Direct instruction is a structured teaching method focused on explicit, systematic teaching of specific skills or concepts, ensuring clear objectives and guided practice. This approach enhances learning efficiency by providing step-by-step instructions, immediate feedback, and frequent assessments to monitor student progress. Discover how direct instruction can transform your teaching strategies by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
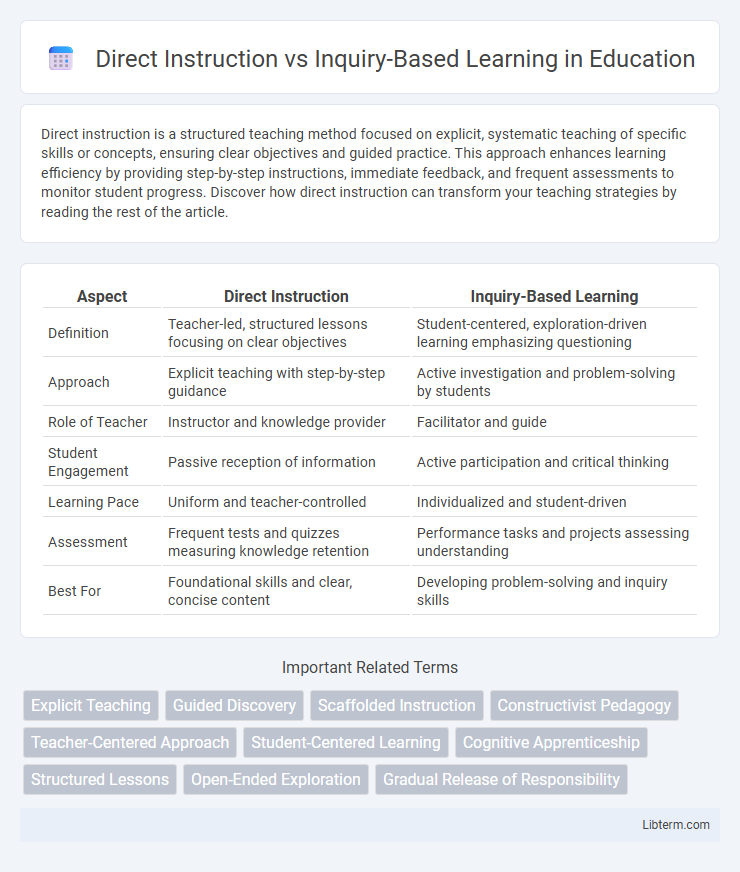
| Aspect | Direct Instruction | Inquiry-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-led, structured lessons focusing on clear objectives | Student-centered, exploration-driven learning emphasizing questioning |
| Approach | Explicit teaching with step-by-step guidance | Active investigation and problem-solving by students |
| Role of Teacher | Instructor and knowledge provider | Facilitator and guide |
| Student Engagement | Passive reception of information | Active participation and critical thinking |
| Learning Pace | Uniform and teacher-controlled | Individualized and student-driven |
| Assessment | Frequent tests and quizzes measuring knowledge retention | Performance tasks and projects assessing understanding |
| Best For | Foundational skills and clear, concise content | Developing problem-solving and inquiry skills |
Understanding Direct Instruction: Key Features
Direct Instruction emphasizes explicit teaching through structured lessons and clear, measurable objectives designed to ensure mastery of specific skills. It relies on scripted curriculum, frequent assessment, and immediate feedback to guide student learning efficiently. This method prioritizes teacher-led explanations and modeling to minimize misconceptions and reinforce foundational knowledge.
What Is Inquiry-Based Learning? Core Principles
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on student-driven exploration where learners pose questions, investigate problems, and construct knowledge through active engagement. Core principles include fostering curiosity, promoting critical thinking, encouraging collaboration, and emphasizing the process of discovery over rote memorization. This approach contrasts with Direct Instruction by prioritizing experiential learning and learner autonomy in the educational process.
Historical Background: Evolution of Teaching Methods
Direct Instruction, developed in the 1960s by Siegfried Engelmann, emphasized structured, teacher-led lessons to ensure mastery of fundamental skills through repetition and clear guidance. Inquiry-Based Learning, rooted in John Dewey's early 20th-century progressive education theories, promotes student-centered exploration and critical thinking by encouraging learners to investigate questions and problems actively. The evolution from Direct Instruction to Inquiry-Based Learning reflects a shift from behaviorist approaches focusing on rote memorization toward constructivist paradigms prioritizing discovery and conceptual understanding.
Comparing Teacher Roles: Direct vs Inquiry-Based
In Direct Instruction, teachers take a central role by delivering structured lessons with explicit guidance, ensuring clear learning objectives and immediate feedback. Inquiry-Based Learning positions teachers as facilitators who encourage student exploration, critical thinking, and self-directed discovery, fostering autonomy and deeper understanding. The contrast highlights a shift from teacher-centered control in Direct Instruction to student-centered support in Inquiry-Based Learning environments.
Student Engagement: Participation and Motivation
Direct Instruction promotes student engagement through structured, clear guidance, which often leads to higher initial participation and quick mastery of skills. Inquiry-Based Learning enhances motivation by fostering curiosity and active exploration, encouraging students to take ownership of their learning process. Research shows that combining both methods can optimize student participation and sustain long-term motivation in diverse educational settings.
Impact on Learning Outcomes and Achievement
Direct Instruction delivers clear, structured teaching with explicit objectives, which consistently improves academic achievement, particularly in foundational skills like reading and math. Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and deep understanding by engaging students in exploration and problem-solving, enhancing long-term retention and conceptual grasp. Research indicates that combining Direct Instruction with Inquiry-Based strategies can maximize learning outcomes by balancing skill acquisition and cognitive development.
Adaptability Across Subjects and Grade Levels
Direct Instruction offers a structured approach that easily adapts to various subjects and grade levels through clear, scripted lessons and targeted practice. Inquiry-Based Learning fosters adaptability by encouraging student-driven exploration, which can be tailored to diverse content areas and developmental stages by adjusting the complexity of questions and investigations. Both methods support differentiated learning, but Direct Instruction emphasizes consistency, while Inquiry-Based Learning promotes flexibility in cognitive engagement.
Addressing Diverse Learner Needs
Direct Instruction provides structured, clear guidance that benefits learners who require explicit support and step-by-step explanations, making it effective for foundational skill development. Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging exploration and student-driven discovery, which stimulates engagement among diverse learners with varying interests and learning styles. Combining these approaches allows educators to tailor instruction, balancing explicit teaching with opportunities for independent inquiry to address the full spectrum of learner needs.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Direct Instruction faces challenges such as limited student engagement and reduced opportunities for critical thinking due to its teacher-centered nature. Inquiry-Based Learning often struggles with inconsistent outcomes and requires significant teacher expertise to guide students effectively without causing confusion. Both approaches can be constrained by classroom time, resource availability, and varying student readiness levels impacting overall effectiveness.
Blending Direct Instruction and Inquiry for Optimal Results
Blending direct instruction and inquiry-based learning leverages the structured guidance of explicit teaching with the critical thinking and engagement fostered by student-driven exploration, creating a balanced educational approach. Research shows this hybrid method enhances knowledge retention and promotes deeper understanding by allowing foundational skills to be established through direct instruction, while inquiry nurtures problem-solving and creativity. Implementing a strategically sequenced combination, where direct instruction provides essential concepts followed by inquiry activities, results in improved academic performance and learner autonomy.
Direct Instruction Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com