An integrated curriculum combines multiple subject areas into cohesive learning experiences, enhancing students' critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach fosters connections between concepts, making education more relevant and engaging for learners. Discover how an integrated curriculum can transform Your teaching methods and student outcomes in the rest of this article.
Table of Comparison
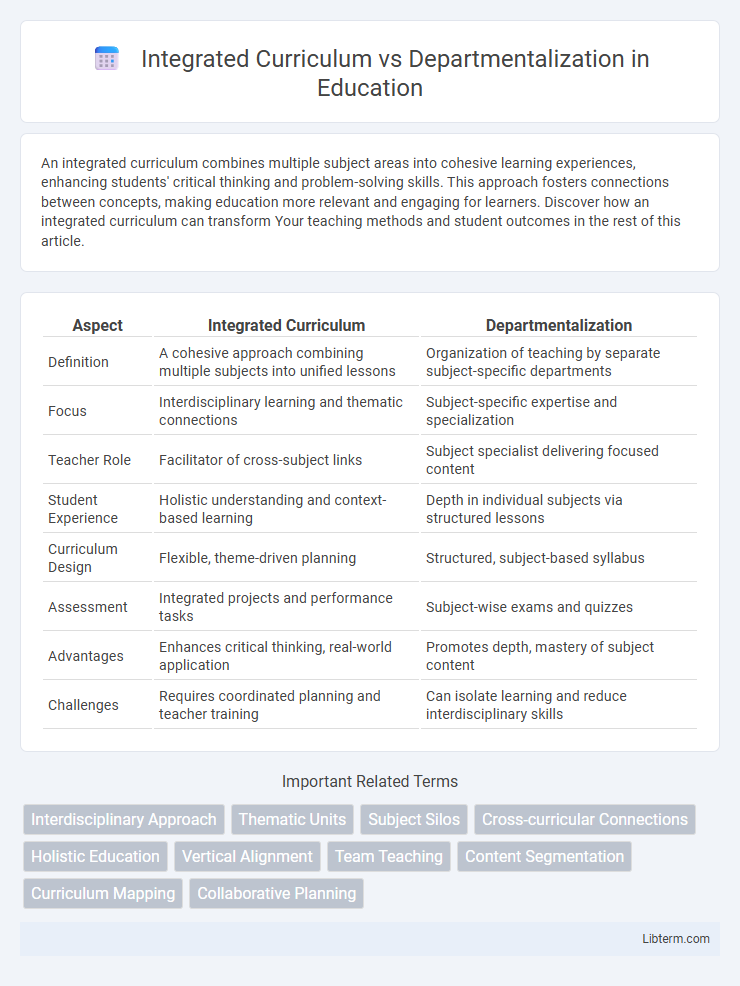
| Aspect | Integrated Curriculum | Departmentalization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A cohesive approach combining multiple subjects into unified lessons | Organization of teaching by separate subject-specific departments |
| Focus | Interdisciplinary learning and thematic connections | Subject-specific expertise and specialization |
| Teacher Role | Facilitator of cross-subject links | Subject specialist delivering focused content |
| Student Experience | Holistic understanding and context-based learning | Depth in individual subjects via structured lessons |
| Curriculum Design | Flexible, theme-driven planning | Structured, subject-based syllabus |
| Assessment | Integrated projects and performance tasks | Subject-wise exams and quizzes |
| Advantages | Enhances critical thinking, real-world application | Promotes depth, mastery of subject content |
| Challenges | Requires coordinated planning and teacher training | Can isolate learning and reduce interdisciplinary skills |
Understanding Integrated Curriculum
Integrated Curriculum fosters interdisciplinary learning by combining subjects around central themes, promoting deeper understanding and application of knowledge. It enhances critical thinking and collaboration among students by connecting concepts from various fields in a cohesive manner. This approach contrasts with Departmentalization, which segments education into isolated subject areas, often limiting the synthesis of ideas across disciplines.
Defining Departmentalization in Education
Departmentalization in education refers to organizing instruction by dividing subjects into separate departments, each managed by specialized teachers focused on a specific academic discipline. This structure enhances subject expertise and curriculum depth but may limit interdisciplinary connections. Contrasting with integrated curriculum, departmentalization emphasizes subject-specific knowledge and streamlined administration within schools.
Historical Overview of Teaching Models
The historical overview of teaching models reveals that integrated curriculum emerged in the early 20th century as a response to rigid departmentalization, aiming to connect subjects and foster interdisciplinary learning. Departmentalization, rooted in the 19th century, standardized education by dividing knowledge into distinct subject areas for specialized instruction. Over time, shifts in educational philosophy emphasized holistic understanding, leading to increased adoption of integrated curriculum approaches to enhance student engagement and real-world application.
Key Features of Integrated Curriculum
Integrated Curriculum emphasizes thematic learning where subjects are interconnected, promoting holistic understanding and real-world application. It fosters collaboration among educators to design interdisciplinary lessons that enhance critical thinking and problem-solving skills. This approach contrasts with Departmentalization, which organizes instruction by discrete subject areas, often limiting context and integration.
Core Principles of Departmentalization
Departmentalization organizes an educational curriculum by dividing subjects into distinct departments such as math, science, language arts, and social studies, promoting specialized instruction and expertise. Core principles include grouping related subject matter to facilitate focused skill development, enabling resource specialization, and establishing clear administrative responsibilities within each department. This structure contrasts with the integrated curriculum's holistic approach by emphasizing subject-specific knowledge, standardized assessment, and curriculum coherence across different content areas.
Benefits of Integrated Curriculum Approaches
Integrated curriculum enhances interdisciplinary learning by connecting concepts across subjects, fostering critical thinking and real-world application. It promotes deeper student engagement through thematic units that make learning more relevant and meaningful. Collaborative teaching in integrated approaches supports diverse learning styles, improving overall academic achievement and retention.
Advantages of Departmentalized Structures
Departmentalized structures streamline educational delivery by grouping subjects into specialized departments, allowing teachers to focus on their areas of expertise and improve instructional quality. This model enhances curriculum depth and rigor by promoting subject mastery and providing students with access to highly qualified educators in each field. Furthermore, departmentalization facilitates efficient resource allocation and targeted professional development, contributing to a more organized and effective educational environment.
Common Challenges and Limitations
Integrated curriculum often faces challenges in balancing content depth across subjects, leading to potential gaps in specialized knowledge, while departmentalization excels in subject expertise but can create fragmented learning experiences. Resource allocation and teacher collaboration present limitations in both approaches, with integrated curriculum demanding extensive cross-disciplinary coordination and departmentalization often limited by siloed communication. Student assessment complexities arise as integrated models struggle with unified evaluation criteria, whereas departmentalized systems may emphasize compartmentalized testing, impacting holistic skill development.
Impact on Student Learning and Engagement
Integrated curriculum fosters deeper student learning and engagement by connecting multiple disciplines around common themes, promoting critical thinking and real-world application. Departmentalization, with its subject-specific focus, often emphasizes mastery of discrete content but may limit interdisciplinary understanding and reduce student motivation. Research indicates that integrated approaches enhance collaboration skills and intrinsic motivation, leading to improved academic performance and sustained interest in learning.
Choosing the Right Model for Your School
Choosing the right model for your school depends on student needs, educational goals, and resource availability. An integrated curriculum promotes interdisciplinary learning and critical thinking by connecting subjects, while departmentalization offers subject specialization and administrative organization. Schools with diverse student populations and collaborative teaching staff often benefit most from an integrated curriculum, whereas those prioritizing subject expertise and clear accountability may prefer departmentalization.
Integrated Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com