Cluster grouping enhances data analysis by organizing similar items into distinct groups, improving pattern recognition and decision-making processes. Efficient cluster grouping algorithms can handle large datasets, enabling more accurate insights and streamlined workflows. Explore the rest of the article to discover how cluster grouping can optimize your data strategy.
Table of Comparison
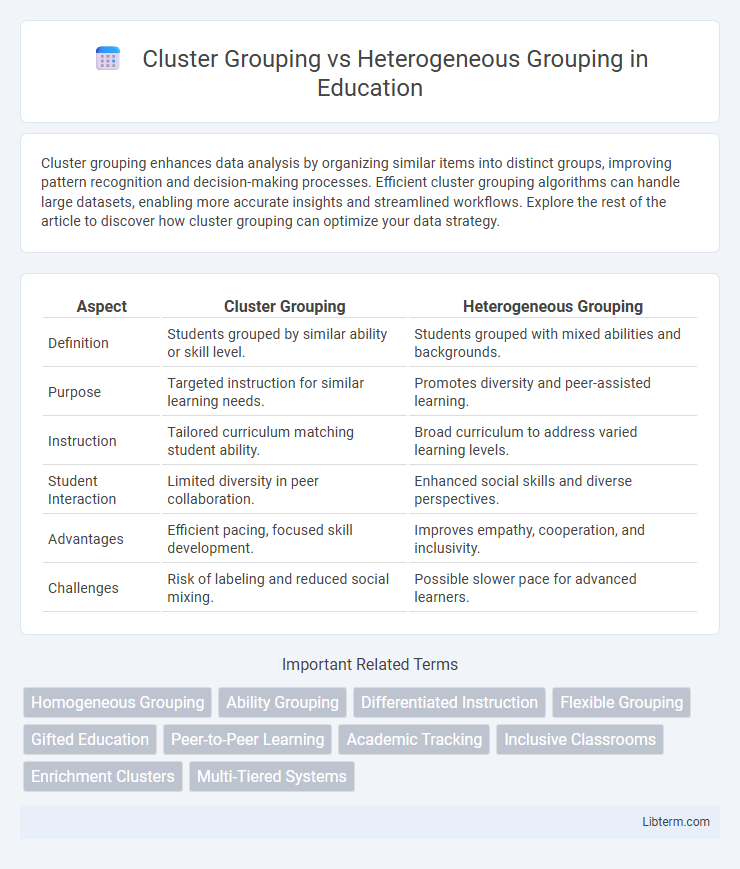
| Aspect | Cluster Grouping | Heterogeneous Grouping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Students grouped by similar ability or skill level. | Students grouped with mixed abilities and backgrounds. |
| Purpose | Targeted instruction for similar learning needs. | Promotes diversity and peer-assisted learning. |
| Instruction | Tailored curriculum matching student ability. | Broad curriculum to address varied learning levels. |
| Student Interaction | Limited diversity in peer collaboration. | Enhanced social skills and diverse perspectives. |
| Advantages | Efficient pacing, focused skill development. | Improves empathy, cooperation, and inclusivity. |
| Challenges | Risk of labeling and reduced social mixing. | Possible slower pace for advanced learners. |
Understanding Cluster Grouping
Cluster grouping organizes students with similar abilities or interests into the same group, enhancing targeted instruction and fostering a focused learning environment. This method supports differentiated teaching by allowing educators to tailor lessons to specific skill levels, improving academic outcomes for both advanced learners and those needing remedial support. Understanding cluster grouping reveals its effectiveness in promoting peer collaboration within homogenous groups, which can boost confidence and engagement.
What is Heterogeneous Grouping?
Heterogeneous grouping is an instructional strategy that organizes students into diverse groups based on varying abilities, backgrounds, and skill levels to promote collaborative learning and peer support. This approach enhances critical thinking and social interaction by encouraging students to share different perspectives and expertise. Studies show heterogeneous groups improve problem-solving skills and foster inclusive classroom environments compared to cluster grouping, which places students with similar abilities together.
Key Differences Between Cluster and Heterogeneous Grouping
Cluster grouping organizes students based on similar abilities or skills, allowing targeted instruction that meets specific learning needs. Heterogeneous grouping mixes students of diverse abilities and backgrounds to promote peer learning, collaboration, and social development. The key difference lies in the purpose: cluster grouping aims for specialized, ability-focused teaching, while heterogeneous grouping fosters inclusive, varied interaction and support.
Benefits of Cluster Grouping for Gifted Learners
Cluster grouping allows gifted learners to engage deeply with challenging content tailored to their advanced abilities, fostering intellectual growth and motivation. This method enables peer collaboration among students with similar academic strengths, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills. Concentrating gifted students in one group also supports targeted instruction by teachers, improving educational outcomes and social-emotional development.
Advantages of Heterogeneous Grouping in Classrooms
Heterogeneous grouping in classrooms promotes diverse perspectives, enhancing critical thinking and problem-solving skills among students of varying abilities and backgrounds. This approach fosters inclusive learning environments, encouraging collaboration and peer support that boost social development and empathy. Research shows heterogeneous groups increase overall academic engagement and help close achievement gaps by leveraging the strengths of all students.
Academic Outcomes: Cluster vs Heterogeneous Grouping
Cluster grouping, which groups students by similar academic ability, often enhances academic outcomes by allowing targeted instruction that matches students' learning pace and style. Research indicates that cluster groups boost achievement and engagement for high-ability learners through enriched curriculum and peer collaboration. In contrast, heterogeneous grouping promotes diverse peer interactions but can dilute instructional focus, sometimes leading to uneven academic progress among students with varied abilities.
Social-Emotional Impact on Students
Cluster grouping places students with similar abilities together, fostering a sense of belonging and reducing social anxiety by creating a supportive peer environment; this often enhances self-esteem and motivation. Heterogeneous grouping promotes diverse interactions and empathy by mixing varying skill levels, which can improve social skills but may also challenge students' confidence if disparities are too pronounced. Research indicates that the social-emotional impact depends largely on group dynamics and the teacher's role in facilitating inclusive interactions.
Challenges and Limitations of Both Approaches
Cluster grouping often faces challenges such as reinforcing existing skill gaps and limiting peer diversity, which can hinder holistic learning and social development. Heterogeneous grouping presents limitations like potential frustration for lower-achieving students due to mismatched skill levels and the difficulty for teachers to address varied learning needs effectively. Both approaches require careful management to balance academic growth and student engagement while mitigating the risk of stereotype reinforcement or uneven participation.
Choosing the Right Grouping Strategy
Choosing the right grouping strategy depends on instructional goals and student needs; cluster grouping groups students with similar abilities to tailor instruction and accelerate learning for advanced learners, while heterogeneous grouping mixes diverse skill levels to promote collaboration and peer learning. Cluster groups enhance targeted support and enrichment for specific skill sets, whereas heterogeneous groups encourage diverse perspectives and social development. Balancing these approaches requires analyzing student profiles, curriculum complexity, and desired outcomes to optimize engagement and achievement.
Best Practices for Effective Classroom Grouping
Cluster grouping enhances targeted instruction by grouping students with similar abilities, enabling tailored lesson plans and fostering peer support within homogeneous skill levels. Heterogeneous grouping promotes diverse perspectives and collaborative problem-solving, mixing students of varying abilities to encourage peer learning and social development. Best practices for effective classroom grouping involve aligning group type with learning objectives, regularly assessing group effectiveness, and balancing skill levels to maintain engagement and challenge for all students.
Cluster Grouping Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com