Passive learning involves absorbing information without active engagement, such as listening to lectures or reading without interaction. This method often leads to lower retention and understanding compared to active learning techniques. Discover how shifting your approach can enhance your learning effectiveness throughout this article.
Table of Comparison
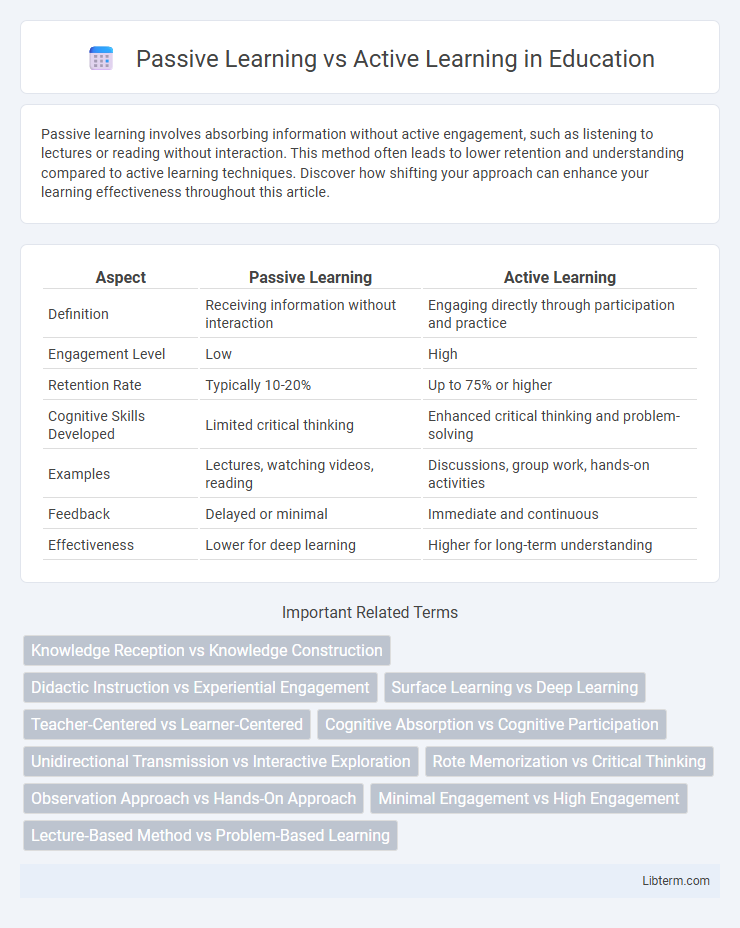
| Aspect | Passive Learning | Active Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Receiving information without interaction | Engaging directly through participation and practice |
| Engagement Level | Low | High |
| Retention Rate | Typically 10-20% | Up to 75% or higher |
| Cognitive Skills Developed | Limited critical thinking | Enhanced critical thinking and problem-solving |
| Examples | Lectures, watching videos, reading | Discussions, group work, hands-on activities |
| Feedback | Delayed or minimal | Immediate and continuous |
| Effectiveness | Lower for deep learning | Higher for long-term understanding |
Introduction to Passive and Active Learning
Passive learning involves students receiving information through lectures or reading without direct engagement, which often results in lower retention rates. Active learning requires learners to participate actively through discussions, problem-solving, or hands-on activities, enhancing comprehension and memory. Research shows that active learning strategies increase student performance by up to 25% compared to passive methods.
Defining Passive Learning
Passive learning involves absorbing information through listening, reading, or watching without direct engagement or interaction, often characterized by note-taking and memorization. It relies heavily on the learner as a recipient of knowledge rather than a participant in the learning process. This method contrasts with active learning, which emphasizes critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration to deepen understanding and retention.
Defining Active Learning
Active learning involves engaging students directly in the learning process through discussions, problem-solving, case studies, and hands-on activities, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Unlike passive learning, where students receive information without interaction, active learning promotes critical thinking, collaboration, and application of knowledge. Techniques such as group work, interactive simulations, and frequent feedback are essential components that define active learning methodologies.
Key Differences Between Passive and Active Learning
Passive learning involves receiving information without direct interaction or engagement, typically through lectures or reading. Active learning requires participation and critical thinking, such as discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities. The key difference lies in student involvement, where active learning fosters deeper understanding and retention compared to the more observational nature of passive learning.
Benefits of Passive Learning
Passive learning enhances information absorption by allowing learners to receive content without immediate pressure to respond, promoting better retention through repeated exposure. It supports the development of foundational knowledge by enabling focused observation and listening, which is essential for understanding complex subjects. This method also provides flexibility in pacing, accommodating diverse learning styles and allowing students to revisit material as needed.
Benefits of Active Learning
Active learning significantly enhances knowledge retention and critical thinking skills by engaging students directly in the learning process through discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities. This approach fosters deeper understanding and improves long-term memory compared to passive learning methods, which typically involve listening or reading without interaction. Educational research from institutions like Harvard University highlights that active learning increases student performance and motivation, making it a preferred strategy in modern classrooms.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Passive learning often leads to lower retention rates due to minimal student engagement and limited opportunities for critical thinking, making it difficult to assess understanding effectively. Active learning presents challenges such as increased preparation time for instructors and potential resistance from students accustomed to traditional methods. Both approaches may struggle with scalability in large classrooms, where personalized feedback and participation can be constrained.
Situations Best Suited for Passive or Active Learning
Passive learning excels in situations requiring the efficient absorption of foundational knowledge, such as lectures, presentations, or multimedia content where learners need to receive information without immediate interaction. Active learning is best suited for environments promoting critical thinking, problem-solving, and collaboration, including group discussions, hands-on projects, and case studies, enabling learners to engage deeply with the material. Choosing between passive and active learning depends on goals like knowledge acquisition speed versus skill development and retention.
Integrating Passive and Active Learning Strategies
Integrating passive and active learning strategies enhances knowledge retention by balancing content absorption with practical application. Combining lectures or reading materials (passive learning) with discussions, problem-solving, and hands-on activities (active learning) fosters deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. This blended approach addresses diverse learning preferences and improves overall cognitive engagement.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Learning Method
Selecting the right learning method depends on individual goals, learning styles, and context. Active learning enhances critical thinking and retention through engagement and interaction, making it ideal for deep understanding and skill development. Passive learning can be efficient for initial exposure or absorbing large volumes of information, but combining both methods often yields the most effective educational outcomes.
Passive Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com