Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits while still completing their secondary education, significantly accelerating their academic progress. This program offers cost savings, exposure to college-level coursework, and a smoother transition to higher education institutions. Explore the full article to learn how dual enrollment can enhance your educational journey and open new opportunities.
Table of Comparison
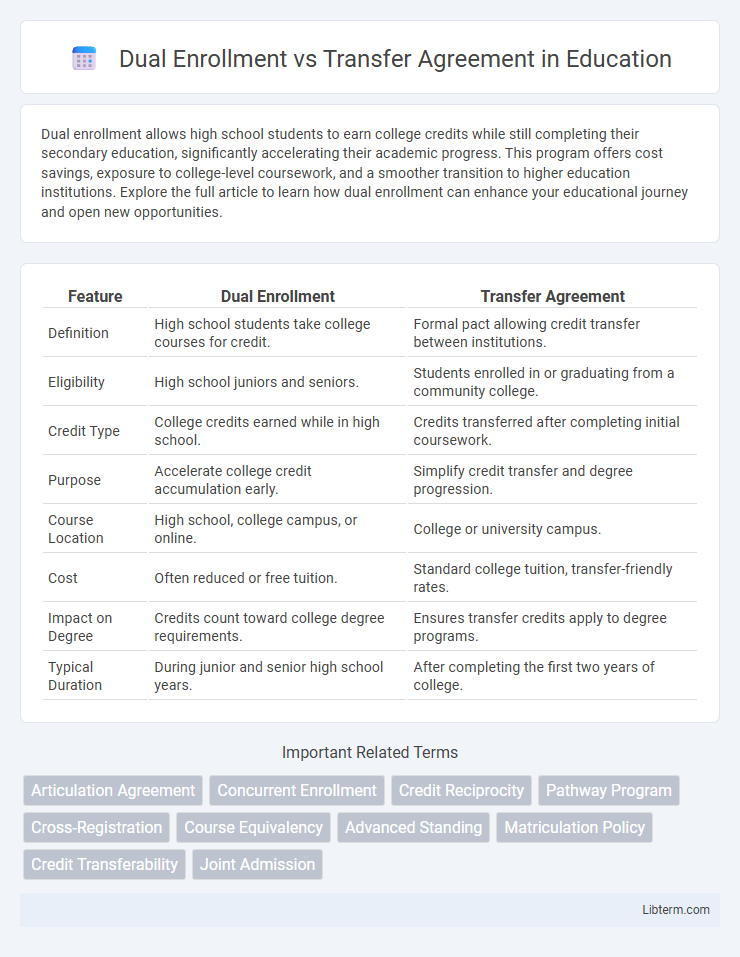
| Feature | Dual Enrollment | Transfer Agreement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | High school students take college courses for credit. | Formal pact allowing credit transfer between institutions. |
| Eligibility | High school juniors and seniors. | Students enrolled in or graduating from a community college. |
| Credit Type | College credits earned while in high school. | Credits transferred after completing initial coursework. |
| Purpose | Accelerate college credit accumulation early. | Simplify credit transfer and degree progression. |
| Course Location | High school, college campus, or online. | College or university campus. |
| Cost | Often reduced or free tuition. | Standard college tuition, transfer-friendly rates. |
| Impact on Degree | Credits count toward college degree requirements. | Ensures transfer credits apply to degree programs. |
| Typical Duration | During junior and senior high school years. | After completing the first two years of college. |
Understanding Dual Enrollment Programs
Dual enrollment programs allow high school students to take college courses and earn credits before graduating, accelerating their academic progress and reducing future tuition costs. These programs provide access to college-level curriculum while maintaining high school enrollment, often supported by partnerships between local high schools and colleges. Understanding dual enrollment helps students make informed decisions about early college exposure compared to transfer agreements that facilitate credit transfer after college enrollment.
What Are Transfer Agreements?
