Didactic teaching focuses on structured, clear, and direct instruction where the teacher imparts knowledge to students through lectures and demonstrations. This method emphasizes the transmission of factual information and foundational concepts to build a solid understanding. Explore the rest of the article to discover how didactic teaching can enhance your educational approach.
Table of Comparison
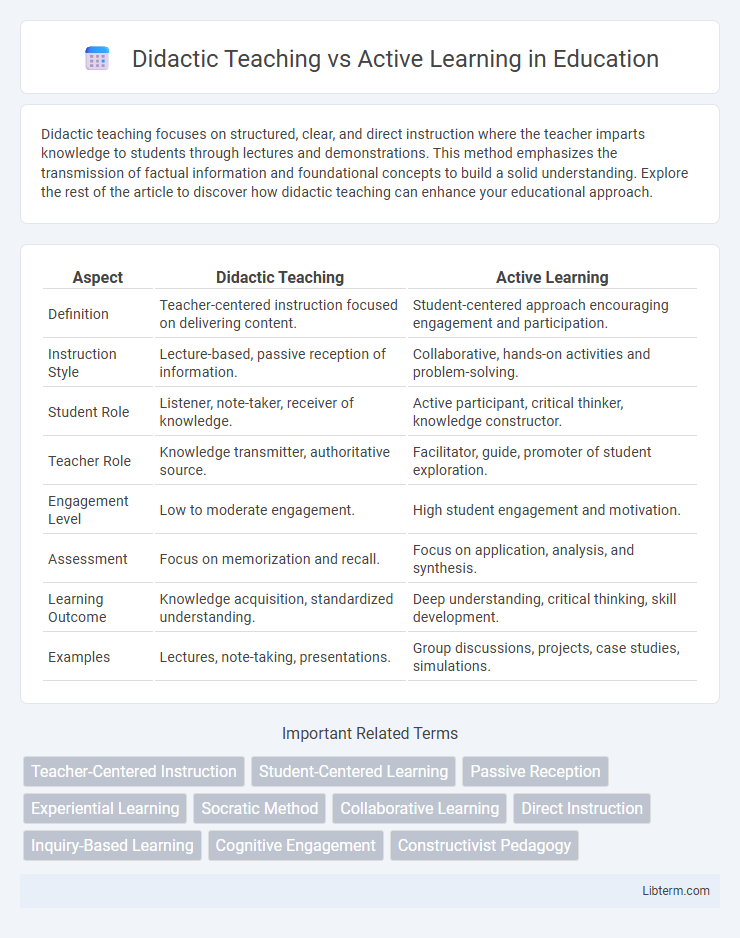
| Aspect | Didactic Teaching | Active Learning |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Teacher-centered instruction focused on delivering content. | Student-centered approach encouraging engagement and participation. |
| Instruction Style | Lecture-based, passive reception of information. | Collaborative, hands-on activities and problem-solving. |
| Student Role | Listener, note-taker, receiver of knowledge. | Active participant, critical thinker, knowledge constructor. |
| Teacher Role | Knowledge transmitter, authoritative source. | Facilitator, guide, promoter of student exploration. |
| Engagement Level | Low to moderate engagement. | High student engagement and motivation. |
| Assessment | Focus on memorization and recall. | Focus on application, analysis, and synthesis. |
| Learning Outcome | Knowledge acquisition, standardized understanding. | Deep understanding, critical thinking, skill development. |
| Examples | Lectures, note-taking, presentations. | Group discussions, projects, case studies, simulations. |
Introduction to Didactic Teaching and Active Learning
Didactic teaching centers on structured, instructor-led delivery of information, emphasizing clear explanations and organized content presentation to facilitate knowledge acquisition. Active learning engages students through interactive activities such as discussions, problem-solving, and collaborative tasks, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking. Both methods aim to enhance educational outcomes but differ fundamentally in their approach to student involvement and cognition.
