The IB Curriculum offers a comprehensive, globally recognized education framework designed to develop critical thinking, intercultural understanding, and rigorous academic skills across six subject groups. It emphasizes inquiry-based learning, real-world application, and encourages students to become active, compassionate lifelong learners. Discover how the IB Curriculum can shape Your educational journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
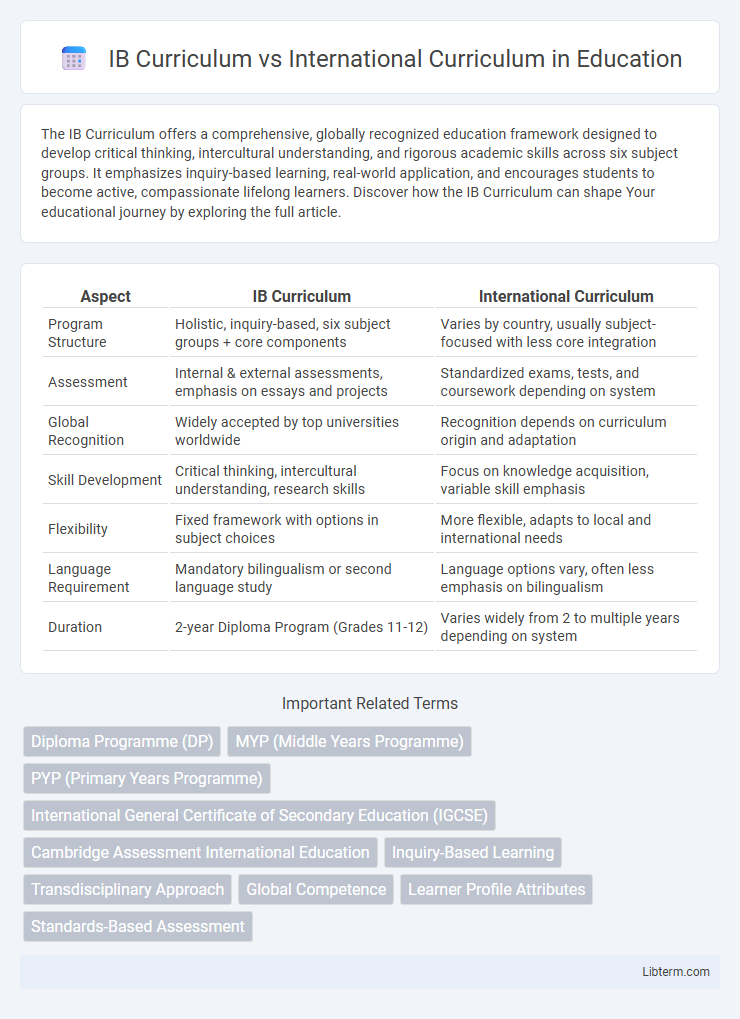
| Aspect | IB Curriculum | International Curriculum |
|---|---|---|
| Program Structure | Holistic, inquiry-based, six subject groups + core components | Varies by country, usually subject-focused with less core integration |
| Assessment | Internal & external assessments, emphasis on essays and projects | Standardized exams, tests, and coursework depending on system |
| Global Recognition | Widely accepted by top universities worldwide | Recognition depends on curriculum origin and adaptation |
| Skill Development | Critical thinking, intercultural understanding, research skills | Focus on knowledge acquisition, variable skill emphasis |
| Flexibility | Fixed framework with options in subject choices | More flexible, adapts to local and international needs |
| Language Requirement | Mandatory bilingualism or second language study | Language options vary, often less emphasis on bilingualism |
| Duration | 2-year Diploma Program (Grades 11-12) | Varies widely from 2 to multiple years depending on system |
Overview of IB Curriculum
The IB Curriculum emphasizes a holistic, inquiry-based approach to education that fosters critical thinking, intercultural understanding, and global engagement across six subject groups. It incorporates the core components of Theory of Knowledge (TOK), the Extended Essay (EE), and Creativity, Activity, Service (CAS) to develop well-rounded learners. This framework is designed to prepare students for rigorous academic challenges and lifelong learning in an international context.
