Mastery-Based Progression ensures learners fully understand each topic before moving forward, promoting deeper retention and skill development. This approach emphasizes competency over time spent, allowing you to advance at your own pace and solidify knowledge effectively. Explore the article to discover how Mastery-Based Progression can transform your learning experience.
Table of Comparison
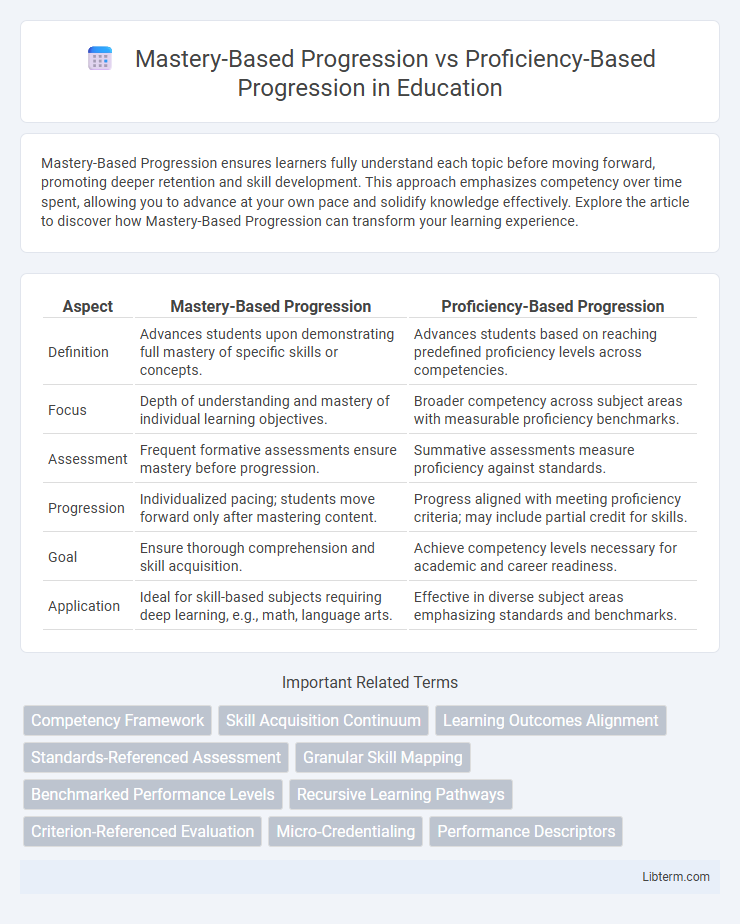
| Aspect | Mastery-Based Progression | Proficiency-Based Progression |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Advances students upon demonstrating full mastery of specific skills or concepts. | Advances students based on reaching predefined proficiency levels across competencies. |
| Focus | Depth of understanding and mastery of individual learning objectives. | Broader competency across subject areas with measurable proficiency benchmarks. |
| Assessment | Frequent formative assessments ensure mastery before progression. | Summative assessments measure proficiency against standards. |
| Progression | Individualized pacing; students move forward only after mastering content. | Progress aligned with meeting proficiency criteria; may include partial credit for skills. |
| Goal | Ensure thorough comprehension and skill acquisition. | Achieve competency levels necessary for academic and career readiness. |
| Application | Ideal for skill-based subjects requiring deep learning, e.g., math, language arts. | Effective in diverse subject areas emphasizing standards and benchmarks. |
Understanding Mastery-Based Progression
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes students achieving a deep understanding of each concept before moving forward, ensuring retention and application of knowledge. This approach adapts pacing to individual learning needs, promoting personalized education paths and minimizing gaps in comprehension. Unlike Proficiency-Based Progression, which measures readiness through meeting predefined benchmarks, Mastery-Based Progression focuses on complete mastery of skills to support long-term academic success.
