Diagnostic assessment identifies learners' existing knowledge and skills to tailor instruction effectively. It helps uncover gaps and strengths, ensuring personalized learning strategies for optimal progress. Explore the rest of the article to understand how diagnostic assessments can improve your educational outcomes.
Table of Comparison
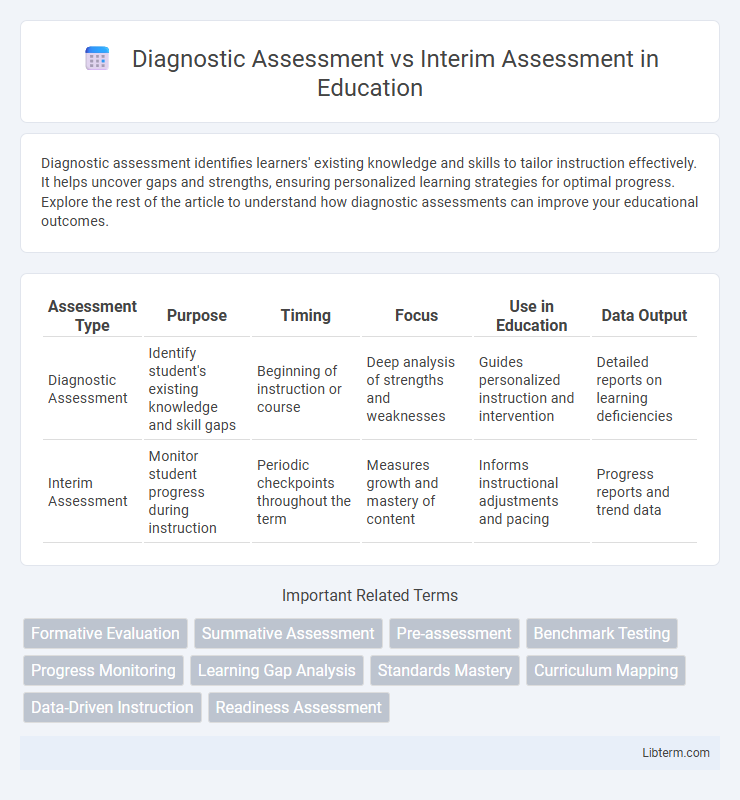
| Assessment Type | Purpose | Timing | Focus | Use in Education | Data Output |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diagnostic Assessment | Identify student's existing knowledge and skill gaps | Beginning of instruction or course | Deep analysis of strengths and weaknesses | Guides personalized instruction and intervention | Detailed reports on learning deficiencies |
| Interim Assessment | Monitor student progress during instruction | Periodic checkpoints throughout the term | Measures growth and mastery of content | Informs instructional adjustments and pacing | Progress reports and trend data |
Understanding Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' existing knowledge, skills, and learning gaps before instruction begins, enabling targeted teaching strategies. It often involves detailed tests or evaluations designed to uncover specific learning difficulties or misconceptions. Unlike interim assessments that measure progress during instruction, diagnostic assessments provide a foundational understanding of student needs to guide curriculum planning.
Exploring Interim Assessment
Interim assessments provide educators with valuable, data-driven insights on student progress during specific intervals of the academic year, enabling timely instructional adjustments to enhance learning outcomes. Unlike diagnostic assessments, which identify students' initial strengths and weaknesses, interim assessments track growth and proficiency against standards over time, supporting targeted interventions before high-stakes testing. The continuous feedback loop generated by interim assessments improves curriculum alignment and resource allocation, fostering a more responsive and effective educational environment.
Key Purposes: Diagnostic vs Interim Assessment
Diagnostic assessments identify students' existing knowledge gaps and misconceptions to guide targeted instruction and personalized learning plans. Interim assessments measure student progress at regular intervals within the academic year to inform instructional adjustments and predict end-of-year performance. Both types of assessments enhance data-driven decision-making but differ in timing and specific instructional goals.
Timing and Implementation Differences
Diagnostic assessments occur at the beginning of an instructional period to identify students' existing knowledge, skills, and misunderstandings, guiding tailored teaching strategies. Interim assessments are administered periodically throughout the instructional cycle to monitor progress and adjust instruction based on student performance data. Implementing diagnostic assessments requires initial time investment for comprehensive analysis, while interim assessments are designed for frequent, timely feedback to inform ongoing instructional decisions.
Types of Data Collected
Diagnostic assessments collect comprehensive data on students' prior knowledge, skills, and learning gaps to guide individualized instruction, focusing on qualitative and formative data such as student misconceptions and learning needs. Interim assessments gather quantitative performance data at regular intervals to monitor progress toward academic standards, emphasizing standardized test scores, benchmarks, and proficiency levels. Both types of assessments provide critical data, but diagnostic data is detailed and diagnostic by nature, while interim data tracks overall progress and informs instructional adjustments.
Impact on Instructional Planning
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' prior knowledge and learning gaps, enabling precise customization of instructional plans to address specific needs. Interim assessment tracks student progress throughout the school year, informing timely adjustments to teaching strategies and pacing. Together, these assessments promote data-driven instructional planning that enhances student outcomes and supports targeted interventions.
Benefits of Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessments provide detailed insights into students' strengths and weaknesses before instruction begins, enabling educators to tailor teaching strategies to individual learning needs. These assessments identify specific skill gaps and misconceptions, allowing for targeted interventions that improve overall learning outcomes. By pinpointing precise areas for improvement, diagnostic assessments support personalized learning plans and promote better academic progress compared to interim assessments.
Benefits of Interim Assessment
Interim assessments offer actionable insights throughout the academic year, enabling timely interventions that improve student learning outcomes. These assessments provide educators with ongoing data to adjust instructional strategies, ensuring alignment with curriculum standards and student needs. By facilitating early identification of learning gaps, interim assessments support targeted support that enhances overall academic performance.
Limitations and Challenges
Diagnostic assessments often face challenges such as limited scope in capturing the full range of student abilities and potential biases that can affect accuracy. Interim assessments may encounter limitations related to timing and frequency, potentially causing disruptions in instruction and providing a narrow snapshot of student progress. Both types of assessments require careful interpretation to avoid misinforming instructional decisions due to contextual factors and varying student engagement levels.
Choosing the Right Assessment Approach
Diagnostic assessment identifies students' existing knowledge gaps and learning needs before instruction begins, enabling targeted interventions and personalized learning plans. Interim assessment measures student progress at intervals throughout the instructional period to inform instruction adjustments and monitor growth toward standards. Selecting the right assessment approach depends on the instructional goals: use diagnostic assessments for initial learning diagnosis and interim assessments for tracking ongoing progress and adapting teaching strategies.
Diagnostic Assessment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com