Effective supervisory practices enhance team performance and foster a positive work environment by providing clear guidance and consistent feedback. Strong supervisors develop leadership skills that help identify strengths and address challenges, boosting overall productivity and morale. Explore the rest of this article to discover techniques that can elevate your supervisory abilities.
Table of Comparison
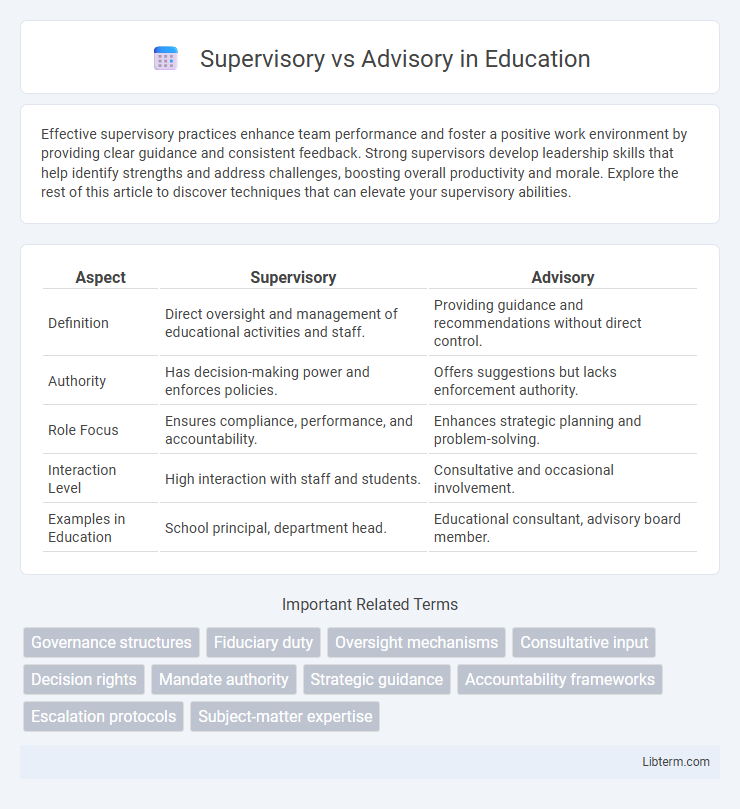
| Aspect | Supervisory | Advisory |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Direct oversight and management of educational activities and staff. | Providing guidance and recommendations without direct control. |
| Authority | Has decision-making power and enforces policies. | Offers suggestions but lacks enforcement authority. |
| Role Focus | Ensures compliance, performance, and accountability. | Enhances strategic planning and problem-solving. |
| Interaction Level | High interaction with staff and students. | Consultative and occasional involvement. |
| Examples in Education | School principal, department head. | Educational consultant, advisory board member. |
Understanding Supervisory and Advisory Roles
Supervisory roles involve direct oversight, management, and accountability for team performance, ensuring tasks align with organizational goals and compliance standards. Advisory roles focus on providing expert guidance, strategic recommendations, and informed insights without exercising direct control or decision-making authority. Understanding the distinction between these roles clarifies responsibilities, enhances collaboration, and optimizes organizational efficiency in achieving objectives.
Key Differences Between Supervisory and Advisory Functions
Supervisory functions involve monitoring, directing, and ensuring compliance with policies and regulations within an organization, while advisory functions provide expert guidance and recommendations without direct decision-making authority. Supervisory roles typically have accountability for outcomes and enforce rules, whereas advisory roles focus on analysis and strategic counsel to influence decisions. The key difference lies in the level of control and responsibility: supervisors actively manage processes, whereas advisors support through expertise and insights.
Scope of Responsibility in Supervisory vs Advisory Positions
Supervisory positions hold direct responsibility for managing teams, overseeing daily operations, and ensuring task completion, with authority to make decisions and enforce policies. Advisory roles focus on providing expert guidance, recommendations, and strategic insights without direct control over implementation or personnel management. The scope of responsibility in supervisory roles is operational and executional, while advisory roles emphasize influence and consultation.
Decision-Making: Supervisory Authority vs Advisory Guidance
Supervisory authority involves direct decision-making power, enabling supervisors to enforce rules, allocate resources, and ensure compliance within an organization. In contrast, advisory guidance provides expert recommendations without binding authority, allowing decision-makers to consider options while retaining ultimate control. The distinction lies in the ability to impose decisions versus offering informed perspectives to influence outcomes.
Communication Styles in Supervisory and Advisory Roles
Supervisory roles demand direct, clear, and authoritative communication styles to ensure tasks are completed efficiently and standards are met, emphasizing clarity and directive feedback. Advisory roles prioritize collaborative, open-ended communication, fostering dialogue and offering expert suggestions without imposing decisions. Effective communication in supervisory contexts centers on control and accountability, while advisory roles emphasize guidance and partnership.
Impact on Organizational Structure: Supervisory vs Advisory
The impact on organizational structure differs significantly between supervisory and advisory roles. Supervisory roles involve direct authority over teams, defining clear hierarchies and accountability lines, which streamlines decision-making and operational control. Advisory roles, conversely, influence through expertise and recommendations without altering hierarchical dynamics, fostering collaborative environments that support strategic flexibility and innovation.
Accountability and Reporting Relationships
Supervisory roles hold direct accountability for employee performance and maintain formal reporting relationships, ensuring adherence to organizational policies and objectives. Advisory roles provide expertise and recommendations without direct authority, influencing decision-making without being accountable for implementation outcomes. Clear distinctions in accountability and reporting lines define the operational boundaries between supervisory and advisory functions within corporate structures.
Skill Sets Required for Supervisory and Advisory Effectiveness
Supervisory effectiveness requires strong leadership skills, including decision-making, conflict resolution, and performance management to ensure team accountability and productivity. Advisory effectiveness demands expertise in communication, industry knowledge, and analytical thinking to provide strategic guidance and foster informed decision-making. Both roles benefit from emotional intelligence and adaptability, but supervisors focus more on operational control while advisors emphasize insight and influence.
Real-World Examples of Supervisory and Advisory Roles
Supervisory roles include positions such as team leaders or project managers who directly oversee employee tasks and ensure goal completion, exemplified by a construction site supervisor managing daily operations and worker safety. Advisory roles typically involve experts like financial consultants or legal advisors who provide strategic guidance without direct authority, illustrated by a company hiring a cybersecurity advisor to recommend risk mitigation strategies. In practical settings, supervisors enforce policies and maintain workflow, while advisors influence decisions through specialized knowledge and recommendations.
Choosing the Right Role for Organizational Success
Supervisory roles involve direct management and accountability for team performance, emphasizing task delegation, progress monitoring, and enforcing compliance with organizational standards. Advisory roles focus on providing expert guidance, strategic insights, and recommendations without direct authority, supporting decision-makers to optimize outcomes. Selecting the right role depends on organizational needs: supervisory positions drive execution and operational control, while advisory roles enhance strategic planning and innovation.
Supervisory Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com