Synthesizing involves combining different ideas, data, or information to form a coherent whole that reveals new insights or solutions. This process is essential for critical thinking and decision-making, enabling you to connect diverse perspectives and create innovative outcomes. Explore the rest of the article to learn effective strategies for mastering synthesis in your work and studies.
Table of Comparison
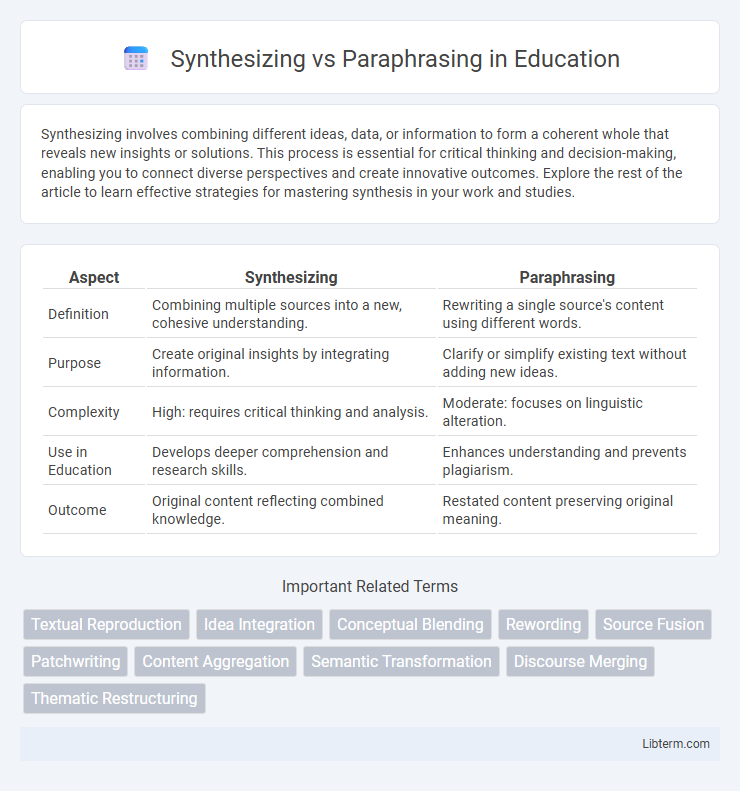
| Aspect | Synthesizing | Paraphrasing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple sources into a new, cohesive understanding. | Rewriting a single source's content using different words. |
| Purpose | Create original insights by integrating information. | Clarify or simplify existing text without adding new ideas. |
| Complexity | High: requires critical thinking and analysis. | Moderate: focuses on linguistic alteration. |
| Use in Education | Develops deeper comprehension and research skills. | Enhances understanding and prevents plagiarism. |
| Outcome | Original content reflecting combined knowledge. | Restated content preserving original meaning. |
Understanding Synthesizing: A Definition
Synthesizing involves combining information from multiple sources to create a new, cohesive understanding or insight, rather than merely restating existing ideas. It requires analyzing and integrating diverse perspectives to produce original conclusions that reflect a comprehensive grasp of the topic. This process enhances critical thinking by connecting concepts and generating innovative content beyond simple paraphrasing.
What is Paraphrasing? Key Concepts
Paraphrasing involves restating someone else's ideas or information in your own words while retaining the original meaning, crucial for avoiding plagiarism in academic writing. It requires understanding the source material deeply, then expressing the key concepts clearly and concisely without copying the original phrasing. Effective paraphrasing maintains the intent of the original text while adapting vocabulary and sentence structure to fit the new context.
Core Differences Between Synthesizing and Paraphrasing
Synthesizing involves combining information from multiple sources to create a new, cohesive understanding or perspective, while paraphrasing restates a single source's information in different words without altering the original meaning. Synthesizing requires critical thinking and integration of ideas, whereas paraphrasing focuses on clarity and simplification of existing content. Key differences include synthesis generating original insights versus paraphrasing preserving the original text's intent with modified phrasing.
When to Synthesize Information
Synthesizing information is essential when integrating multiple sources to create a coherent understanding or new perspective on a topic. It is most effective during research-heavy projects, literature reviews, or analytical essays where combining diverse viewpoints reveals patterns and deeper insights. Paraphrasing, in contrast, is best suited for restating specific information clearly without altering the original meaning.
Effective Paraphrasing Techniques
Effective paraphrasing techniques involve thoroughly understanding the original text, using synonyms and altering sentence structure while maintaining the original meaning. Synthesizing requires combining information from multiple sources to create a cohesive narrative, whereas paraphrasing focuses on rewording a single source. Emphasizing clarity and accuracy during paraphrasing ensures content integrity and avoids plagiarism.
Common Mistakes: Synthesizing vs Paraphrasing
Confusing paraphrasing with synthesizing often leads to common mistakes, such as simply rewording a single source instead of integrating multiple perspectives. Synthesizing requires combining information from various texts to create a new, cohesive understanding, whereas paraphrasing only involves restating content in different words. Overlooking this distinction can result in disorganized writing and a lack of original analysis.
Benefits of Synthesizing in Academic Writing
Synthesizing in academic writing integrates information from multiple sources, creating a cohesive and original argument that demonstrates deep understanding and critical thinking. This process enhances the clarity and strength of the thesis by connecting diverse perspectives and evidence, fostering a comprehensive analysis. Synthesizing also minimizes plagiarism risks by generating new insights rather than merely restating existing content.
Paraphrasing to Avoid Plagiarism
Paraphrasing involves rewording original content while retaining the core meaning to create unique expressions and avoid plagiarism. Effective paraphrasing requires understanding the source material deeply and rewriting it with different vocabulary and sentence structures without changing the intended message. Proper citation combined with skillful paraphrasing ensures academic integrity and uniqueness in written work.
Integrating Synthesizing and Paraphrasing in Research
Integrating synthesizing and paraphrasing in research enhances the clarity and originality of scholarly writing by combining information from multiple sources while rewording the content to avoid plagiarism. Synthesizing allows researchers to merge diverse perspectives into a coherent narrative, while paraphrasing ensures that the integrated ideas are expressed in the researcher's unique voice. Effective use of both techniques improves the depth of analysis and strengthens the argument by demonstrating critical engagement with the literature.
Tips for Mastering Both Skills
Mastering synthesizing requires combining information from multiple sources to create a cohesive and original perspective, emphasizing understanding context and identifying common themes. Effective paraphrasing involves rewriting content in your own words while maintaining the original meaning, so practice varying sentence structures and expanding vocabulary to avoid plagiarism. Regularly cross-check your work for accuracy and clarity to ensure both skills enhance your writing quality and credibility.
Synthesizing Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com