Transfer agreements are formal arrangements between community colleges and four-year universities that guarantee credit transfer, ensuring students can continue their education without losing progress. These agreements outline specific courses that will be accepted by the receiving institution, simplifying the transfer process and reducing the risk of credit loss. By providing a clear pathway, transfer agreements support students in achieving a seamless transition toward earning a bachelor's degree.
Key Differences Between Dual Enrollment and Transfer Agreements
Dual enrollment allows high school students to take college courses for credit simultaneously with their high school curriculum, while transfer agreements are formal arrangements between institutions that guarantee credit transfer for completed courses. Dual enrollment credits count toward both high school and college requirements, accelerating degree completion, whereas transfer agreements ensure that credits earned at one college apply toward a degree at another institution. Key differences include the timing of credit acquisition--dual enrollment occurs during high school, transfer agreements apply post-secondary--and the flexibility of credit acceptance, with transfer agreements providing predefined pathways for seamless credit recognition.
Eligibility Criteria for Dual Enrollment
Eligibility criteria for Dual Enrollment typically require high school students to maintain a minimum GPA, usually around 2.5 to 3.0, and obtain parental consent along with school counselor approval. Students must often be juniors or seniors, although some programs allow sophomores to participate based on academic readiness. Standardized test scores or placement exams are frequently used to assess eligibility and ensure students can handle college-level coursework while still in high school.
Transfer Agreement Requirements Explained
Transfer agreements require students to complete specific coursework, maintain a minimum GPA, and submit official transcripts for seamless credit transfer between institutions. These agreements often outline mandatory courses aligned with the receiving university's program to ensure academic continuity. Clear adherence to these criteria guarantees that credits earned are recognized, reducing credit loss and accelerating degree completion.
Academic Benefits of Dual Enrollment
Dual Enrollment programs provide high school students with the opportunity to earn college credits while completing their secondary education, significantly accelerating their academic progress and reducing overall college costs. Students benefit from exposure to rigorous college-level coursework, which enhances critical thinking skills and better prepares them for future college demands. This academic advantage often leads to higher college retention and graduation rates compared to peers who enter college without dual enrollment experience.
Pros and Cons of Transfer Agreements
Transfer agreements facilitate seamless credit transfer between institutions, enabling students to pursue advanced degrees without retaking equivalent courses, which reduces overall education costs and time to graduation. However, these agreements may limit flexibility in course selection and require strict adherence to predefined curricula, potentially restricting students from exploring diverse academic interests. Furthermore, discrepancies in course equivalency evaluations can lead to unexpected credit loss, necessitating careful planning and consultation with academic advisors.
Comparing Cost Savings: Dual Enrollment vs Transfer
Dual enrollment programs typically offer significant cost savings by allowing high school students to take college courses at reduced or no tuition fees, often funded by state initiatives or school districts, whereas transfer agreements provide cost benefits primarily by ensuring credit acceptance but may not reduce initial college expenses. Dual enrollment reduces total college credits needed post-high school, thereby lowering overall tuition costs, while transfer agreements focus on seamless credit transfer between institutions, potentially avoiding repetition of courses and additional fees. Comparing these options, dual enrollment offers upfront savings on tuition, whereas transfer agreements optimize affordability through credit recognition once college enrollment begins.
Impact on College Admissions and Credits
Dual enrollment programs allow high school students to earn college credits that often transfer directly to participating institutions, enhancing college admissions profiles by demonstrating academic rigor and saving time and tuition costs. Transfer agreements, on the other hand, guarantee that credits earned at one college will be accepted by another, providing a clear pathway to degree completion but requiring careful alignment with the receiving institution's curriculum. Both options impact college admissions by influencing credit transferability, course selection, and overall academic planning, making them critical considerations for prospective students seeking efficient and recognized credit accumulation.
Choosing the Right Path: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right path between dual enrollment and transfer agreements depends on factors such as academic goals, cost efficiency, and seamless credit transferability. Dual enrollment allows high school students to earn college credits early, providing a head start on degree completion with potential tuition savings. Transfer agreements guarantee that credits earned at one institution will be accepted by another, ensuring continuity and reducing the risk of credit loss during transfer.
Dual Enrollment Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com