Pluridisciplinary approaches integrate multiple academic disciplines to solve complex problems and generate innovative solutions. By combining diverse perspectives, researchers can deepen understanding and create more holistic strategies. Explore the rest of the article to discover how pluridisciplinarity can enhance Your projects and research outcomes.
Table of Comparison
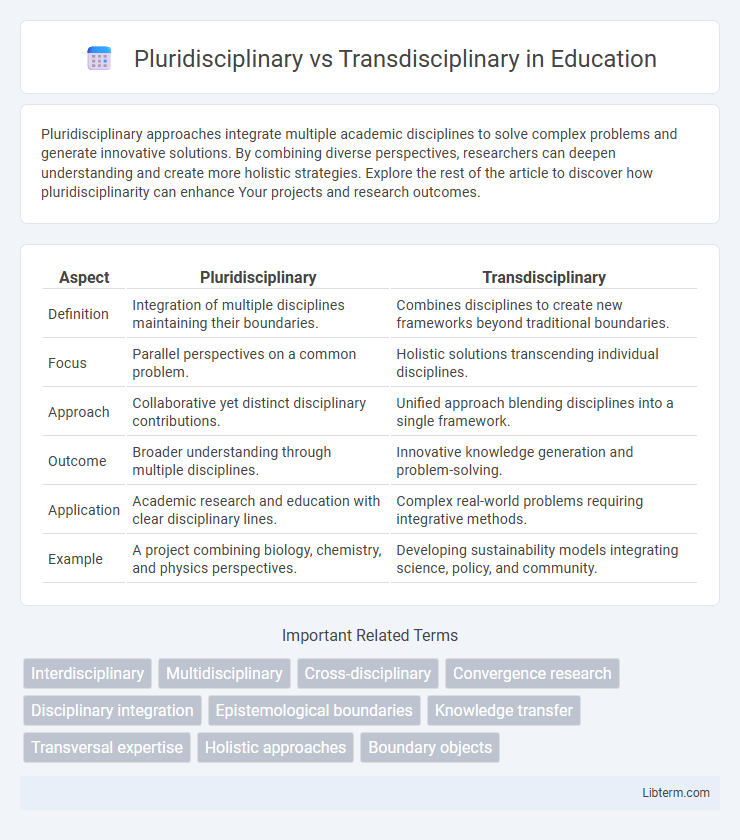
| Aspect | Pluridisciplinary | Transdisciplinary |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Integration of multiple disciplines maintaining their boundaries. | Combines disciplines to create new frameworks beyond traditional boundaries. |
| Focus | Parallel perspectives on a common problem. | Holistic solutions transcending individual disciplines. |
| Approach | Collaborative yet distinct disciplinary contributions. | Unified approach blending disciplines into a single framework. |
| Outcome | Broader understanding through multiple disciplines. | Innovative knowledge generation and problem-solving. |
| Application | Academic research and education with clear disciplinary lines. | Complex real-world problems requiring integrative methods. |
| Example | A project combining biology, chemistry, and physics perspectives. | Developing sustainability models integrating science, policy, and community. |
Introduction to Pluridisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Approaches
Pluridisciplinary approaches integrate multiple academic disciplines, allowing experts from distinct fields to work side by side while maintaining their disciplinary boundaries, fostering comprehensive perspectives without fully merging methodologies. Transdisciplinary approaches transcend traditional disciplinary limits by creating new frameworks and knowledge systems that synthesize concepts and methods from various fields to address complex real-world problems holistically. Both approaches enhance problem-solving capacity, but transdisciplinarity emphasizes integration and co-creation of knowledge beyond mere collaboration.
Defining Pluridisciplinarity
Pluridisciplinary approaches integrate methods and perspectives from multiple disciplines while maintaining their distinct boundaries, allowing experts to collaborate without merging their fields entirely. This contrasts with transdisciplinary research, which transcends traditional disciplinary limits to create new frameworks and knowledge. Pluridisciplinarity enables comprehensive analysis by combining diverse expertise without fully synthesizing the disciplines involved.
