Diagnostic feedback provides detailed information about your performance to help identify strengths and areas for improvement, enhancing your learning process. This targeted guidance allows you to understand specific mistakes and correct them effectively. Explore the rest of the article to discover how diagnostic feedback can transform your educational journey.
Table of Comparison
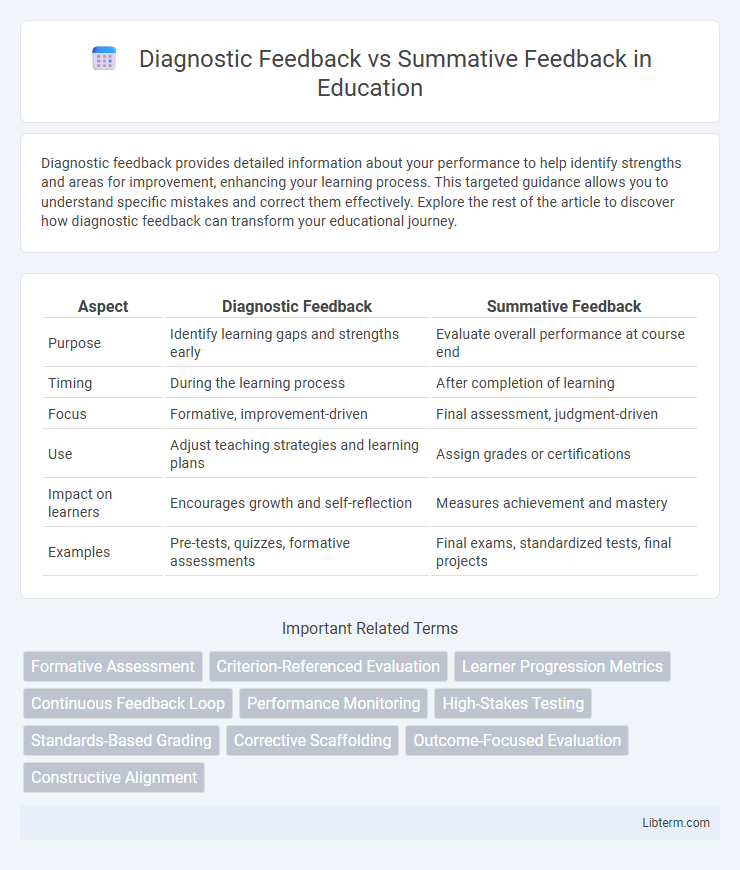
| Aspect | Diagnostic Feedback | Summative Feedback |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Identify learning gaps and strengths early | Evaluate overall performance at course end |
| Timing | During the learning process | After completion of learning |
| Focus | Formative, improvement-driven | Final assessment, judgment-driven |
| Use | Adjust teaching strategies and learning plans | Assign grades or certifications |
| Impact on learners | Encourages growth and self-reflection | Measures achievement and mastery |
| Examples | Pre-tests, quizzes, formative assessments | Final exams, standardized tests, final projects |
Introduction to Diagnostic and Summative Feedback
Diagnostic feedback identifies learners' strengths and weaknesses early in the learning process to tailor instruction effectively. Summative feedback evaluates overall performance after instruction to measure achievement against learning objectives. Both feedback types support educational outcomes by informing teaching strategies and assessing competency completion.
Defining Diagnostic Feedback
Diagnostic feedback is a formative assessment tool used to identify students' current knowledge, skills, and misconceptions before instruction begins. It provides detailed insights that help educators tailor teaching strategies to address individual learning gaps effectively. This type of feedback emphasizes proactive intervention, promoting a deeper understanding and continuous improvement throughout the learning process.
Defining Summative Feedback
Summative feedback provides a comprehensive evaluation of a student's performance at the end of an instructional period, typically used for grading or certification purposes. It summarizes learning achievements and helps educators make decisions about progression, course effectiveness, and curriculum adjustments. Unlike diagnostic feedback, summative feedback does not offer detailed guidance for improvement during the learning process but rather assesses overall competency against established standards.
Key Differences Between Diagnostic and Summative Feedback
Diagnostic feedback identifies students' current knowledge gaps and learning needs by providing detailed, formative insights early in the instructional process. Summative feedback evaluates overall student performance at the end of an instructional unit, focusing on final outcomes and grading. Key differences include the timing--diagnostic is ongoing and formative, whereas summative is conclusive and evaluative--and the purpose, with diagnostic aimed at guiding future learning and summative intended to assess achievement.
Purpose and Goals of Diagnostic Feedback
Diagnostic feedback aims to identify students' current knowledge gaps and misconceptions to inform tailored instruction and improve learning outcomes. Its primary goal is to provide targeted insights that guide both learners and educators in addressing specific challenges before moving forward in the curriculum. Unlike summative feedback, which evaluates overall performance after instruction, diagnostic feedback supports formative assessment by promoting deeper understanding and skill development.
Purpose and Goals of Summative Feedback
Summative feedback serves to evaluate overall student performance after instruction, providing a conclusive assessment of learning outcomes. Its primary goal is to measure mastery of content, often contributing to final grades or certification decisions. This type of feedback helps educators identify curriculum effectiveness and informs stakeholders about achievement levels.
Advantages of Diagnostic Feedback in Learning
Diagnostic feedback enhances learning by identifying specific student errors and misconceptions early, allowing targeted interventions that improve understanding and skills acquisition. It supports continuous learning by providing timely, personalized information that guides students in adjusting their strategies before final assessments. This form of feedback fosters metacognitive awareness, encouraging self-regulation and deeper engagement with the material.
Limitations of Summative Feedback
Summative feedback often lacks specificity, providing only a final assessment without detailed insights into the learning process, which limits its usefulness for improvement. It typically occurs at the end of a learning period, offering little opportunity for students to act on the feedback to enhance their understanding or skills. Its emphasis on grading can create stress and inhibit intrinsic motivation, reducing the overall effectiveness of the educational experience.
Best Practices for Implementing Feedback Strategies
Effective implementation of diagnostic feedback involves timely, specific, and actionable insights that guide learners in identifying strengths and areas for improvement, fostering a growth mindset. Best practices for summative feedback emphasize clarity, objectivity, and alignment with learning objectives to accurately measure student achievement and inform stakeholders about overall performance. Combining both feedback types through iterative assessment cycles enhances personalized learning and supports continuous academic development.
Choosing the Right Feedback Approach for Different Contexts
Diagnostic feedback targets specific learning gaps by providing detailed information on errors and misconceptions, making it ideal for formative assessments and ongoing skill development. Summative feedback offers overall evaluations often in the form of grades or scores, suited for assessing final mastery or performance at the end of a learning period. Selecting the appropriate feedback approach depends on context: diagnostic feedback enhances learning processes during instruction, while summative feedback is more effective for measuring outcomes and informing decisions such as certification or progression.
Diagnostic Feedback Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com