Auditory learning involves absorbing information primarily through listening, utilizing sounds, spoken words, and rhythms to enhance memory and comprehension. Your ability to engage with lectures, discussions, and audio materials can significantly improve your retention and understanding of complex subjects. Explore the full article to discover strategies tailored to maximize your auditory learning potential.
Table of Comparison
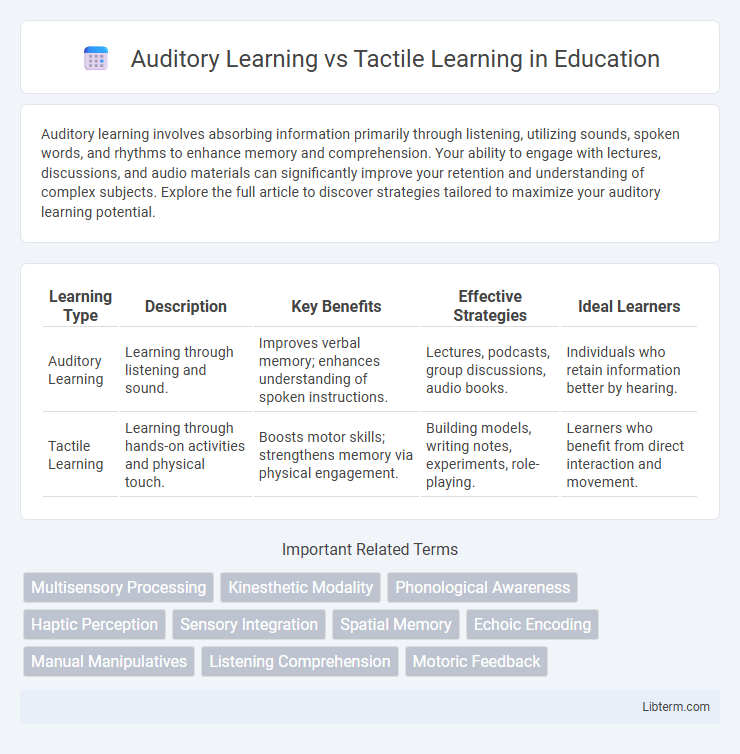
| Learning Type | Description | Key Benefits | Effective Strategies | Ideal Learners |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auditory Learning | Learning through listening and sound. | Improves verbal memory; enhances understanding of spoken instructions. | Lectures, podcasts, group discussions, audio books. | Individuals who retain information better by hearing. |
| Tactile Learning | Learning through hands-on activities and physical touch. | Boosts motor skills; strengthens memory via physical engagement. | Building models, writing notes, experiments, role-playing. | Learners who benefit from direct interaction and movement. |
Introduction to Learning Styles
Auditory learning involves processing information through listening and sound, often benefiting from lectures, discussions, and audio materials. Tactile learning emphasizes hands-on experiences, where learners engage physically with materials to enhance comprehension and retention. Understanding these distinct learning styles allows educators to create tailored instructional strategies that cater to individual preferences, promoting more effective knowledge acquisition.
Defining Auditory Learning
Auditory learning is a style where individuals absorb and retain information primarily through listening and sound-based stimuli, such as lectures, discussions, and audio recordings. This learning method emphasizes the importance of tone, rhythm, and verbal cues to enhance comprehension and memory retention. Auditory learners often excel in environments that utilize spoken instructions and auditory repetition for effective knowledge acquisition.
Defining Tactile Learning
Tactile learning involves acquiring knowledge through physical touch and hands-on activities, emphasizing the use of the sense of touch to understand and retain information. This learning style engages motor skills and spatial awareness, often benefiting kinesthetic learners who prefer manipulating objects to grasp concepts. Unlike auditory learning, which relies on listening and verbal instructions, tactile learning fosters deeper comprehension through direct sensory interaction and movement.
Key Differences Between Auditory and Tactile Learning
Auditory learning relies on hearing and listening to retain information, making it effective for those who comprehend through spoken words, sounds, and discussions. Tactile learning involves hands-on activities and physical touch, which helps learners understand concepts by manipulating objects and engaging in physical movement. Key differences include the sensory channel used--auditory learning utilizes auditory stimuli, while tactile learning depends on kinesthetic experiences.
Advantages of Auditory Learning
Auditory learning enhances memory retention by engaging the brain's ability to process and recall spoken information, making it ideal for lectures and discussions. This learning style supports improved language development, listening comprehension, and auditory processing skills, benefiting both academic and social interactions. Auditory learners can quickly adapt to learning environments where oral instructions and verbal explanations are predominant, promoting efficient knowledge acquisition.
Advantages of Tactile Learning
Tactile learning enhances memory retention by engaging the sense of touch, allowing learners to physically manipulate objects and better understand abstract concepts. This hands-on approach supports kinesthetic learners in developing fine motor skills and spatial awareness. Furthermore, tactile learning encourages active participation and increases motivation, making complex information more accessible and memorable.
Challenges Faced by Auditory Learners
Auditory learners often struggle in noisy or visually distracting environments, which impair their ability to focus on spoken instructions. They may find it difficult to retain information presented through written or hands-on activities, limiting their engagement in tactile or visual learning contexts. Challenges also include difficulty processing complex information without auditory cues or discussions, impacting comprehension and memory retention.
Challenges Faced by Tactile Learners
Tactile learners often face challenges such as difficulty processing information through auditory or visual means alone, which can lead to slower comprehension in traditional lecture-based environments. Limited access to hands-on materials and activities hinders their ability to fully engage and retain information, impacting academic performance. Moreover, tactile learners may struggle with fine motor skills or sensory processing issues, complicating their learning experience and requiring tailored instructional strategies.
Strategies to Support Each Learning Style
Auditory learning strategies include using verbal repetition, engaging in discussions, and incorporating mnemonic devices or audio recordings to reinforce information retention. Tactile learning techniques emphasize hands-on activities, such as building models, using manipulatives, and writing notes by hand to enhance kinesthetic engagement. Tailoring study methods to auditory learners with listening exercises and tactile learners with physical involvement improves comprehension and memory outcomes.
Choosing the Best Approach for Individual Needs
Auditory learning emphasizes processing information through listening, making techniques like lectures and discussions effective for individuals with strong verbal memory. Tactile learning involves hands-on activities and physical manipulation to enhance understanding, benefiting those who retain information better through touch and movement. Selecting the best approach depends on assessing individual preferences, cognitive strengths, and the specific learning context to optimize retention and engagement.
Auditory Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com