Traditional classroom settings foster direct interaction between teachers and students, promoting hands-on learning and immediate feedback. These environments support structured lessons and social development through in-person collaboration. Discover how traditional classrooms shape educational experiences and benefit your learning by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
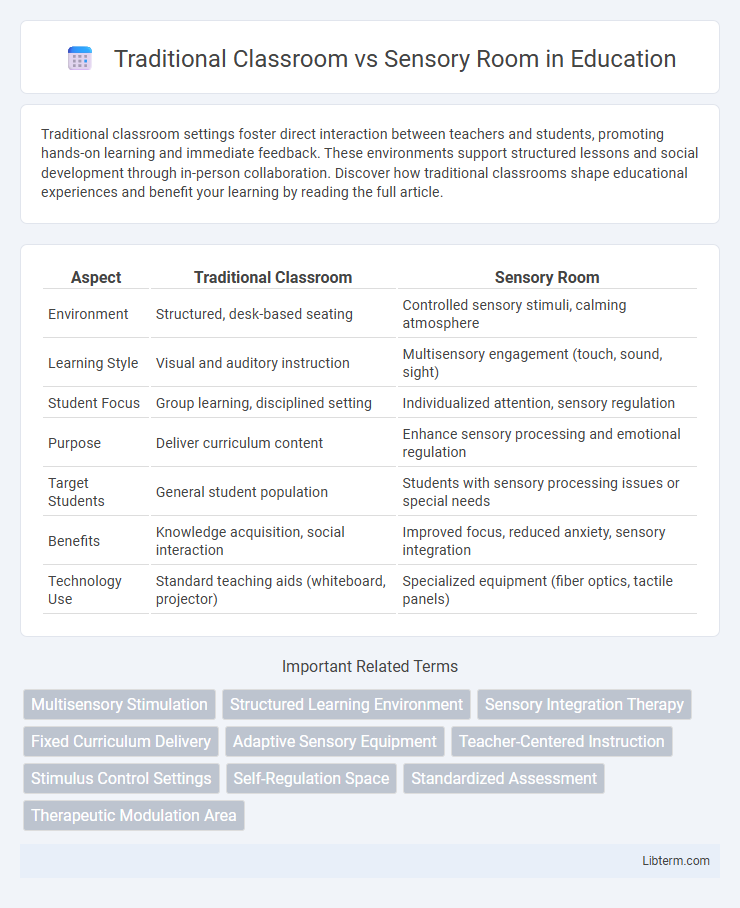
| Aspect | Traditional Classroom | Sensory Room |
|---|---|---|
| Environment | Structured, desk-based seating | Controlled sensory stimuli, calming atmosphere |
| Learning Style | Visual and auditory instruction | Multisensory engagement (touch, sound, sight) |
| Student Focus | Group learning, disciplined setting | Individualized attention, sensory regulation |
| Purpose | Deliver curriculum content | Enhance sensory processing and emotional regulation |
| Target Students | General student population | Students with sensory processing issues or special needs |
| Benefits | Knowledge acquisition, social interaction | Improved focus, reduced anxiety, sensory integration |
| Technology Use | Standard teaching aids (whiteboard, projector) | Specialized equipment (fiber optics, tactile panels) |
Introduction: Understanding Learning Environments
Traditional classrooms prioritize structured instruction with standardized seating and limited sensory stimuli, aiming to accommodate large groups of students efficiently. Sensory rooms provide controlled environments with varied sensory inputs designed to enhance focus, reduce anxiety, and support diverse learning needs, especially for students with sensory processing challenges. Comparing these environments highlights the importance of adaptive learning spaces to improve student engagement and educational outcomes.
Defining the Traditional Classroom
The traditional classroom typically features rows of desks facing a teacher's lectern, emphasizing structured lessons, standardized curricula, and auditory learning. This environment prioritizes visual and verbal instruction with limited sensory stimuli, aimed at maintaining focus and discipline. It contrasts with sensory rooms, which incorporate tactile, auditory, and visual elements to support sensory processing and individualized learning needs.
