Inquiry-based learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving by encouraging students to ask questions and explore topics deeply. This approach promotes active engagement and nurtures curiosity, allowing learners to construct knowledge based on their own experiences. Discover how inquiry-based learning can transform your educational experience by reading the rest of the article.
Table of Comparison
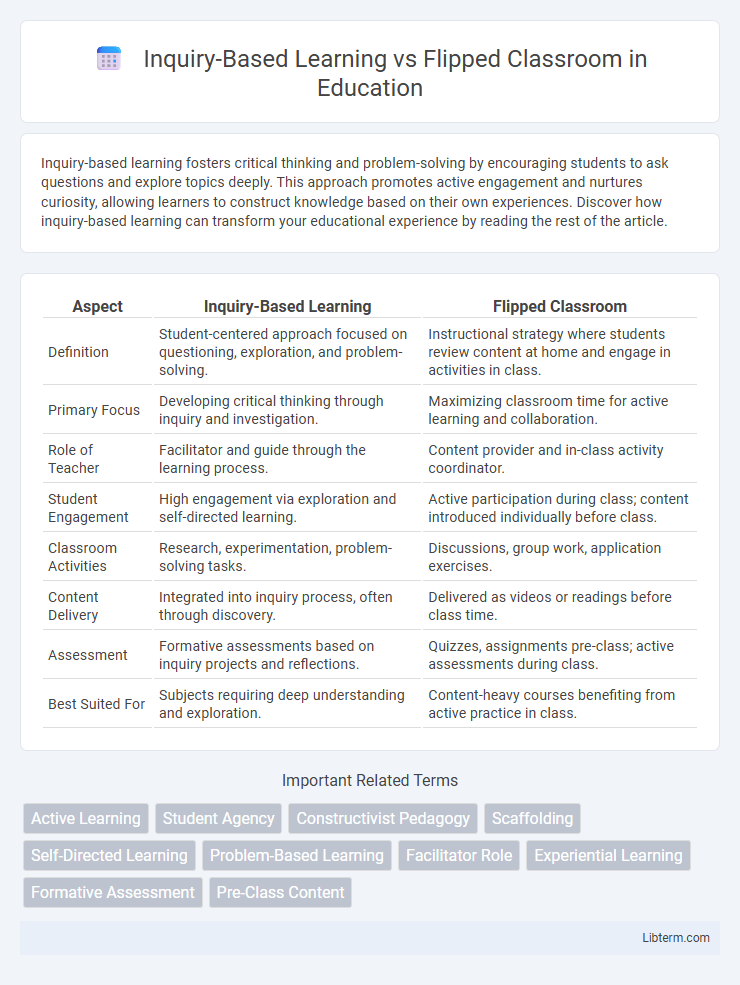
| Aspect | Inquiry-Based Learning | Flipped Classroom |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Student-centered approach focused on questioning, exploration, and problem-solving. | Instructional strategy where students review content at home and engage in activities in class. |
| Primary Focus | Developing critical thinking through inquiry and investigation. | Maximizing classroom time for active learning and collaboration. |
| Role of Teacher | Facilitator and guide through the learning process. | Content provider and in-class activity coordinator. |
| Student Engagement | High engagement via exploration and self-directed learning. | Active participation during class; content introduced individually before class. |
| Classroom Activities | Research, experimentation, problem-solving tasks. | Discussions, group work, application exercises. |
| Content Delivery | Integrated into inquiry process, often through discovery. | Delivered as videos or readings before class time. |
| Assessment | Formative assessments based on inquiry projects and reflections. | Quizzes, assignments pre-class; active assessments during class. |
| Best Suited For | Subjects requiring deep understanding and exploration. | Content-heavy courses benefiting from active practice in class. |
Introduction to Inquiry-Based Learning and Flipped Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and critical thinking through questioning and investigation, fostering deeper understanding and intellectual curiosity. The Flipped Classroom model reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside of class, allowing in-person time for active learning and collaborative problem-solving. Both approaches enhance engagement and promote mastery by prioritizing student-centered pedagogy over passive lecture formats.
