The demonstration method effectively engages learners through hands-on experience, enhancing understanding by allowing them to observe and practice skills in real-time. This approach reinforces theoretical knowledge by showcasing practical applications, making complex concepts more accessible and memorable. Explore the rest of the article to discover how incorporating demonstrations can transform your learning or teaching experience.
Table of Comparison
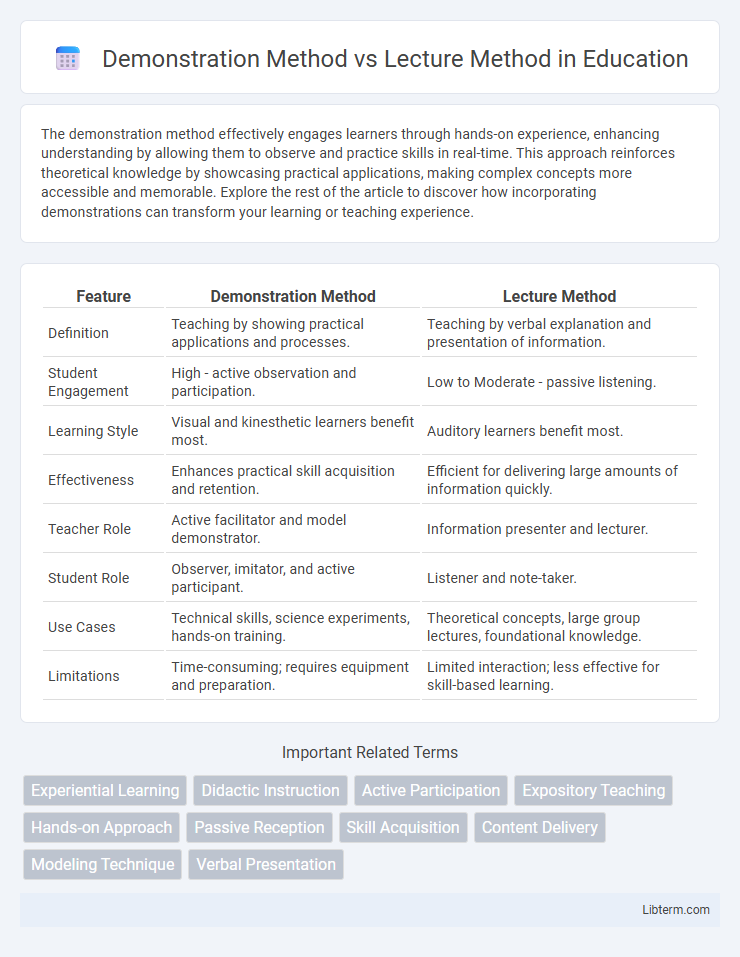
| Feature | Demonstration Method | Lecture Method |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teaching by showing practical applications and processes. | Teaching by verbal explanation and presentation of information. |
| Student Engagement | High - active observation and participation. | Low to Moderate - passive listening. |
| Learning Style | Visual and kinesthetic learners benefit most. | Auditory learners benefit most. |
| Effectiveness | Enhances practical skill acquisition and retention. | Efficient for delivering large amounts of information quickly. |
| Teacher Role | Active facilitator and model demonstrator. | Information presenter and lecturer. |
| Student Role | Observer, imitator, and active participant. | Listener and note-taker. |
| Use Cases | Technical skills, science experiments, hands-on training. | Theoretical concepts, large group lectures, foundational knowledge. |
| Limitations | Time-consuming; requires equipment and preparation. | Limited interaction; less effective for skill-based learning. |
Introduction to Teaching Methods
The Demonstration Method emphasizes active learning by visually showing processes or skills, enhancing students' understanding through observation and practice. The Lecture Method relies on verbal delivery to efficiently transmit information to large groups but may engage learners less actively. Combining both methods in teaching optimizes knowledge retention and caters to diverse learning preferences.
Overview of the Demonstration Method
The Demonstration Method is an instructional strategy that emphasizes hands-on learning through visual presentation and practical execution of concepts. It allows learners to observe processes in real time, enhancing comprehension and retention by engaging multiple senses. This method is particularly effective in teaching complex skills and procedures that require step-by-step guidance.
Key Features of the Lecture Method
The Lecture Method emphasizes structured oral delivery of content by an instructor to a large audience, prioritizing information dissemination and clarity. It relies heavily on verbal communication, often supported by visual aids such as slides or charts, facilitating a one-way transmission of knowledge. Key features include efficient coverage of extensive material, standardized presentation, and the ability to address theoretical concepts systematically.
Student Engagement in Both Methods
The Demonstration Method significantly enhances student engagement by providing visual and kinesthetic experiences that facilitate active learning and better retention. In contrast, the Lecture Method often leads to passive reception of information, potentially causing decreased attention and limited interaction among students. Empirical studies show that combining demonstration with interactive elements markedly boosts student motivation and comprehension compared to traditional lectures alone.
Effectiveness in Knowledge Retention
The Demonstration Method significantly enhances knowledge retention by engaging multiple senses, allowing learners to observe and practice concepts in real-time, which reinforces understanding and memory. In contrast, the Lecture Method primarily relies on auditory delivery, which often leads to lower retention rates due to passive learning and limited interaction. Studies indicate that demonstrated content can improve retention by up to 75%, whereas lecture-only approaches typically yield retention rates closer to 20-30%.
Practical Applications: Demonstration vs Lecture
The demonstration method enhances practical understanding by visually showcasing processes and techniques, allowing learners to directly observe and replicate actions, which is crucial in hands-on fields like engineering or medicine. In contrast, the lecture method primarily delivers theoretical knowledge through verbal explanation, making it less effective for skills that require physical practice or visual learning. Practical applications benefit more from demonstration as it bridges the gap between theory and real-world execution, fostering better retention and competency in tasks.
Advantages of the Demonstration Method
The demonstration method enhances learning by providing visual and practical experience, making complex concepts easier to understand and retain. It actively engages learners, improving skills through hands-on practice and immediate feedback. This method also caters to diverse learning styles, increasing overall comprehension and motivation compared to passive lecture presentations.
Limitations of the Lecture Method
The lecture method often results in passive learning, limiting student engagement and interaction, which hinders knowledge retention and critical thinking development. It fails to accommodate diverse learning styles, making it challenging for students to grasp complex concepts without practical experience. Furthermore, the one-way communication restricts immediate feedback and personalized instruction, reducing overall learning effectiveness compared to the demonstration method.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Classroom
Choosing the right teaching method depends on the learning objectives and student needs; the demonstration method effectively enhances practical skills and visual understanding, making it ideal for subjects requiring hands-on experience. The lecture method suits delivering theoretical knowledge to large groups but may limit student engagement and interaction. Combining both approaches can optimize comprehension and retention by balancing passive listening with active participation.
Conclusion: Demonstration vs Lecture Method
The demonstration method enhances learning through visual and practical engagement, reinforcing understanding and retention by actively involving students in the process. The lecture method primarily delivers knowledge verbally, making it efficient for covering large amounts of information but often less effective for skill acquisition. Selecting between demonstration and lecture methods depends on educational goals, with demonstrations better suited for hands-on learning and lectures ideal for theoretical instruction.
Demonstration Method Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com