The equity gap refers to the disparity in investment and funding available to underrepresented entrepreneurs and startups, often leaving promising ventures undercapitalized. This financial divide can hinder innovation and economic growth by limiting access to resources crucial for business success. Discover how addressing the equity gap can transform opportunities and empower your journey in the article below.
Table of Comparison
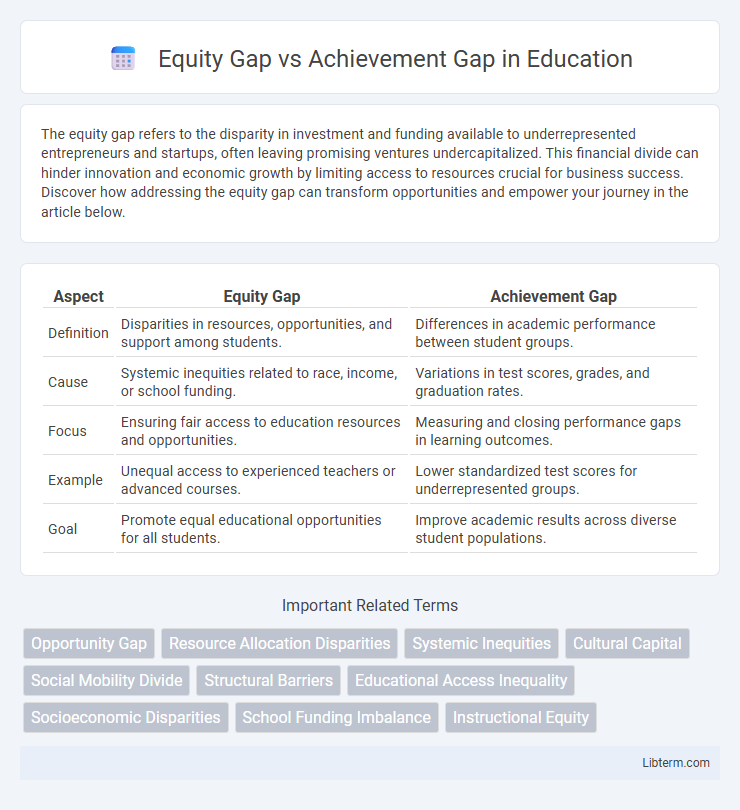
| Aspect | Equity Gap | Achievement Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disparities in resources, opportunities, and support among students. | Differences in academic performance between student groups. |
| Cause | Systemic inequities related to race, income, or school funding. | Variations in test scores, grades, and graduation rates. |
| Focus | Ensuring fair access to education resources and opportunities. | Measuring and closing performance gaps in learning outcomes. |
| Example | Unequal access to experienced teachers or advanced courses. | Lower standardized test scores for underrepresented groups. |
| Goal | Promote equal educational opportunities for all students. | Improve academic results across diverse student populations. |
Understanding the Equity Gap
The equity gap refers to systemic disparities in access to resources and opportunities that disproportionately affect marginalized groups, contrasting with the achievement gap, which measures the differences in academic performance outcomes among students. Understanding the equity gap involves examining factors such as unequal funding, biased curricula, and lack of support services that hinder equitable education. Addressing the equity gap requires targeted interventions that promote inclusion, resource allocation, and culturally responsive teaching to create a level playing field for all learners.
Defining the Achievement Gap
The achievement gap refers to the persistent disparity in academic performance between groups of students, often categorized by race, socioeconomic status, or ethnicity. This gap is measured through standardized test scores, graduation rates, and college enrollment statistics, highlighting inequities in educational outcomes. Addressing the achievement gap requires understanding systemic barriers that affect student learning and success.
Key Differences Between Equity and Achievement Gaps
The Equity Gap refers to disparities in access to resources, opportunities, and support systems essential for learning, often influenced by socioeconomic status, race, or geographic location. The Achievement Gap measures differences in academic performance, such as test scores and graduation rates, between student groups. Understanding that the Equity Gap addresses systemic barriers while the Achievement Gap reflects outcomes is crucial for targeted educational interventions.
Historical Origins of Both Gaps
The equity gap and achievement gap both stem from historical systemic inequalities rooted in segregation, discriminatory policies, and unequal access to resources. The achievement gap reflects disparities in academic performance primarily caused by these structural barriers, while the equity gap encompasses broader socio-economic and institutional factors that limit opportunities for marginalized groups. Understanding their historical origins in practices such as redlining, unequal school funding, and exclusionary education policies is crucial for addressing persistent educational disparities.
Causes of the Equity Gap in Education
The equity gap in education arises from systemic disparities such as unequal access to quality resources, socio-economic status, and institutional biases that limit opportunities for marginalized students. Unlike the achievement gap, which measures differences in academic performance, the equity gap focuses on the root causes, including resource allocation, funding inequalities, and disparities in school infrastructure. Addressing these causes requires targeted policies that promote fair access to quality education, culturally responsive teaching, and support systems for underserved communities.
Factors Driving the Achievement Gap
The achievement gap is driven by factors such as socioeconomic status, access to quality education, and family support, which influence student performance and learning opportunities. Equity gaps highlight disparities in resources and systemic barriers that disproportionately affect marginalized groups, exacerbating educational inequities. Addressing these factors requires targeted interventions to ensure equitable access to educational tools, experienced teachers, and supportive learning environments.
Impact on Student Outcomes
The equity gap significantly affects student outcomes by limiting access to resources, quality instruction, and learning opportunities for marginalized groups, resulting in disparities in academic achievement. The achievement gap reflects measurable differences in test scores, graduation rates, and college readiness between student groups, highlighting the consequences of unequal educational experiences. Closing the equity gap is essential to improving overall student performance and ensuring all students reach their full potential.
Strategies to Close the Equity Gap
Targeted resource allocation and culturally responsive teaching practices effectively close the equity gap by addressing systemic barriers that hinder marginalized students' academic success. Implementing inclusive curricula and fostering community partnerships support equitable access to high-quality education, promoting long-term achievement improvements. Data-driven interventions and professional development empower educators to meet diverse learners' needs, narrowing disparities between student groups.
Approaches to Addressing the Achievement Gap
Targeted intervention programs that provide personalized instruction based on students' unique learning needs help close the achievement gap, especially in underserved communities. Expanding access to high-quality early childhood education and tutoring services supports consistent academic progress. Data-driven strategies incorporating ongoing assessment and culturally responsive teaching further enhance student outcomes and reduce disparities in achievement.
Why Clarifying These Terms Matters for Educators
Clarifying the terms Equity Gap and Achievement Gap enables educators to accurately identify and address the root causes of student disparities, focusing on systemic inequalities rather than solely academic performance. Understanding the Equity Gap highlights barriers such as access to resources, socio-economic factors, and institutional bias that contribute to unequal opportunities. Differentiating these concepts guides targeted interventions, policy decisions, and inclusive teaching strategies to promote equitable educational outcomes for all students.
Equity Gap Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com