What is a Sensory Room?
A sensory room is a specially designed environment that provides controlled sensory experiences to help individuals relax, focus, and regulate their emotions. Equipped with tools such as soft lighting, textured objects, and calming sounds, sensory rooms support sensory integration therapy and cater to various needs, particularly for children with autism or sensory processing disorders. Unlike traditional classrooms, sensory rooms emphasize personalized sensory input rather than structured academic instruction.
Key Differences Between Traditional Classrooms and Sensory Rooms
Traditional classrooms typically emphasize structured academic instruction with desks, whiteboards, and group activities, prioritizing cognitive learning and standardized curriculum delivery. Sensory rooms focus on providing a controlled environment designed to stimulate or soothe the senses through specialized equipment like weighted blankets, sensory lighting, and tactile objects, catering to individuals with sensory processing challenges or developmental disorders. The key difference lies in their purpose: traditional classrooms aim for knowledge acquisition and social interaction, while sensory rooms concentrate on sensory integration and emotional regulation.
Sensory Stimuli and Their Impact on Learning
Sensory rooms utilize controlled sensory stimuli such as lights, sounds, textures, and scents to create a calming environment that enhances focus and reduces anxiety, promoting better learning outcomes. Compared to traditional classrooms, sensory rooms address diverse sensory processing needs, supporting students with sensory integration challenges and improving cognitive engagement. Research shows that tailored sensory input in these environments can significantly boost attention, behavior regulation, and information retention.
Academic Outcomes: Comparing Learning Effectiveness
Traditional classrooms emphasize structured curriculum delivery through lectures and group activities, promoting standardized academic outcomes measured by tests and assignments. Sensory rooms offer individualized, multi-sensory experiences designed to enhance focus, reduce anxiety, and improve engagement, particularly benefiting students with sensory processing challenges or neurodevelopmental disorders. Studies indicate that integrating sensory rooms can lead to improved attention, behavior, and academic performance, highlighting their potential as a complementary tool to traditional teaching methods.
Emotional and Behavioral Benefits
Traditional classrooms provide structured learning environments that support social interaction and routine, which can help stabilize emotional regulation in many students. Sensory rooms offer targeted sensory input through specialized equipment, promoting relaxation and reducing anxiety or behavioral outbursts for individuals with sensory processing challenges. Combining these approaches can enhance emotional well-being and improve behavior management, especially for children with autism spectrum disorder or attention deficit hyperactivity disorder.
Inclusivity for Students with Special Needs
Traditional classrooms often lack the adaptive resources necessary to support students with special needs, leading to challenges in engagement and learning. Sensory rooms provide a controlled environment that harnesses multisensory stimuli to enhance focus, reduce anxiety, and promote inclusivity for diverse learners. Implementing sensory rooms alongside traditional settings ensures tailored learning experiences that accommodate varying sensory processing requirements and improve educational outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Environment
Traditional classrooms often struggle with sensory overload due to noise, limited movement, and rigid seating arrangements that can hinder concentration and engagement for students with sensory processing difficulties. Sensory rooms provide controlled, calming environments designed to support sensory regulation but face limitations such as restricted space, high setup costs, and limited integration with broader academic curricula. Each setting requires tailored strategies to address diverse learning needs, with traditional classrooms needing adaptive tools and sensory rooms requiring structured programming to maximize their therapeutic benefits.
Choosing the Right Setting: Factors to Consider
Selecting the right educational environment involves assessing the individual needs of students, including sensory processing abilities and learning styles. Traditional classrooms offer structured curriculum delivery and peer socialization, while sensory rooms provide controlled stimuli to support emotional regulation and focus. Factors such as the presence of sensory processing disorders, behavioral challenges, and the goal of fostering self-regulation should guide the decision between conventional classroom settings and sensory room integration.
Traditional Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com