Criterion-referenced assessment measures your performance against a fixed set of predetermined criteria or learning standards rather than comparing you to other learners. This approach helps identify specific strengths and areas for improvement, providing clear insight into mastery of skills or knowledge. Explore the rest of the article to understand how criterion-referenced assessments can benefit your learning journey.
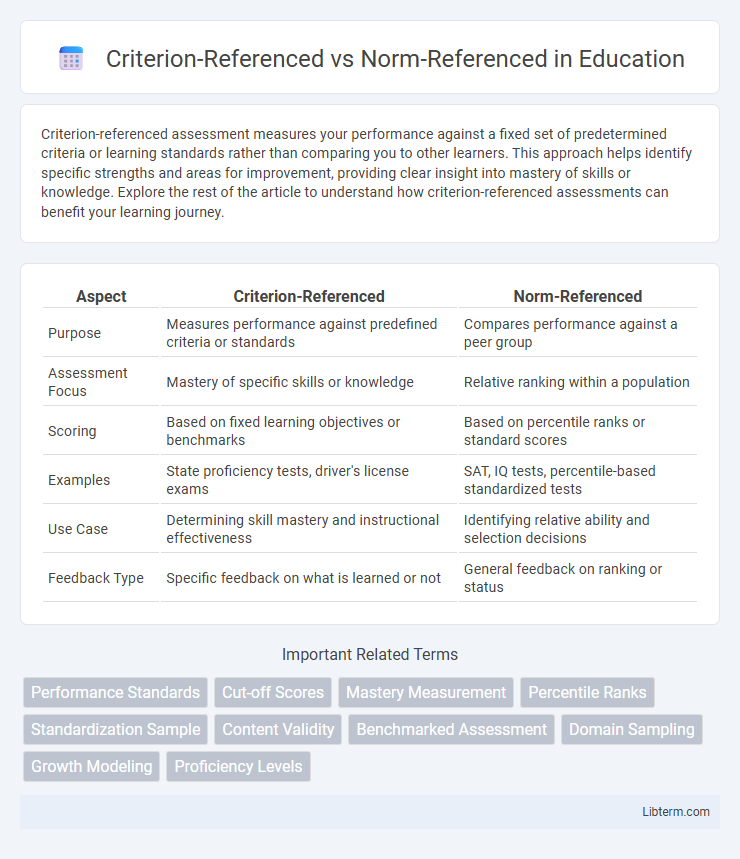
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Criterion-Referenced | Norm-Referenced |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Measures performance against predefined criteria or standards | Compares performance against a peer group |
| Assessment Focus | Mastery of specific skills or knowledge | Relative ranking within a population |
| Scoring | Based on fixed learning objectives or benchmarks | Based on percentile ranks or standard scores |
| Examples | State proficiency tests, driver's license exams | SAT, IQ tests, percentile-based standardized tests |
| Use Case | Determining skill mastery and instructional effectiveness | Identifying relative ability and selection decisions |
| Feedback Type | Specific feedback on what is learned or not | General feedback on ranking or status |
Introduction to Measurement and Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessments measure student performance against a fixed set of predetermined criteria or learning standards, providing specific information about mastery of content. Norm-referenced assessments rank students in comparison to their peers, highlighting relative performance within a group. Understanding the distinction between these assessment types is crucial in educational measurement for selecting appropriate tools that align with instructional goals and evaluating student achievement accurately.
Defining Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessment evaluates a student's performance based on predefined learning objectives or standards, measuring mastery of specific skills or knowledge. Unlike norm-referenced assessments that compare results against a peer group, criterion-referenced tests determine whether each test taker meets established criteria or benchmarks. This approach ensures clear identification of strengths and areas for improvement tied directly to curriculum goals.
Defining Norm-Referenced Assessment
Norm-referenced assessment evaluates a student's performance by comparing it to a peer group, establishing a rank or percentile indicating relative standing. This type of assessment identifies how well individuals perform in relation to others rather than measuring specific learning objectives. It is commonly used in standardized testing to classify students into categories such as top performers, average, or below average.
Key Differences Between Criterion-Referenced and Norm-Referenced
Criterion-referenced assessments measure a student's performance against a predefined set of criteria or learning standards, focusing on whether specific skills or knowledge have been mastered. Norm-referenced assessments compare a student's performance to that of a peer group, ranking individuals to determine relative standing. Key differences include the purpose of evaluation, interpretation of scores, and instructional use, with criterion-referenced emphasizing mastery and norm-referenced emphasizing comparative ranking.
Advantages of Criterion-Referenced Assessment
Criterion-referenced assessments provide precise measurement of student mastery by comparing performance against fixed learning standards, leading to targeted instructional improvements. These assessments offer clear feedback on specific skills and knowledge, enabling personalized learning paths and reducing ambiguity in evaluating student progress. By fostering a focus on individual achievement rather than peer comparison, criterion-referenced assessments promote mastery learning and support equitable educational outcomes.
Advantages of Norm-Referenced Assessment
Norm-referenced assessments provide a clear comparison of a student's performance relative to peers, enabling educators to identify and address individual learning needs effectively. These assessments facilitate widespread benchmarking and placement decisions by ranking students along a performance continuum. The standardized nature of norm-referenced tests ensures consistency and reliability in measuring diverse abilities across large populations.
Limitations and Challenges of Each Approach
Criterion-referenced assessments face limitations such as defining clear, measurable criteria that accurately reflect diverse learner outcomes and struggles with potential lack of motivation if all students meet the criteria easily. Norm-referenced tests present challenges including cultural and socioeconomic biases that can skew results and often fail to provide diagnostic feedback for individual skill development. Both approaches require careful implementation to balance fairness, validity, and meaningful performance insights.
Appropriate Uses for Criterion-Referenced Tests
Criterion-referenced tests are most appropriate for assessing specific skills or knowledge against predefined standards, making them ideal for measuring mastery in educational settings or certification programs. These tests provide clear information on whether a student meets learning objectives, supporting individualized instruction and curriculum adjustments. Unlike norm-referenced tests, criterion-referenced assessments help educators identify areas needing improvement without comparison to peers.
Appropriate Uses for Norm-Referenced Tests
Norm-referenced tests are appropriate for comparing an individual's performance to a defined population or peer group, such as in standardized IQ testing or college admissions where ranking is critical. These tests effectively identify relative strengths and weaknesses among examinees by placing scores within percentile ranks or stanines. They are ideal in educational settings to allocate resources, identify gifted students, or screen for learning disabilities based on comparison to normative data.
Choosing the Right Assessment Method
Selecting the appropriate assessment method depends on the purpose of evaluation: criterion-referenced assessments measure student performance against predefined standards or learning objectives, providing clear insight into mastery of specific skills. Norm-referenced assessments compare a student's performance to that of a peer group, useful for ranking and identifying relative standing within a population. Understanding these distinctions helps educators choose assessments that align with instructional goals and accurately reflect student learning outcomes.
Criterion-Referenced Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com