Flexible grouping allows educators to tailor instruction by forming dynamic groups based on students' current needs, skills, and interests. This strategy promotes personalized learning, enhancing engagement and academic growth by adjusting group composition regularly. Discover how flexible grouping can transform Your teaching approach and improve student outcomes in the full article.
Table of Comparison
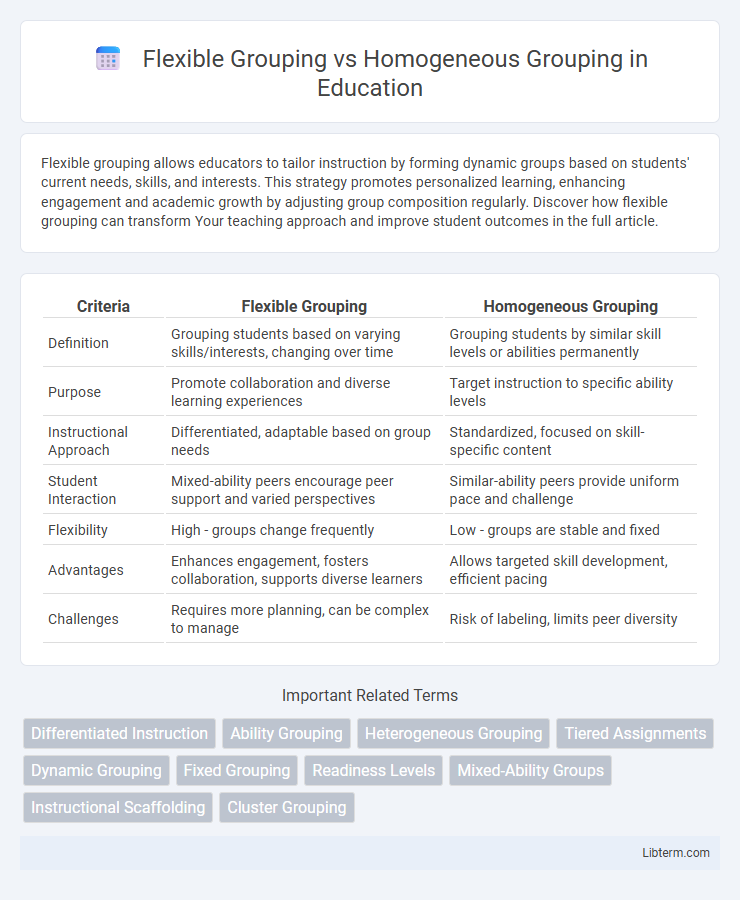
| Criteria | Flexible Grouping | Homogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Grouping students based on varying skills/interests, changing over time | Grouping students by similar skill levels or abilities permanently |
| Purpose | Promote collaboration and diverse learning experiences | Target instruction to specific ability levels |
| Instructional Approach | Differentiated, adaptable based on group needs | Standardized, focused on skill-specific content |
| Student Interaction | Mixed-ability peers encourage peer support and varied perspectives | Similar-ability peers provide uniform pace and challenge |
| Flexibility | High - groups change frequently | Low - groups are stable and fixed |
| Advantages | Enhances engagement, fosters collaboration, supports diverse learners | Allows targeted skill development, efficient pacing |
| Challenges | Requires more planning, can be complex to manage | Risk of labeling, limits peer diversity |
Understanding Flexible Grouping in Education
Flexible grouping in education involves organizing students based on varying criteria such as skill level, interest, or learning style, allowing dynamic shifts to meet diverse learning needs. This strategy promotes individualized instruction and peer collaboration by grouping students temporarily for targeted activities rather than fixed homogeneous groups. Research shows that flexible grouping enhances student engagement and academic achievement by fostering differentiated instruction and accommodating varying progress rates.
Defining Homogeneous Grouping
Homogeneous grouping involves organizing students based on similar abilities, skill levels, or learning needs to tailor instruction more effectively. This approach allows teachers to target specific challenges and provide more focused support, improving academic outcomes for each group. By clustering learners with comparable proficiency, homogeneous grouping promotes efficient skill development and accelerates mastery of content.
Key Differences Between Flexible and Homogeneous Grouping
Flexible grouping organizes students based on varying skill levels, interests, or learning needs, allowing for dynamic changes over time to enhance personalized instruction. Homogeneous grouping sorts students strictly by similar abilities or achievement levels for targeted skill development but remains static throughout a learning unit. Key differences include flexibility in group composition, responsiveness to student progress, and adaptability to diverse learning objectives.
Benefits of Flexible Grouping for Student Engagement
Flexible grouping enhances student engagement by allowing learners to collaborate with diverse peers, fostering varied perspectives and critical thinking skills. It supports personalized learning by adapting groups based on students' abilities, interests, and learning needs, promoting motivation and active participation. This dynamic approach encourages social interaction and peer support, creating an inclusive classroom environment where students remain more invested in their educational experience.
Academic Outcomes of Homogeneous Grouping
Homogeneous grouping, where students with similar academic abilities are grouped together, often leads to improved academic outcomes by allowing targeted instruction that addresses specific learning needs. Research indicates that students in homogeneous groups tend to show higher levels of mastery in core subjects such as mathematics and reading due to tailored curriculum pacing and depth. This grouping strategy facilitates more efficient use of resources and instructional methods, ultimately boosting student achievement and confidence in their academic skills.
Addressing Diverse Learning Needs with Flexible Grouping
Flexible grouping enhances differentiated instruction by allowing educators to form temporary groups based on students' varying skill levels, interests, or learning styles, thereby addressing diverse learning needs effectively. This approach contrasts with homogeneous grouping, where students are permanently grouped by ability, often limiting personalized support and engagement. By regularly adjusting group composition, flexible grouping promotes collaboration, motivation, and targeted intervention tailored to individual student growth.
Social and Emotional Impacts of Grouping Strategies
Flexible grouping fosters diverse interactions, promoting social skills and emotional resilience by allowing students to learn from varied peers. Homogeneous grouping may strengthen emotional comfort and self-esteem through similarity but risks limiting exposure to diverse perspectives, potentially impacting social development. Balancing these strategies helps optimize social-emotional learning by combining familiarity with opportunities for broader social engagement.
Challenges and Limitations of Flexible and Homogeneous Grouping
Flexible grouping often faces challenges in managing diverse learning paces and maintaining consistent assessment standards, while it requires frequent adjustments that can strain teacher resources. Homogeneous grouping limits peer learning opportunities and may reinforce achievement gaps, as students with similar abilities receive uniform instruction without exposure to varied perspectives. Both grouping methods struggle with balancing individualized support and fostering collaborative skill development in heterogeneous classrooms.
Best Practices for Implementing Effective Grouping in Classrooms
Effective grouping in classrooms balances flexible grouping and homogeneous grouping to optimize student learning outcomes. Implement flexible grouping by regularly assessing student progress and adjusting groups based on skill levels, learning styles, and specific instructional goals to foster collaboration and differentiation. Use homogeneous grouping selectively for targeted skill reinforcement, ensuring clear objectives and monitoring to prevent fixed ability labeling and maintain motivation.
Flexible vs. Homogeneous Grouping: Making the Right Choice
Flexible grouping enhances individualized learning by allowing students to shift between groups based on skill levels, interests, or learning needs, promoting adaptability and differentiated instruction. Homogeneous grouping organizes students by similar abilities or characteristics, aiming to streamline instruction and address specific skill gaps effectively. Educators should assess classroom dynamics, learning objectives, and student diversity to determine whether the fluidity of flexible grouping or the targeted focus of homogeneous grouping best supports academic growth.
Flexible Grouping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com