Core Principles of Inquiry-Based Learning
Inquiry-Based Learning centers on fostering student curiosity through questioning, exploration, and critical thinking, emphasizing active engagement and knowledge construction. It prioritizes student-driven investigation where learners formulate questions, gather data, and develop solutions collaboratively. This approach contrasts with Flipped Classroom models, which invert traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside class, allowing in-class time for interactive activities rather than focusing primarily on inquiry exploration.
Fundamental Concepts of the Flipped Classroom Model
The flipped classroom model fundamentally restructures traditional teaching by delivering instructional content, often through videos, outside of class, enabling active learning during face-to-face sessions. This approach emphasizes student-centered engagement, where classroom time is dedicated to collaborative problem-solving, discussions, and applying concepts rather than passive listening. Key principles include pre-class preparation, interactive in-class activities, and continuous formative assessment to reinforce understanding.
Key Differences Between Inquiry-Based Learning and Flipped Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning emphasizes student-driven exploration and questioning to develop understanding, while the Flipped Classroom reverses traditional teaching by delivering instructional content outside class and using in-person time for practice and interaction. Inquiry-Based Learning fosters critical thinking and problem-solving through open-ended tasks, whereas the Flipped Classroom prioritizes content absorption at home and active learning activities during class sessions. Both approaches enhance engagement but differ fundamentally in structuring content delivery and learner autonomy.
Student Engagement: Inquiry-Based vs Flipped Methods
Inquiry-based learning fosters deep student engagement by encouraging curiosity and active exploration of topics, promoting critical thinking and problem-solving skills. The flipped classroom enhances engagement by shifting direct instruction outside of class, allowing in-class time for interactive activities and personalized teacher support. Both methods increase student participation, but inquiry-based learning emphasizes autonomous knowledge discovery while flipped classrooms focus on applying pre-learned concepts collaboratively.
Teacher Roles in Both Approaches
Teachers in Inquiry-Based Learning act as facilitators who guide students through questioning, exploration, and problem-solving, encouraging critical thinking and independent discovery. In the Flipped Classroom model, teachers shift to a more interactive role during in-class time, focusing on clarifying concepts, leading discussions, and providing personalized support after students engage with instructional content at home. Both approaches require educators to foster active learning environments but differ in timing and the nature of teacher-student interactions.
Learning Outcomes and Skills Development
Inquiry-Based Learning enhances critical thinking and problem-solving skills by encouraging students to explore questions and develop hypotheses independently, leading to deeper conceptual understanding. The Flipped Classroom model improves active learning and comprehension by delivering instructional content outside of class, allowing in-class time for collaborative activities and personalized support. Both methodologies significantly boost student engagement and promote the development of higher-order cognitive skills, yet Inquiry-Based Learning places greater emphasis on curiosity and investigation, while the Flipped Classroom optimizes class time for application and interaction.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Approach
Inquiry-Based Learning faces challenges such as requiring extensive teacher training to effectively guide open-ended student investigations and the difficulty in assessing learning outcomes due to its non-linear nature. The Flipped Classroom demands significant student self-discipline and access to digital resources outside class, potentially widening the digital divide. Both approaches risk uneven participation and may struggle in large or under-resourced classrooms, impacting the scalability and consistency of learning experiences.
Integrating Inquiry-Based and Flipped Strategies
Integrating inquiry-based learning and flipped classroom strategies enhances student engagement by combining active exploration with pre-class content absorption, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. This hybrid approach allows learners to prepare through flipped video lectures or readings before class, freeing up in-person time for collaborative inquiry and problem-solving activities guided by the instructor. Research shows this integration improves concept retention and fosters a learner-centered environment where students take ownership of their education.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Classroom
Inquiry-Based Learning fosters student curiosity through exploration and critical thinking, ideal for classrooms emphasizing deep understanding and problem-solving skills. Flipped Classroom reverses traditional instruction by delivering content outside class and focusing on active learning during sessions, suitable for time-sensitive curricula and maximizing in-person collaboration. Selecting the right method depends on your students' learning preferences, subject complexity, and available technological resources to enhance engagement and academic outcomes.
Inquiry-Based Learning Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com