Colloquial language reflects everyday conversation, making communication relatable and natural. It includes slang, idioms, and informal expressions that vary by region and culture. Explore the rest of the article to understand how colloquial language shapes your interactions and writing style.
Table of Comparison
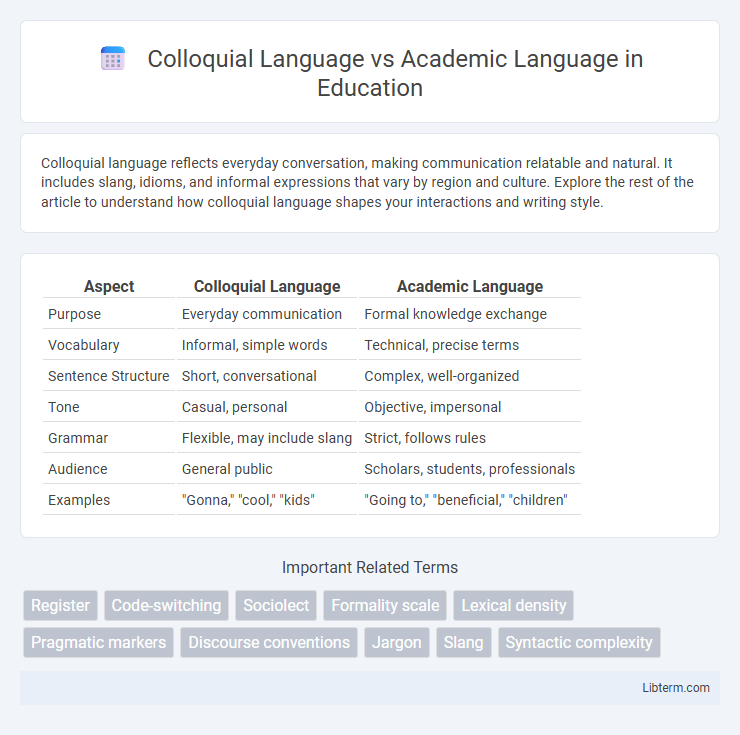
| Aspect | Colloquial Language | Academic Language |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Everyday communication | Formal knowledge exchange |
| Vocabulary | Informal, simple words | Technical, precise terms |
| Sentence Structure | Short, conversational | Complex, well-organized |
| Tone | Casual, personal | Objective, impersonal |
| Grammar | Flexible, may include slang | Strict, follows rules |
| Audience | General public | Scholars, students, professionals |
| Examples | "Gonna," "cool," "kids" | "Going to," "beneficial," "children" |
Understanding Colloquial Language
Colloquial language consists of informal expressions and everyday vocabulary that vary by region and social groups, making it essential for effective casual communication and cultural immersion. Understanding colloquial language enhances comprehension of native speakers' natural speech patterns, idioms, and humor, which are often absent in academic texts. Mastery of colloquial language also supports social integration and helps learners navigate real-life conversations beyond formal contexts.
Defining Academic Language
Academic language is a formal register used in educational and professional settings, characterized by precise vocabulary, complex sentence structures, and discipline-specific terminology. It emphasizes clarity, objectivity, and logical organization to effectively convey complex ideas and arguments. Mastery of academic language is essential for successful reading, writing, and communication within scholarly contexts.
Key Differences Between Colloquial and Academic Language
Colloquial language features informal vocabulary, contractions, and slang used in everyday conversation, while academic language relies on formal vocabulary, precise terminology, and structured sentence construction. The tone of colloquial language is casual and personal, contrasting with the objective and impersonal tone maintained in academic writing. Additionally, academic language prioritizes clarity, coherence, and evidence-based arguments, whereas colloquial language emphasizes ease of understanding and conversational flow.
Contexts for Colloquial Language Usage
Colloquial language is primarily used in informal contexts such as everyday conversations, social media interactions, and casual writing, where a relaxed and familiar tone is appropriate. It reflects regional dialects, slang, and idiomatic expressions that facilitate quick and relatable communication among peers. Understanding the context of use helps distinguish colloquial language from academic language, which demands formality, precision, and adherence to standardized grammar in scholarly or professional settings.
Appropriate Settings for Academic Language
Academic language is essential in formal settings such as universities, research papers, and professional conferences where clarity, precision, and objectivity are prioritized. This formal register uses specialized vocabulary, structured syntax, and avoids contractions or slang to ensure the communication is credible and universally understood among scholars. Using academic language appropriately enhances the effectiveness of knowledge dissemination, critical analysis, and scholarly discussion.
Advantages of Colloquial Language
Colloquial language enhances communication by making interactions more natural, relatable, and easier to understand for diverse audiences. It fosters a sense of community and emotional connection, enabling speakers to express personality and cultural identity effectively. Its informal nature also encourages spontaneity and creativity, which can improve engagement and ease of learning in conversational contexts.
Benefits of Academic Language
Academic language enhances clarity and precision in communication, fostering critical thinking and comprehension in educational settings. It supports the development of formal writing skills essential for research, professional discourse, and knowledge dissemination. Mastery of academic language increases opportunities for academic and career advancement by meeting standardized expectations in scholarly and professional environments.
Common Challenges in Switching Between Styles
Switching between colloquial and academic language often presents challenges such as adjusting vocabulary from informal expressions to precise, technical terms and shifting sentence structures from simple, conversational forms to complex, formal constructions. Speakers may struggle with tone modulation, as academic language demands objectivity and formality, contrasting with the personal and emotive style of colloquial speech. This transition requires mastering context-appropriate language use, ensuring clarity and credibility in academic settings while maintaining naturalness in everyday communication.
Impact on Communication and Understanding
Colloquial language enhances relatability and ease of comprehension in everyday conversations, promoting natural interaction and emotional connection. Academic language, characterized by formal vocabulary and structured syntax, ensures precision, clarity, and objectivity essential for scholarly discourse and critical analysis. The choice between colloquial and academic language directly impacts communication effectiveness, influencing how information is interpreted and understood within different contexts.
Tips for Balancing Colloquial and Academic Language
Balancing colloquial and academic language requires adapting your tone to the audience while maintaining clarity and formality appropriate for academic contexts. Use colloquial expressions sparingly to engage readers or illustrate points but prioritize precise vocabulary and structured sentences to uphold credibility. Incorporate transitional phrases and subject-specific terminology to smoothly integrate everyday language without compromising the scholarly style.
Colloquial Language Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com