An inclusion classroom integrates students of all abilities, fostering a collaborative and supportive learning environment where diversity is celebrated. This approach encourages personalized teaching strategies that address individual needs while promoting social interaction and mutual respect. Discover how inclusion classrooms can benefit your child and transform educational experiences by reading the full article.
Table of Comparison
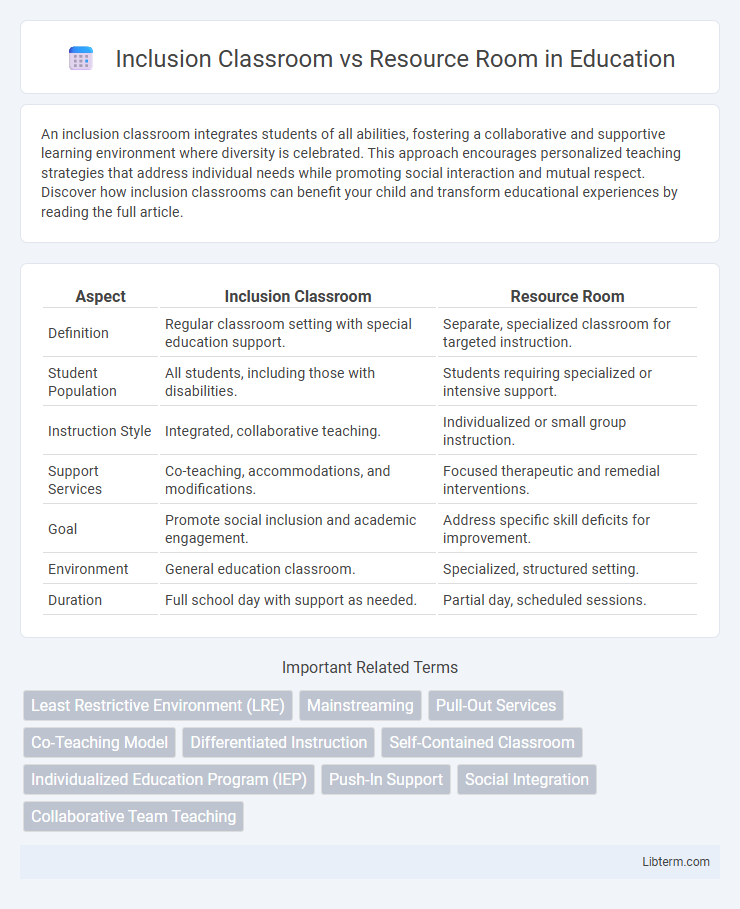
| Aspect | Inclusion Classroom | Resource Room |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regular classroom setting with special education support. | Separate, specialized classroom for targeted instruction. |
| Student Population | All students, including those with disabilities. | Students requiring specialized or intensive support. |
| Instruction Style | Integrated, collaborative teaching. | Individualized or small group instruction. |
| Support Services | Co-teaching, accommodations, and modifications. | Focused therapeutic and remedial interventions. |
| Goal | Promote social inclusion and academic engagement. | Address specific skill deficits for improvement. |
| Environment | General education classroom. | Specialized, structured setting. |
| Duration | Full school day with support as needed. | Partial day, scheduled sessions. |
Defining Inclusion Classrooms and Resource Rooms
Inclusion classrooms are designed to integrate students with disabilities into general education settings, providing support services within the same environment as their peers to promote social interaction and academic participation. Resource rooms offer specialized, small-group instruction for students with disabilities outside the general classroom, focusing on individualized skill development and targeted interventions. Both educational settings aim to address diverse learning needs but differ in their approach and physical environment.
Key Differences Between Inclusion and Resource Room Models
Inclusion classrooms integrate students with disabilities directly into general education settings, promoting social interaction and access to the core curriculum alongside peers. Resource rooms provide specialized, small-group instruction outside the mainstream classroom, targeting individualized skill gaps with focused support. Key differences include the setting, instructional approach, and level of integration, where inclusion emphasizes full participation and resource rooms prioritize tailored remediation.
Benefits of Inclusion Classrooms for Students with Disabilities
Inclusion classrooms promote social interaction and peer learning by integrating students with disabilities into general education settings, fostering acceptance and reducing stigma. These classrooms provide access to the same curriculum as their non-disabled peers, enhancing academic growth through differentiated instruction tailored to individual needs. Improved self-esteem and communication skills are notable benefits as students engage in collaborative activities, preparing them for real-world environments and promoting independence.
Advantages of Resource Room Support
Resource room support offers targeted, individualized instruction tailored to students with specific learning needs, enhancing their academic progress through specialized teaching methods and materials. This setting provides a lower student-to-teacher ratio, which allows for more focused attention and immediate feedback, promoting skill mastery and confidence. Support in resource rooms also facilitates the development of personalized learning plans and accommodations, ensuring that students receive appropriate intervention aligned with their unique educational goals.
Challenges in Implementing Inclusion Classrooms
Inclusion classrooms present challenges such as accommodating diverse learning needs without sufficient specialized support or resources, leading to potential academic and social difficulties for students with disabilities. Teachers often face increased workloads and require specialized training to effectively differentiate instruction while managing a heterogeneous classroom environment. Limited access to individualized interventions and collaboration with resource room staff can hinder the full implementation of inclusive education models.
Common Issues with Resource Room Programs
Resource room programs often face challenges such as limited individualized support due to high student-to-teacher ratios, which can hinder the effectiveness of tailored instruction. Scheduling conflicts and insufficient collaboration between resource room staff and general education teachers contribute to inconsistencies in implementing individualized education plans (IEPs). Furthermore, resource rooms may lack adequate materials and specialized resources, impacting the quality of interventions for students with disabilities.
Academic Outcomes: Inclusion vs. Resource Room
Inclusion classrooms foster improved academic outcomes by integrating students with diverse learning needs directly into general education settings, promoting peer interaction and access to the core curriculum. Resource rooms offer targeted, individualized instruction for students who require specialized support, often resulting in gains in specific skill areas but less exposure to the broader classroom environment. Studies indicate that inclusion environments generally support higher overall academic achievement and social development when supplemented with appropriate accommodations and support services.
Social-Emotional Impact on Students
Inclusion classrooms foster social-emotional growth by promoting peer interaction, collaboration, and a sense of belonging among diverse learners. Resource rooms provide targeted support, helping students build confidence and coping skills in a smaller, less distracting environment. Both settings contribute uniquely to emotional resilience and social development, depending on individual student needs.
Teachers’ Roles in Each Educational Setting
Teachers in inclusion classrooms facilitate diverse learning by adapting lessons and providing support within the general education environment, promoting collaboration among students with varied abilities. In resource rooms, educators deliver specialized, individualized instruction targeting students' specific learning needs, often employing tailored interventions and frequent progress monitoring. Both roles require expertise in differentiated instruction and behavior management to optimize student outcomes in their respective settings.
Choosing the Best Approach for Individual Student Needs
Selecting between an inclusion classroom and a resource room depends on the student's unique learning profile and support requirements. Inclusion classrooms offer diverse peer interactions and foster social skills, while resource rooms provide targeted, specialized instruction tailored to specific challenges. Evaluating academic goals, behavioral needs, and the level of individualized support ensures the most effective educational environment for each student.
Inclusion Classroom Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com