Defining Didactic Teaching: Key Features
Didactic teaching is characterized by a structured, instructor-centered approach where information is conveyed through lectures and direct instruction, emphasizing content delivery and knowledge absorption. Key features include a clear curriculum, teacher authority, and minimal student interaction, facilitating efficient transmission of facts and concepts. This method prioritizes passive learning and memorization over collaboration and critical thinking skills development.
Understanding Active Learning Strategies
Active learning strategies emphasize student engagement through activities such as discussions, problem-solving, case studies, and collaborative projects, which enhance comprehension and critical thinking skills. Unlike didactic teaching that centers on passive knowledge transmission through lectures, active learning fosters deeper understanding by encouraging learners to interact with the material and apply concepts practically. Research in educational psychology confirms that active learning improves retention, motivation, and overall academic performance compared to traditional didactic methods.
Historical Evolution of Teaching Methods
Didactic teaching, rooted in ancient traditions, emphasizes teacher-centered instruction where knowledge is transmitted directly to students, a method dominant from classical times through the early 20th century. Active learning emerged prominently in the mid-20th century as educators and psychologists, influenced by constructivist theories of Piaget and Vygotsky, advocated for student engagement, collaboration, and critical thinking to enhance deeper understanding. The transition reflects a paradigm shift driven by cognitive science advancements, educational reforms, and the recognition that experiential learning fosters higher-order cognitive skills compared to passive reception in didactic models.
Comparing Learning Outcomes: Didactic vs Active Approaches
Comparing learning outcomes, active learning consistently demonstrates higher retention rates and deeper understanding compared to didactic teaching. Research shows students engaged in active learning methods, such as problem-solving and collaborative activities, outperform peers receiving traditional lectures in critical thinking and application skills. While didactic teaching effectively delivers foundational knowledge, active learning's emphasis on participation enhances long-term comprehension and skill development.
Student Engagement in Both Teaching Methods
Didactic teaching often limits student engagement by emphasizing passive listening and note-taking, resulting in lower interaction and critical thinking. Active learning strategies increase student engagement through collaborative activities, problem-solving, and real-time feedback, fostering deeper understanding and retention. Research shows that active learning environments promote higher motivation and participation compared to traditional didactic methods.
Teacher’s Role: Facilitator vs Knowledge Provider
In didactic teaching, the teacher primarily acts as a knowledge provider, delivering structured information and maintaining control over the learning process to ensure content accuracy and clarity. Conversely, in active learning, the teacher serves as a facilitator, guiding students through exploration, collaboration, and critical thinking to foster deeper understanding and engagement. This shift from authoritative instruction to supportive interaction transforms the classroom dynamic, promoting student autonomy and personalized learning experiences.
Assessing Retention and Critical Thinking Skills
Assessing retention in didactic teaching often relies on memorization and recall through standardized tests, while active learning encourages deeper understanding measured by application-based assessments. Critical thinking skills develop more robustly in active learning environments where students engage in problem-solving, discussion, and analysis rather than passively receiving information. Research indicates that active learning strategies significantly improve long-term retention and higher-order cognitive abilities compared to traditional didactic methods.
Challenges and Limitations of Each Method
Didactic teaching often faces challenges such as reduced student engagement and limited opportunities for critical thinking, resulting in passive knowledge absorption. Active learning, while promoting deeper understanding and collaboration, can be hindered by time constraints, inadequate instructor training, and resistance from students accustomed to traditional methods. Both approaches require careful implementation to balance content delivery with interactive participation and to address diverse learning styles effectively.
Choosing the Right Approach for Effective Education
Didactic teaching, characterized by structured lectures and direct instruction, effectively delivers foundational knowledge and ensures curriculum coverage. Active learning engages students through discussion, problem-solving, and hands-on activities, promoting deeper understanding and critical thinking skills. Selecting the right approach depends on educational goals, content complexity, and student needs, often combining both methods yields optimal learning outcomes.
Didactic Teaching Infographic
 libterm.com
libterm.com