Overview of International Curriculum
The International Curriculum encompasses a diverse range of educational frameworks designed to promote global citizenship, intercultural understanding, and academic excellence across countries. It integrates language acquisition, inquiry-based learning, and critical thinking skills to prepare students for international higher education and diverse career paths. Schools offering International Curriculum often tailor programs such as Cambridge Assessment International Education or the IB Diploma to meet diverse student needs, ensuring flexibility and broad recognition worldwide.
Key Philosophical Differences
The IB curriculum emphasizes holistic education through its learner profile, promoting intercultural understanding and critical thinking as core values. In contrast, the International Curriculum often centers on standardized academic benchmarks tailored to global educational frameworks with less focus on personal development. IB's philosophy integrates inquiry-based learning and global citizenship, whereas International Curricula prioritize subject-specific expertise and adaptability across diverse educational systems.
Structure and Program Levels
The IB Curriculum is structured into four main programs: Primary Years Programme (PYP), Middle Years Programme (MYP), Diploma Programme (DP), and Career-related Programme (CP), each designed to cater to specific age groups and learning stages. In contrast, the International Curriculum typically refers to a broader set of educational systems, such as the Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) or International General Certificate of Secondary Education (IGCSE), that offer tiered levels like Lower Secondary, IGCSE, and A-Levels. The IB's integrated approach emphasizes inquiry-based learning and international-mindedness across all levels, while the International Curriculum provides flexible pathways with subject-specific specialization and examination options tailored to diverse academic needs.
Assessment Methods
The IB Curriculum employs formative and summative assessments, including internal assessments, extended essays, and oral presentations, designed to evaluate critical thinking and intercultural understanding. In contrast, many International Curriculums rely more heavily on standardized exams and end-of-course assessments to measure knowledge acquisition and subject proficiency. Both approaches integrate continuous assessment, but the IB emphasizes holistic evaluation and learner reflection to foster lifelong skills.
Curriculum Content and Flexibility
The IB Curriculum emphasizes inquiry-based learning with a holistic approach across six subject groups, promoting critical thinking and intercultural understanding through a structured yet interdisciplinary framework. International Curricula, such as the British or American systems, offer more specialized and flexible subject choices, allowing schools to tailor content to regional needs and student preferences. The IB's core components, including Theory of Knowledge and the Extended Essay, provide a unique depth not typically found in other international programs, balancing rigor with adaptability.
Teacher Qualifications and Training
The IB Curriculum mandates that teachers undergo specialized IB training workshops to ensure adherence to its rigorous educational standards and philosophy, emphasizing inquiry-based and student-centered learning. In contrast, international curricula such as Cambridge or American systems often require teachers to hold recognized teaching certifications and may offer less standardized professional development tailored specifically to the curriculum. The depth and consistency of teacher training in the IB program contribute to a more uniform instructional approach compared to the variable requirements found in broader international curricula.
Global Recognition and University Acceptance
The IB Curriculum is globally recognized for its rigorous academic standards and emphasis on critical thinking, making it highly valued by top universities worldwide, including Ivy League and Russell Group institutions. International Curriculums such as the Cambridge International Examinations (CIE) and International Baccalaureate Diploma Programme (IBDP) also enjoy widespread acceptance but vary in recognition depending on the region and specific university requirements. Universities increasingly prefer IB graduates for their holistic education and international mindedness, enhancing acceptance rates and scholarship opportunities across global higher education institutions.
Student Experience and Skill Development
IB Curriculum emphasizes holistic student experience by promoting inquiry-based learning, critical thinking, and intercultural understanding, fostering skills essential for global citizenship. The International Curriculum offers a broader framework with flexibility, often integrating national standards and diverse pedagogies, which may result in varied skill development outcomes depending on implementation. Both curricula prioritize language proficiency and problem-solving, but IB's structured approach ensures consistent development of independent research and reflective skills.
Choosing the Right Curriculum for Your Child
Selecting the right curriculum for your child involves understanding the unique strengths of the IB Curriculum, which emphasizes critical thinking, global-mindedness, and inquiry-based learning, versus broader International Curricula that may offer diverse national standards and flexible subject choices. The IB program's structured framework across Primary Years, Middle Years, and the Diploma Program supports holistic development and university readiness, while other International Curricula can cater to specific educational philosophies or regional requirements. Parents should consider their child's learning style, future academic goals, and cultural adaptability when choosing between these curricula to ensure a supportive and effective educational experience.
IB Curriculum Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com