Defining Transdisciplinarity
Transdisciplinarity integrates knowledge and methods beyond traditional disciplinary boundaries to address complex real-world problems holistically. Unlike pluridisciplinary approaches that juxtapose disciplines without integration, transdisciplinarity seeks to create a unified framework that transcends individual fields. This approach emphasizes collaboration among academic disciplines, non-academic participants, and stakeholders to generate innovative solutions and transformative insights.
Key Differences Between Pluridisciplinarity and Transdisciplinarity
Pluridisciplinarity involves multiple disciplines working side by side to address a common issue while maintaining their disciplinary boundaries, whereas transdisciplinarity transcends these boundaries to integrate knowledge from various fields into a unified framework. Pluridisciplinary research often results in parallel insights, whereas transdisciplinary approaches foster the co-creation of new methodologies and theories that synthesize diverse perspectives. The key difference lies in the degree of integration and collaboration, with transdisciplinarity emphasizing holistic problem-solving beyond traditional academic silos.
Historical Evolution of Pluridisciplinary and Transdisciplinary Practices
Pluridisciplinary practices trace their origins to early 20th-century academic collaborations where multiple disciplines worked side by side without integrating methods, primarily seen in projects combining physics, biology, and engineering. Transdisciplinary approaches emerged later in the 1970s, emphasizing the transcendence of disciplinary boundaries to create holistic frameworks addressing complex societal issues, notably in environmental science and sustainability. This evolution reflects a shift from parallel disciplinary contributions to integrated knowledge production involving stakeholders beyond academia.
Benefits of Pluridisciplinary Collaboration
Pluridisciplinary collaboration integrates expertise from multiple disciplines, enhancing problem-solving by combining diverse perspectives without merging methodologies, which preserves disciplinary depth. This approach fosters innovation and comprehensive analysis by enabling specialists to contribute their unique insights while maintaining clarity in roles and methodologies. The structured interaction in pluridisciplinary teams accelerates decision-making and improves the quality of outcomes across complex projects.
Advantages of Transdisciplinary Integration
Transdisciplinary integration transcends traditional academic boundaries by synthesizing knowledge from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems effectively. This approach fosters innovative solutions through collaborative frameworks that incorporate diverse perspectives, leading to holistic understanding and practical applications beyond theoretical insights. Enhanced stakeholder engagement and real-world applicability mark significant advantages of transdisciplinary methods over pluridisciplinary collaboration.
Challenges in Implementing Both Approaches
Implementing pluridisciplinary approaches often faces challenges related to coordinating experts from distinct disciplines who may have different terminologies, methodologies, and objectives, leading to communication barriers and fragmented outcomes. Transdisciplinary approaches require even deeper integration, demanding the collaboration of academic researchers, practitioners, and stakeholders outside academia, which complicates consensus-building and the synthesis of diverse knowledge systems. Both approaches struggle with institutional constraints, including disciplinary silos in funding, evaluation metrics, and organizational structures that impede seamless cooperation and knowledge co-creation.
Real-World Applications: Case Studies
Pluridisciplinary approaches combine insights from multiple disciplines to address complex real-world problems, as seen in environmental impact assessments involving ecologists, economists, and sociologists. Transdisciplinary methods transcend disciplinary boundaries by integrating academic and non-academic knowledge, exemplified by community-driven urban planning projects that incorporate local residents' experiential data alongside scientific expertise. Case studies in sustainable agriculture demonstrate how pluridisciplinary frameworks analyze soil health, crop yields, and economic factors, while transdisciplinary initiatives engage farmers, scientists, and policymakers to co-create adaptive farming practices.
Choosing the Right Approach for Your Project
Pluridisciplinary approaches integrate multiple disciplines working side by side, maintaining distinct methods and perspectives, ideal for projects requiring specialized expertise without fully merging fields. Transdisciplinary methods transcend traditional boundaries by creating unified frameworks that solve complex problems through holistic collaboration and knowledge co-creation. Selecting the right approach depends on project goals: pluridisciplinary suits clearly defined tasks needing disciplinary depth, while transdisciplinary excels in addressing interconnected, real-world issues demanding innovative, cross-boundary solutions.
Pluridisciplinary Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com