulate individual sounds (phonemes) in spoken language. Vocabulary development enhances language comprehension and communication skills, whereas phonemic awareness is a foundational skill crucial for learning to read and decode words. Key differences include that vocabulary is semantic and meaning-based, whereas phonemic awareness is auditory and sound-based, each targeting distinct aspects of language acquisition.
The Role of Vocabulary in Language Development
Vocabulary plays a crucial role in language development by providing the essential building blocks for communication and comprehension. Strong vocabulary skills enhance reading fluency, enable more precise expression, and support higher-level cognitive processes such as inference and problem-solving. Research indicates that a rich vocabulary directly correlates with improved academic performance and overall language proficiency.
How Phonemic Awareness Supports Reading Skills
Phonemic awareness strengthens reading skills by enabling the recognition and manipulation of individual sounds within words, which is fundamental for decoding and word recognition. This skill facilitates the connection between sounds and letters, improving spelling and reading fluency. Enhanced phonemic awareness directly contributes to stronger vocabulary acquisition by supporting accurate word identification and comprehension.
Interplay Between Vocabulary and Phonemic Awareness
Vocabulary development enhances phonemic awareness by providing meaningful context that supports the identification and manipulation of individual sounds within words. Strong phonemic awareness skills facilitate decoding and pronunciation, which in turn aid vocabulary acquisition by enabling learners to recognize and internalize new words more efficiently. The dynamic interplay between vocabulary and phonemic awareness creates a reciprocal relationship that strengthens overall language proficiency and reading comprehension.
Assessing Vocabulary and Phonemic Awareness in Learners
Assessing vocabulary involves measuring a learner's ability to recognize, understand, and use words in context, often through receptive and expressive tasks such as word definition or sentence completion. Phonemic awareness assessment focuses on a learner's capacity to identify, segment, and manipulate individual sounds in spoken words, typically using phoneme isolation, blending, and deletion exercises. Accurate evaluation of both vocabulary and phonemic awareness provides critical insights into language development and informs targeted instructional strategies.
Effective Strategies to Enhance Vocabulary
Targeted strategies such as explicit instruction and contextual reading significantly enhance vocabulary acquisition by connecting new words to existing knowledge. Incorporating phonemic awareness activities like segmenting and blending sounds supports vocabulary growth by improving decoding skills, facilitating word recognition. Utilizing multimedia tools and interactive discussions further reinforces understanding and retention of vocabulary in diverse learning environments.
Activities for Building Phonemic Awareness
Activities for building phonemic awareness include segmenting words into individual sounds, blending phonemes to form words, and manipulating phonemes by adding, deleting, or substituting sounds. These exercises enhance a child's ability to recognize and manipulate the sound structures of language, which is crucial for developing reading skills. Effective phonemic awareness activities often involve games, rhyming exercises, and oral sound manipulation tasks that focus on auditory discrimination rather than written vocabulary.
Integrating Vocabulary and Phonemic Awareness in Classroom Instruction
Integrating vocabulary and phonemic awareness in classroom instruction enhances reading proficiency by simultaneously building word recognition and sound analysis skills. Effective strategies include using multisensory activities that link phonemes to meaningful vocabulary, such as segmenting sounds in new words and contextualizing them through rich discussions and visual aids. This dual focus supports students' decoding abilities and comprehension, fostering stronger literacy development.
Vocabulary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com