Defining Proficiency-Based Progression
Proficiency-Based Progression defines student advancement through demonstrated skills and knowledge mastery at specified proficiency levels, emphasizing clear benchmarks aligned with curriculum standards. This model requires learners to achieve a predetermined set of competencies before moving forward, ensuring consistent understanding across subjects. Unlike Mastery-Based Progression, which centers on complete mastery, Proficiency-Based Progression accommodates varying degrees of skill acquisition while maintaining academic rigor.
Core Differences: Mastery vs Proficiency
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes deep understanding and complete command of skills before moving forward, ensuring learners achieve a high level of expertise in each topic. Proficiency-Based Progression focuses on meeting predefined performance standards, allowing learners to progress once they demonstrate sufficient competence. The core difference lies in mastery requiring thorough internalization, while proficiency prioritizes functional ability at a satisfactory level.
Curriculum Design Implications
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes students demonstrating a deep understanding of specific skills before advancing, requiring curriculum designers to create modular, competency-focused content with clear, measurable learning objectives. Proficiency-Based Progression prioritizes meeting set proficiency standards across broader skill sets, influencing curriculum development to include flexible pacing, varied assessment methods, and opportunities for remediation and enrichment. Both approaches demand alignment of instructional materials and assessment strategies to ensure consistent skill acquisition and support personalized learning paths.
Assessment Strategies for Both Models
Mastery-based progression assessment strategies emphasize ongoing formative evaluations, such as frequent quizzes and performance tasks, to ensure learners achieve specific competency thresholds before advancing. Proficiency-based progression relies on summative assessments that measure overall skill acquisition against predefined proficiency standards, often utilizing rubrics and standardized tests to validate readiness. Both models incorporate feedback mechanisms, but mastery-based assessments prioritize iterative improvements, while proficiency-based assessments focus on final demonstration of skill mastery.
Impact on Student Motivation and Engagement
Mastery-Based Progression fosters student motivation by emphasizing continuous improvement and personalized learning goals, resulting in higher engagement through a growth mindset. Proficiency-Based Progression enhances motivation by setting clear, measurable standards that students strive to meet, increasing accountability and self-directed learning. Both models promote active participation, but Mastery-Based Progression typically encourages deeper intrinsic motivation through iterative feedback and skill refinement.
Role of Teacher Feedback
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes continuous, detailed teacher feedback to guide students through incremental skill development until achieving complete understanding. Proficiency-Based Progression relies on feedback that verifies readiness at defined proficiency benchmarks, enabling learners to demonstrate competence before advancing. Effective feedback in both models is critical for identifying learning gaps and supporting personalized instruction that adapts to individual student needs.
Scalability in Diverse Learning Environments
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes sequential learning where students must demonstrate complete understanding before advancing, which can challenge scalability in diverse learning environments due to varied pacing needs. Proficiency-Based Progression allows learners to progress upon meeting defined competency standards at their own pace, offering greater flexibility to accommodate diverse skill levels and learning styles. Educational institutions adopting proficiency-based models often achieve better scalability by leveraging adaptive technologies and personalized learning pathways that support heterogeneous student populations.
Measuring Long-Term Learning Outcomes
Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes achieving a comprehensive understanding of foundational skills before advancing, ensuring deep retention and application over time. Proficiency-Based Progression focuses on meeting predefined performance benchmarks, facilitating timely progression but sometimes at the expense of thorough mastery. Measuring long-term learning outcomes reveals that mastery-based models often result in stronger skill retention and adaptability, critical for sustained academic and professional success.
Choosing the Right Progression Model for Your Context
Selecting the appropriate progression model depends on your educational goals, learner needs, and assessment methods. Mastery-Based Progression emphasizes incremental skill development and ensures learners achieve a deep understanding before moving forward, ideal for foundational or skills-intensive subjects. Proficiency-Based Progression focuses on meeting predefined performance standards, suitable for competency-driven environments where demonstrating specific outcomes is critical.
Mastery-Based Progression Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com