An access gap refers to the disparity between individuals or communities in obtaining essential resources, services, or opportunities, such as education, healthcare, or technology. This inequality often stems from socioeconomic, geographic, or infrastructural barriers limiting access. Discover how understanding and addressing the access gap can empower your community by exploring the full article.
Table of Comparison
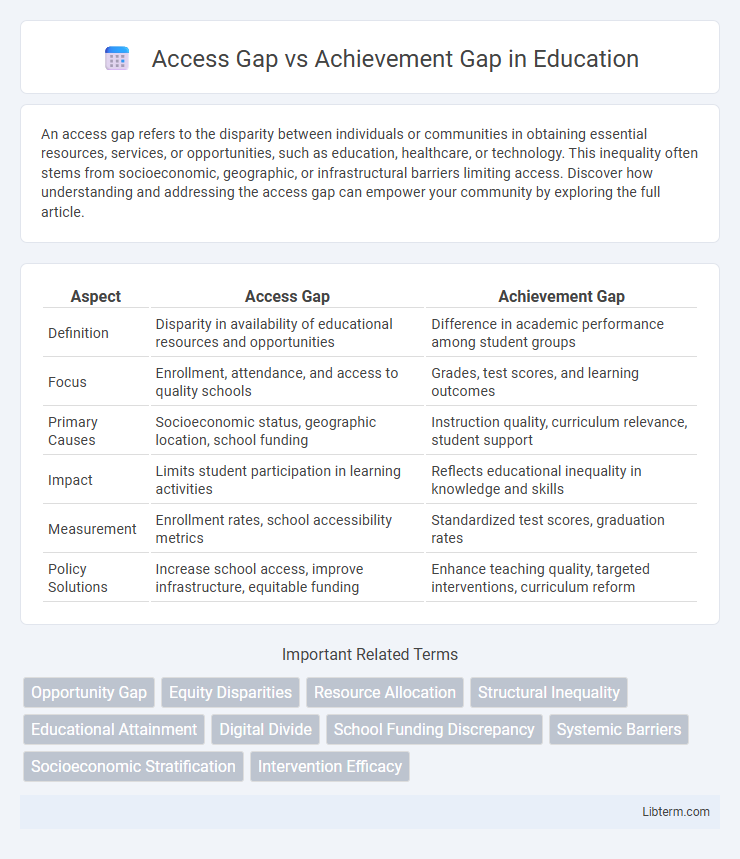
| Aspect | Access Gap | Achievement Gap |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disparity in availability of educational resources and opportunities | Difference in academic performance among student groups |
| Focus | Enrollment, attendance, and access to quality schools | Grades, test scores, and learning outcomes |
| Primary Causes | Socioeconomic status, geographic location, school funding | Instruction quality, curriculum relevance, student support |
| Impact | Limits student participation in learning activities | Reflects educational inequality in knowledge and skills |
| Measurement | Enrollment rates, school accessibility metrics | Standardized test scores, graduation rates |
| Policy Solutions | Increase school access, improve infrastructure, equitable funding | Enhance teaching quality, targeted interventions, curriculum reform |
Defining the Access Gap
The Access Gap refers to the disparity in availability and use of educational resources such as technology, quality teaching, and learning materials among different student groups. It highlights inequalities in early opportunities that affect students' ability to engage fully with educational content. Addressing the Access Gap involves ensuring equitable distribution of resources to support all students equally from the outset.
Understanding the Achievement Gap
The achievement gap refers to the persistent disparity in academic performance between groups of students, often defined by race, socioeconomic status, or ethnicity. It manifests in standardized test scores, graduation rates, and college enrollment, highlighting systemic inequities in education. Addressing the achievement gap requires targeted interventions that improve instructional quality, provide equitable resources, and support students' diverse needs inside and outside the classroom.
Historical Origins of Both Gaps
The Access Gap originated from systemic inequalities in educational resources and opportunities, deeply rooted in segregation and discriminatory policies dating back to the Jim Crow era. The Achievement Gap emerged as a measurable disparity in academic performance among students from different socioeconomic, racial, and ethnic backgrounds, influenced by long-standing inequities in access and quality of education. Historical factors such as unequal school funding, residential segregation, and biased curriculum content have perpetuated both gaps over time.
Key Differences: Access Gap vs Achievement Gap
The Access Gap refers to disparities in availability and opportunities to educational resources, such as technology, qualified teachers, and advanced courses, whereas the Achievement Gap focuses on differences in academic performance outcomes among student groups. Addressing the Access Gap involves ensuring equitable distribution of educational tools and infrastructure, while tackling the Achievement Gap emphasizes improving student learning, test scores, and graduation rates. Recognizing these distinctions is vital for crafting targeted policies that promote both equal opportunity and successful educational attainment.
Factors Contributing to the Access Gap
Limited availability of advanced coursework, insufficient funding for educational resources, and disparities in technology access significantly contribute to the access gap. Socioeconomic status often restricts students' opportunities to enroll in rigorous classes and extracurricular programs, exacerbating inequalities. Geographic location and school district segregation further limit access to quality education, intensifying the divide before academic accomplishments are even measured.
How Access Impacts Achievement
Limited access to quality educational resources such as experienced teachers, advanced coursework, and technology directly hinders student achievement by restricting opportunities for skill development and academic growth. Schools in underserved areas often face resource disparities that contribute to lower test scores, graduation rates, and college enrollment compared to more affluent districts. Bridging the access gap through equitable funding and resource allocation is essential to closing the achievement gap and promoting academic success for all students.
Measuring Gaps: Metrics and Indicators
Measuring the access gap involves analyzing enrollment rates, availability of educational resources, and participation in advanced coursework, highlighting disparities in opportunities. The achievement gap is primarily assessed through standardized test scores, graduation rates, and literacy proficiency to evaluate performance differences among student groups. Reliable metrics for both gaps require disaggregated data by socioeconomic status, race, and geographic location to accurately identify and address educational inequities.
Equity in Education: Bridging the Gaps
The Access Gap refers to disparities in students' availability to educational resources, technology, and quality instruction, while the Achievement Gap highlights differences in academic performance outcomes among diverse student groups. Addressing Equity in Education requires targeted policies that ensure equitable distribution of learning tools and opportunities to marginalized communities. Bridging these gaps fosters inclusive environments that support all learners in reaching their full potential.
Effective Strategies for Closing the Gaps
Targeted interventions like personalized learning plans and equitable resource distribution address both the Access Gap and Achievement Gap by ensuring all students receive necessary tools and support. Implementing culturally responsive teaching coupled with technology integration enhances engagement and helps close disparities in academic outcomes. Data-driven instruction and ongoing progress monitoring enable educators to identify gaps early and adjust strategies to improve student performance effectively.
Future Directions in Educational Equity
Future directions in educational equity emphasize narrowing the access gap by expanding digital resources and technology integration in underserved schools to ensure equal learning opportunities. Addressing the achievement gap requires personalized interventions and data-driven strategies to support diverse student needs and track progress effectively. Policies fostering inclusive curricula and equitable funding models are critical to sustaining long-term improvements in both access and achievement.
Access Gap Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com