Experiential learning immerses you directly in hands-on activities that enhance understanding through real-world experiences. This approach bridges theory and practice, promoting deeper retention and critical thinking skills. Discover how experiential learning can transform your educational journey by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
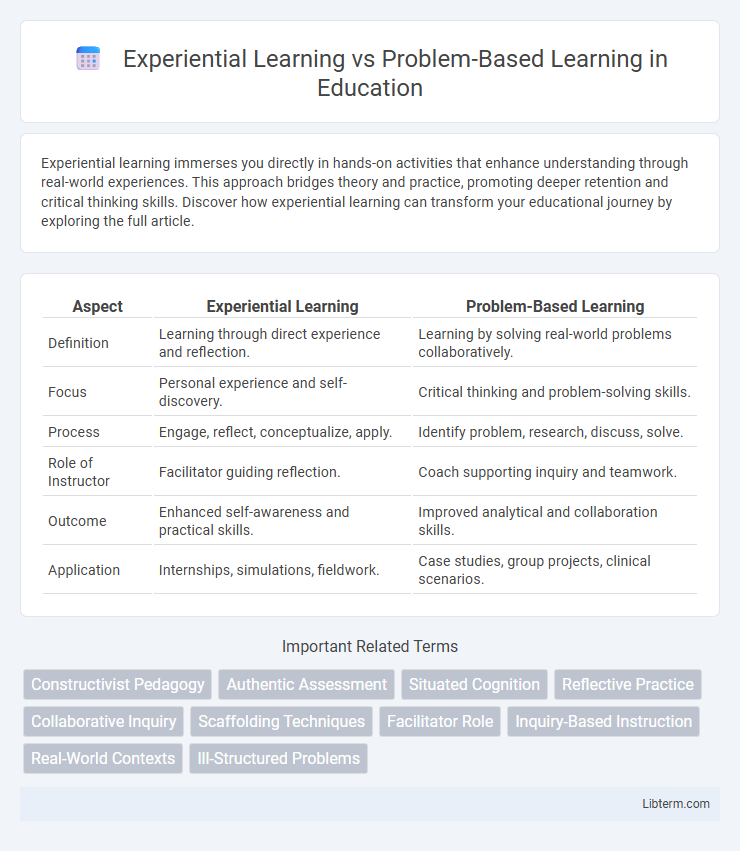
| Aspect | Experiential Learning | Problem-Based Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Learning through direct experience and reflection. | Learning by solving real-world problems collaboratively. |
| Focus | Personal experience and self-discovery. | Critical thinking and problem-solving skills. |
| Process | Engage, reflect, conceptualize, apply. | Identify problem, research, discuss, solve. |
| Role of Instructor | Facilitator guiding reflection. | Coach supporting inquiry and teamwork. |
| Outcome | Enhanced self-awareness and practical skills. | Improved analytical and collaboration skills. |
| Application | Internships, simulations, fieldwork. | Case studies, group projects, clinical scenarios. |
Introduction to Experiential and Problem-Based Learning
Experiential Learning emphasizes learning through direct experience and reflection, often involving hands-on activities that promote deep understanding and skill development. Problem-Based Learning centers around engaging learners in solving complex, real-world problems, fostering critical thinking, collaboration, and the application of knowledge. Both approaches prioritize active learner involvement, yet Experiential Learning is broader, encompassing various experiential activities while Problem-Based Learning specifically focuses on problem-solving scenarios.
Defining Experiential Learning
Experiential learning is an educational approach where learners gain knowledge and skills through direct experience and reflection, emphasizing active participation in real-world activities. This method contrasts with problem-based learning by focusing on immersive experiences rather than solely solving predefined problems. Key elements include concrete experiences, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation, which together enhance deep understanding and practical application.
Understanding Problem-Based Learning
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) centers on students actively solving real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and self-directed learning. This instructional method emphasizes collaborative teamwork and practical application of interdisciplinary knowledge to develop solutions. PBL enhances problem-solving skills by engaging learners in authentic, context-rich scenarios that promote deeper understanding and retention.
Key Differences Between Experiential and Problem-Based Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes direct experience and reflection to develop skills and knowledge through activities such as internships, simulations, and hands-on projects. Problem-based learning centers on collaborative inquiry and problem-solving, where learners tackle complex, real-world problems without predefined solutions, promoting critical thinking and self-directed learning. The key difference lies in experiential learning's focus on active participation and reflection, whereas problem-based learning focuses on exploring and resolving specific problems within a structured group setting.
Core Principles of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning centers on the core principle that knowledge is constructed through direct experience and active reflection, emphasizing a cyclical process involving concrete experience, reflective observation, abstract conceptualization, and active experimentation. This approach fosters deep engagement by allowing learners to immerse themselves in real-world scenarios and critically assess their actions to develop practical skills and understanding. Unlike problem-based learning, which primarily focuses on solving specific issues, experiential learning prioritizes holistic personal growth through continuous interaction and adaptation to varied experiences.
Core Principles of Problem-Based Learning
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) centers on student-driven inquiry where learners collaboratively solve complex, real-world problems, fostering critical thinking and knowledge retention. Core principles of PBL include a learner-centered approach, the use of authentic problems as the starting point for learning, self-directed learning, and development of problem-solving skills through active collaboration. Unlike Experiential Learning, which emphasizes hands-on experience and reflection, PBL prioritizes structured problem identification and iterative solution development as key to mastering content.
Benefits of Experiential Learning
Experiential learning enhances critical thinking and retention by engaging learners in hands-on activities and real-world scenarios, fostering deeper understanding and practical skill acquisition. This method improves learner motivation and adaptability by allowing direct interaction with materials and environments, facilitating immediate feedback and reflection. Experiential learning cultivates problem-solving abilities and teamwork through active participation, better preparing students for complex challenges in professional settings.
Advantages of Problem-Based Learning
Problem-Based Learning (PBL) enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by engaging students in real-world challenges that promote active knowledge construction. It fosters collaboration and communication among learners, preparing them for complex professional environments. PBL's focus on self-directed learning increases retention and adaptability, making it highly effective in disciplines such as medicine, engineering, and business.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Experiential learning often faces challenges such as resource intensity, requiring significant time, materials, and guidance to ensure meaningful engagement, which can limit scalability in large classrooms. Problem-based learning may struggle with student preparedness, as learners sometimes lack foundational knowledge or self-directed learning skills needed to effectively tackle complex problems. Both approaches can be hindered by assessment difficulties, since evaluating practical and cognitive skills rather than traditional exams demands more nuanced, often subjective, metrics.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Learning
Experiential learning emphasizes hands-on experiences where learners actively engage with real-world tasks, fostering deep understanding through direct interaction. Problem-based learning centers on tackling complex, open-ended problems that develop critical thinking and collaborative problem-solving skills. Selecting the right approach depends on learning objectives; experiential learning suits skill acquisition and practical application, while problem-based learning excels in promoting analytical reasoning and teamwork.
Experiential Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com